- Safari Home Icon Safari Home
- recommendations icon Recommended
- icon_Playlist_smlCreated with Sketch. Playlists
- search icon Search
- navigation arrow Expand Nav
- recent items icon History
- topics icon Topics
- tutorials icon Tutorials
- offers icon Offers & Deals
- highlights icon Highlights
- settings icon Settings
- Support
- settings icon Settings days left in your trial..
- Support
Table of Contents for Calculus II
- Twitter
- Facebook
- Google Plus
Next Next Chapter
Idiots Guides: Calculus II
Next Next Chapter
Idiots Guides: Calculus II
Find answers on the fly, or master something new. Subscribe today.
Back to top
2018 window.NREUM||(NREUM={});NREUM.info={"agent":"","licenseKey":"510f1a6865","queueTime":0,"transactionName":"YgdaZ0NSW0cEB0RdWltNfkZfUEFdCgofXFBHDVYdR1pQQxZeRl1QQj1aWkU=","beacon":"bam.nr-data.net","errorBeacon":"bam.nr-data.net","applicationTime":134,"applicationID":"3275661,67267027,67267028"}
About the Author
Chris Monahan has taught high school and college mathematics for more than 30 years. He has a Master of Arts in teaching from Colgate University and a Bachelor of Science from Manhattan College. President of the Association of Mathematics Teachers of New York State in 2009 and 2010, Chris has spoken at annual conferences around the country on the use of technology in the classroom, led workshops, and served on a number of committees for the New York State Education Department (NYSED). He currently consults for the NYSED, where he writes and assesses materials for the Common Core assessments.
APPENDIX
A
Solutions to Youve Got Problems
All the answers to the problems that you found in the Youve Got Problems sidebars throughout the book are listed here, organized by chapter.
Chapter 1
1.Using the relationship that 180 corresponds to radians, set up the proportion 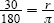 to arrive at
to arrive at 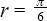 .
.
2.You know that sin(2A) = 2sin(A)cos( A ). Use the Pythagorean identity sin2(A) + cos2(A) = 1 to solve for the value of  becomes
becomes 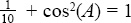 so
so 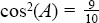 and
and 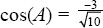 . Therefore,
. Therefore, 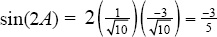 .
.
3.Separate the logarithm of a quotient into the difference of logarithms (change the square root to exponential form, too) 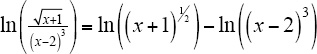 . Use the rule for logarithms of powers to get
. Use the rule for logarithms of powers to get 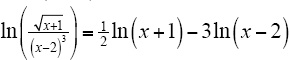 .
.
4.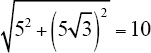 and
and 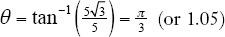 , so the coordinates are
, so the coordinates are 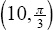 .
.
5.The common ratio for the series is 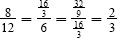 . The first term of the series is 12, so the sum of the infinite geometric series is
. The first term of the series is 12, so the sum of the infinite geometric series is 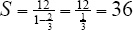 .
.
6.Factor the denominator to (x + 5)(x 1), and rewrite the fraction as 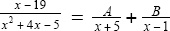 . Multiply by the common denominator: x 19 = A(x 1) + B(x + 5).
. Multiply by the common denominator: x 19 = A(x 1) + B(x + 5).
Set x = 1: 18 = 6B so B = 3.
Set x = 5: 24 = 6A so A = 4.
Therefore,  .
.
Chapter 2
1.Youll get the indeterminate form 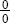 when you substitute x = 2. Factor and reduce the fractional expression and evaluate the limit
when you substitute x = 2. Factor and reduce the fractional expression and evaluate the limit  to get
to get 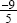 .
.
2.Use the product rule for the first term in the function, 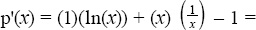 ln(x) + 1 1 = ln(x).
ln(x) + 1 1 = ln(x).
3.Find the first derivative by using the chain rule and the trigonometric identity for the sine of the double angle, k'(x) = 2sin(3x)cos(3x)(3) = 3sin(6x). The second derivative is also found using the chain rule, k''(x) = 3cos(6x)(6) = 18cos(6x).
4.Evaluate the function to get the point through which the line passes, w (2) = 5. Find the derivative of w ( z ) using the quotient rule, 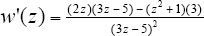 , and evaluate it at z = 2, w '(2) = 11. The equation of the line is w 5 = 11( z 2).
, and evaluate it at z = 2, w '(2) = 11. The equation of the line is w 5 = 11( z 2).
5.Find the value of the first derivative. 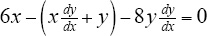 becomes
becomes 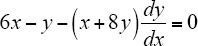 , so
, so 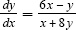 . The derivative of this statement is
. The derivative of this statement is 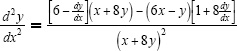 . Substitute what was found for
. Substitute what was found for  to get
to get 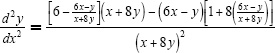 . Simplification beyond this is not necessary (and just plain tedious).
. Simplification beyond this is not necessary (and just plain tedious).
6.f'(c) = 3c2 and 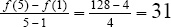 , so 3c2 = 31 implies that
, so 3c2 = 31 implies that 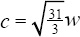 (but not
(but not 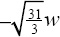 because that is not in the interval [1,5]).
because that is not in the interval [1,5]).
7.f'(

