Ideas for Parents
and Teachers
Pogo Books let children practice
reading informational text while
introducing them to nonfiction
features such as headings, labels,
sidebars, maps, and diagrams,
as well as a table of contents,
glossary, and index. Carefully leveled text with
a strong photo match offers
early fluent readers the support
they need to succeed.
Before Reading
Walk through the book and
point out the various nonfiction
features. Ask the student what
purpose each feature serves. Look at the glossary together.
Read and discuss the words.
Read the Book
Have the child read the book
independently.
Invite him or her to list questions
that arise from reading.
After Reading
Discuss the childs questions.
Talk about how he or she might
find answers to those questions. Prompt the child to think more.
Ask: Have you ever ridden on a
roller coaster? Did you enjoy it? Pogo Books are published by Jump! 5357 Penn Avenue South Minneapolis, MN 55419 www.jumplibrary.com Copyright 2016 Jump! International copyright reserved in all countries. No part of this book may be reproduced in any form
without written permission from the publisher. Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data Pettiford, Rebecca. pages cm. (Amazing structures) Includes index. (Amazing structures) Includes index.
ISBN 978-1-62031-215-5 (hardcover: alk. paper) ISBN 978-1-62496-302-5 (ebook) 1. Roller coastersJuvenile literature. I. Title. GV1860.R64P47 2015 791.068dc23 2014042538 Series Editor: Jenny Fretland VanVoorst Series Designer: Anna Peterson Photo Researcher: Anna Peterson Photo Credits: ChameleonsEye/Shutterstock, ;
Corbis, ;
jaibiru/Shutterstock.com; Shawn Wainwright/Flickr,
;
Thinkstock, cover, .
Printed in the United States of America at
Corporate Graphics in North Mankato, Minnesota.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1
A Thrilling Ride CHAPTER 2
How Roller Coasters Work CHAPTER 3
Building Roller Coasters
CHAPTER
A THRILLING
RIDE
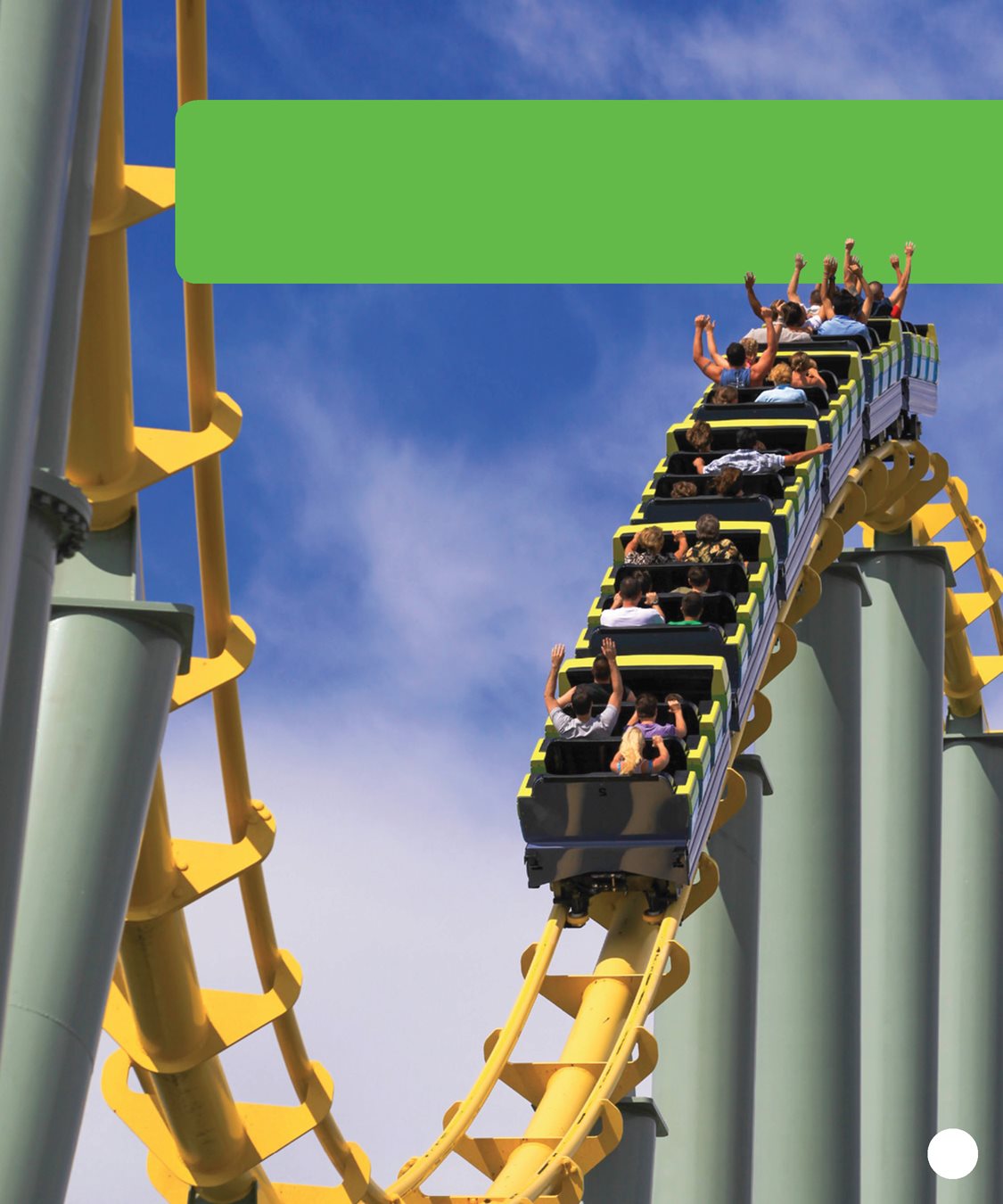
Have you ever been
to an amusement park? Did you ride the roller coasters? CHAPTER 1
People who ride them enjoy the thrill
of fast rides. People have found ways
to make fast rides for a long time. CHAPTER 1
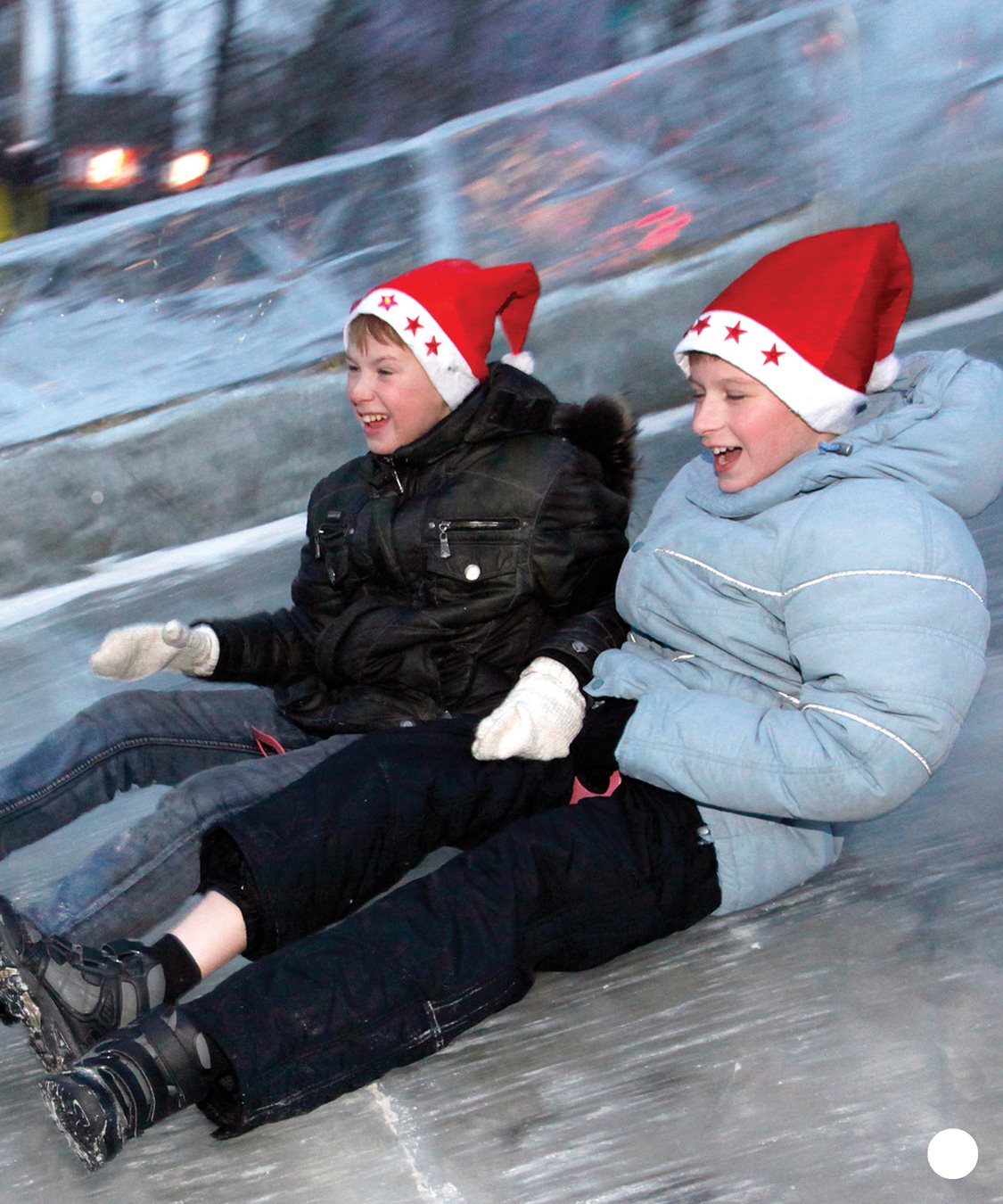
Todays roller coasters started as
something much simpler: a slide. In the 1600s, people in Russia
built tall, wooden ice slides.
