BusinessNews Publishing - Summary: Zero to One: Review and Analysis of Thiel and Masters Book
Here you can read online BusinessNews Publishing - Summary: Zero to One: Review and Analysis of Thiel and Masters Book full text of the book (entire story) in english for free. Download pdf and epub, get meaning, cover and reviews about this ebook. year: 2015, publisher: Business Book Summaries, genre: Business. Description of the work, (preface) as well as reviews are available. Best literature library LitArk.com created for fans of good reading and offers a wide selection of genres:
Romance novel
Science fiction
Adventure
Detective
Science
History
Home and family
Prose
Art
Politics
Computer
Non-fiction
Religion
Business
Children
Humor
Choose a favorite category and find really read worthwhile books. Enjoy immersion in the world of imagination, feel the emotions of the characters or learn something new for yourself, make an fascinating discovery.

- Book:Summary: Zero to One: Review and Analysis of Thiel and Masters Book
- Author:
- Publisher:Business Book Summaries
- Genre:
- Year:2015
- Rating:4 / 5
- Favourites:Add to favourites
- Your mark:
- 80
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Summary: Zero to One: Review and Analysis of Thiel and Masters Book: summary, description and annotation
We offer to read an annotation, description, summary or preface (depends on what the author of the book "Summary: Zero to One: Review and Analysis of Thiel and Masters Book" wrote himself). If you haven't found the necessary information about the book — write in the comments, we will try to find it.
BusinessNews Publishing: author's other books
Who wrote Summary: Zero to One: Review and Analysis of Thiel and Masters Book? Find out the surname, the name of the author of the book and a list of all author's works by series.
Summary: Zero to One: Review and Analysis of Thiel and Masters Book — read online for free the complete book (whole text) full work
Below is the text of the book, divided by pages. System saving the place of the last page read, allows you to conveniently read the book "Summary: Zero to One: Review and Analysis of Thiel and Masters Book" online for free, without having to search again every time where you left off. Put a bookmark, and you can go to the page where you finished reading at any time.
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:



Book Abstract
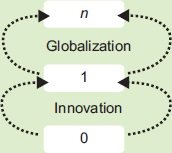
Too many companies today think the essence of innovation is to come up with a better Facebook or a new-and-improved Microsoft. Or to fine-tune and optimize existing lines of business. That's not innovation that's merely globalization which is the art of going from one to many.
True innovation means going from zero to one creating new, fresh and probably strange things that have never before been seen. It's usually technology which facilitates these innovations and the underlying theme of advances in technology is most often finding practical ways to do more with less.
If you want to excel as an innovator in the future, don't set out to copy and improve what someone else has already done. Figure out some job that is entirely new and blaze your own trail. Focus on going from zero to one. That's the real challenge and hope of the future of humanity.
The next Bill Gates will not build an operating system. The next Larry Page or Sergey Brin won't make a search engine. And the next Mark Zuckerberg won't create a social network. If you are copying these guys, you aren't learning from them. Doing what we already know takes the world from 1 to n, adding more of something similar. But every time we create something new, we go from 0 to 1. Unless they invest in the difficult task of creating new things, American companies will fail in the future no matter how big their profits remain today."
- Peter Thiel
About the Author
PETER THIEL is an entrepreneur and investor. He founded PayPal in 1998 and was CEO of the company when it went public in 2002. He was also an early-stage investor in Facebook, LinkedIn, Yelp and dozens of successful technology startups. He is managing partner of the venture capital firm Founders Fund which has invested in SpaceX, Airbnb and many other startups. Peter Thiel leads his own foundation which works to encourage technological innovation and long-term thinking about the future. He is a graduate of Stanford University.
BLAKE MASTERS was a student at Stanford Law School in 2012 when he took notes in Peter Thiel's Class: "Computer Science 183: Startup" which formed the basis for this book. He is a co-founder of Judicata, a legal research technology startup. He graduated from Stanford University and Duke University
Important Note About This Ebook
This is a summary and not a critique or a review of the book. It does not offer judgment or opinion on the content of the book. This summary may not be organized chapter-wise but is an overview of the main ideas, viewpoints and arguments from the book as a whole. This means that the organization of this summary is not a representation of the book.
1. The real challenge
The central challenge for any startup is to question accepted wisdom and rethink business from scratch. Anything else won't have the power to create an entire industry from thin air.
Everybody naturally hopes for a future of progress. When you think about it, however, progress comes in two different forms:

Another way of thinking about this is globalization taking something which already works in one place and making it work everywhere is horizontal progress. Technology is more like vertical progress because it focuses on making available new and better ways to do different or novel things.
Most people and many companies assume globalization will be the main driver of the future of the world but that's incorrect. Technology matters more. The key challenge of the future is to develop new technology which will help everyone do more with less. Globalization without this kind of new technology is unsustainable.
New technology always comes from startups rather than from established corporations. The simple reason for this is it's hard for big organizations to develop something new because there is so much inertia to instead optimize what already exists. Startups have no such restrictions and therefore are free to think differently. To develop some new technology, you need a startup which is big enough to get things done but small enough that you can head in new directions.
The 1990s were the perfect example of chasing growth through globalization versus technology innovations. The decade featured the arrival of the commercialized Internet and ended with the infamous dot-com boom which played like a Silicon Valley gold rush. The inevitable dot-com bust followed.
As a result of the dot-com crash, four big lessons were learned which still guide many of today's business thinkers:
- You're better off making safe incremental advances than in pursuing bold steps forward which have the potential to change the world.
- Your enterprise should stay lean and flexible so you can try things out and iterate your way to success rather than make and execute set plans.
- Don't try and create new markets. Instead, you should go after existing markets by improving what is already offered by your most successful competitors.
- Make viral products which will sell themselves. If you have a product which requires marketing, it's not good enough.
If you think about it carefully though, you'll probably agree the opposite of these principles are more accurate today:
- It's better to go after boldness than it is to get caught up in trivialities.
- Even a bad plan which you have to change later is better than having no plan at all.
- Competitive markets always destroy profits.
- Sales matters just as much as product.
Brilliant thinking is rare, but courage is in even shorter supply than genius."
- Peter Thiel
No one can predict the future exactly, but we know two things: it's going to be different, and it must be rooted in today's world.
- Peter Thiel
Today, our challenge is to both imagine and create the new technologies that can make the 21st century more peaceful and prosperous than the 20th."
- Peter Thiel
2. Become a monopoly
The real goal of any startup is to build a successful company which becomes a monopoly by solving a unique problem for customers. You have to figure out how to rise above your competitors.
The question you should be asking yourself when considering a startup is:
What valuable company is nobody building at present?
The fact of the matter is to breathe life into a startup, you have to create value for your customers using a business model which then captures some of that value for yourself. To achieve that, you will have to spark a new entity which is so good at what it does there are no other close substitutes.
If you want to create and capture lasting value, don't build an undifferentiated commodity business."
- Peter Thiel
People may love and romanticize the idea of competition and being in competitive markets but the brutal reality is when you have perfect competition, all profits get competed away. You've got to fight hard to survive and squeeze out every efficiency that's available to you. Companies in competitive markets are so busy focusing on today's margins they can't afford to invest or plan long-term. Monopolists, by contrast, can afford to think about other things.
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
Similar books «Summary: Zero to One: Review and Analysis of Thiel and Masters Book»
Look at similar books to Summary: Zero to One: Review and Analysis of Thiel and Masters Book. We have selected literature similar in name and meaning in the hope of providing readers with more options to find new, interesting, not yet read works.
Discussion, reviews of the book Summary: Zero to One: Review and Analysis of Thiel and Masters Book and just readers' own opinions. Leave your comments, write what you think about the work, its meaning or the main characters. Specify what exactly you liked and what you didn't like, and why you think so.