![Chris Monahan [Chris Monahan] Calculus II](/uploads/posts/book/119088/thumbs/chris-monahan-chris-monahan-calculus-ii.jpg)






![W. Michael Kelley [W. Michael Kelley] - Calculus I](/uploads/posts/book/119087/thumbs/w-michael-kelley-w-michael-kelley-calculus-i.jpg)


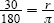 to arrive at
to arrive at 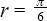 .
. becomes
becomes 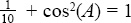 so
so 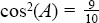 and
and 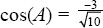 . Therefore,
. Therefore, 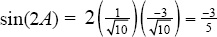 .
.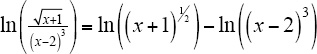 . Use the rule for logarithms of powers to get
. Use the rule for logarithms of powers to get 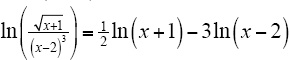 .
. and
and  , so the coordinates are
, so the coordinates are 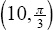 .
.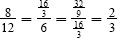 . The first term of the series is 12, so the sum of the infinite geometric series is
. The first term of the series is 12, so the sum of the infinite geometric series is 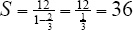 .
.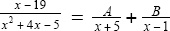 . Multiply by the common denominator: x 19 = A(x 1) + B(x + 5).
. Multiply by the common denominator: x 19 = A(x 1) + B(x + 5). .
.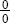 when you substitute x = 2. Factor and reduce the fractional expression and evaluate the limit
when you substitute x = 2. Factor and reduce the fractional expression and evaluate the limit  to get
to get 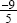 .
.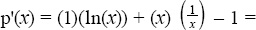 ln(x) + 1 1 = ln(x).
ln(x) + 1 1 = ln(x).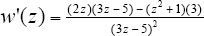 , and evaluate it at z = 2, w '(2) = 11. The equation of the line is w 5 = 11( z 2).
, and evaluate it at z = 2, w '(2) = 11. The equation of the line is w 5 = 11( z 2).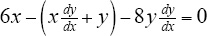 becomes
becomes 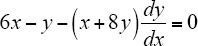 , so
, so 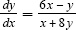 . The derivative of this statement is
. The derivative of this statement is 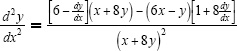 . Substitute what was found for
. Substitute what was found for  to get
to get 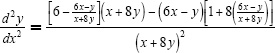 . Simplification beyond this is not necessary (and just plain tedious).
. Simplification beyond this is not necessary (and just plain tedious).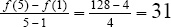 , so 3c2 = 31 implies that
, so 3c2 = 31 implies that 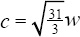 (but not
(but not 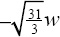 because that is not in the interval [1,5]).
because that is not in the interval [1,5]).