To reach the top, people
climbed stairs. They rode
down the ice on a sled.
Sand at the end of the
slide helped them stop.
What do roller coasters
look like today? DID YOU KNOW? The Switchback Railway
was the first coaster
in the United States.
It opened in 1884 at Coney
Island in Brooklyn, New York. CHAPTER 1
CHAPTER 1
CHAPTER
HOW ROLLER
COASTERS WORK
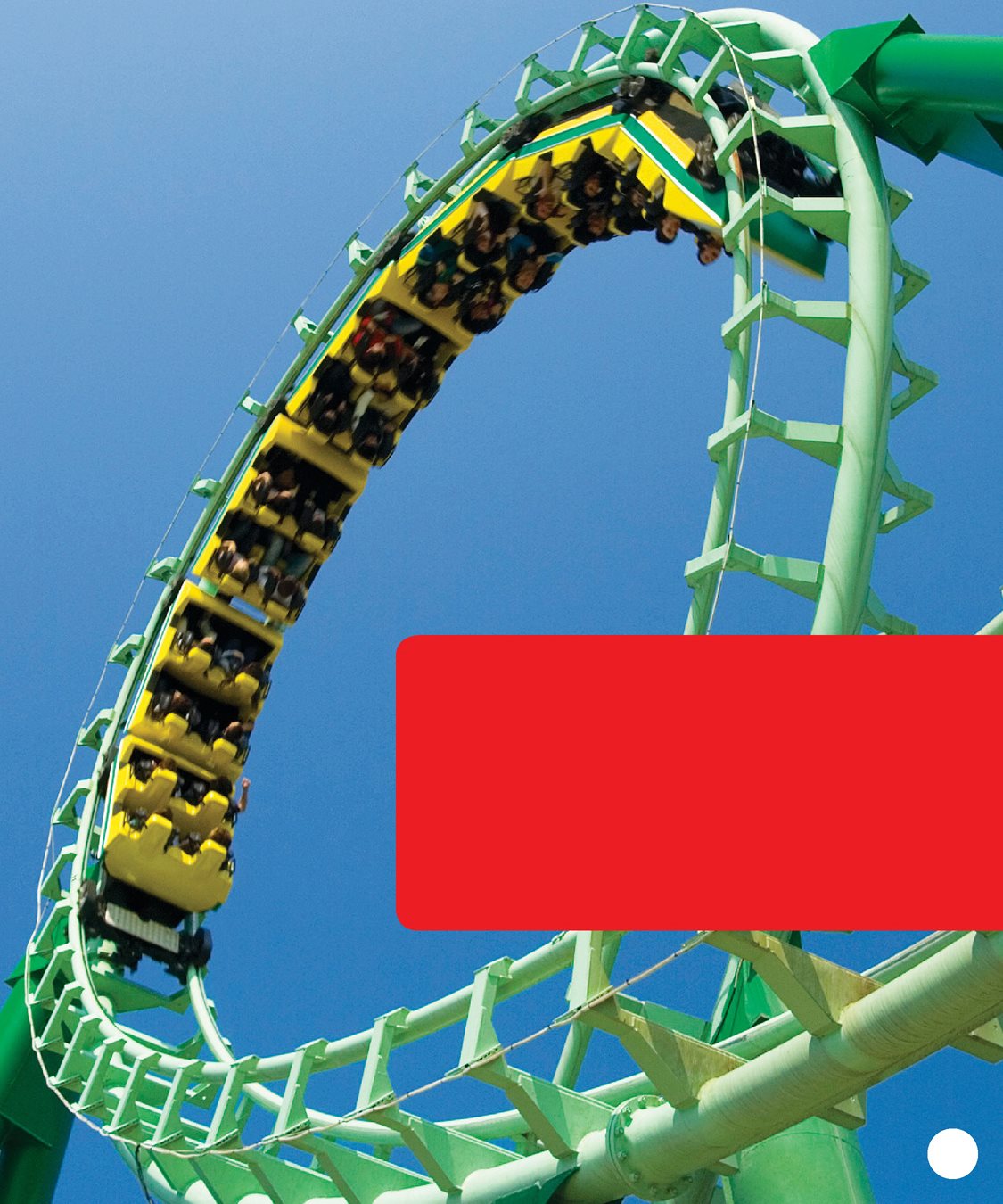
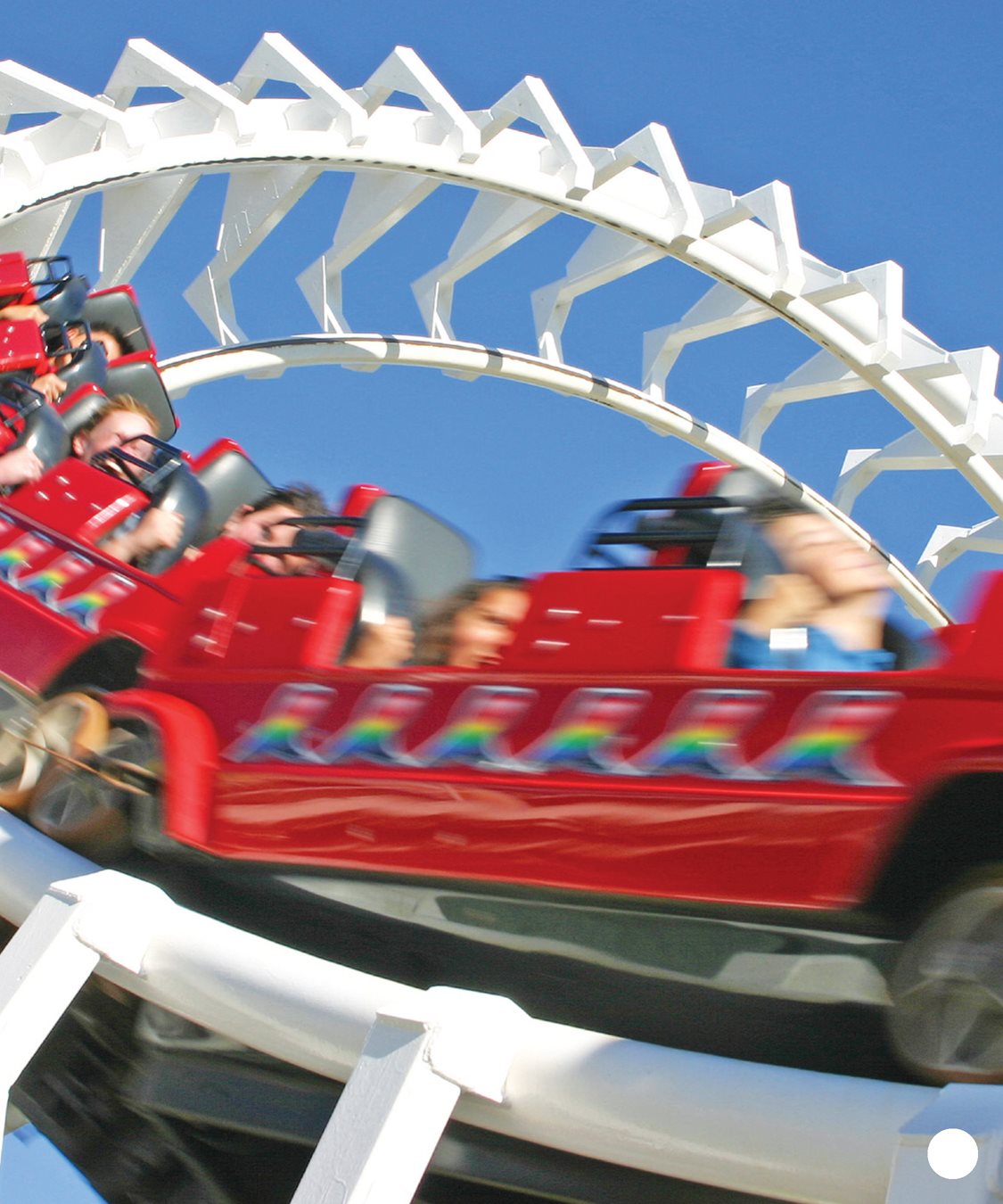
A roller coaster looks like a train.
A chain of open cars moves on a track .
A motor pulls each car up a hill. CHAPTER 2
Suddenly, the car drops.
It twists and turns. At times,
it may be upside down! Starting high is a key part
of how the ride works. CHAPTER 2
CHAPTER 2
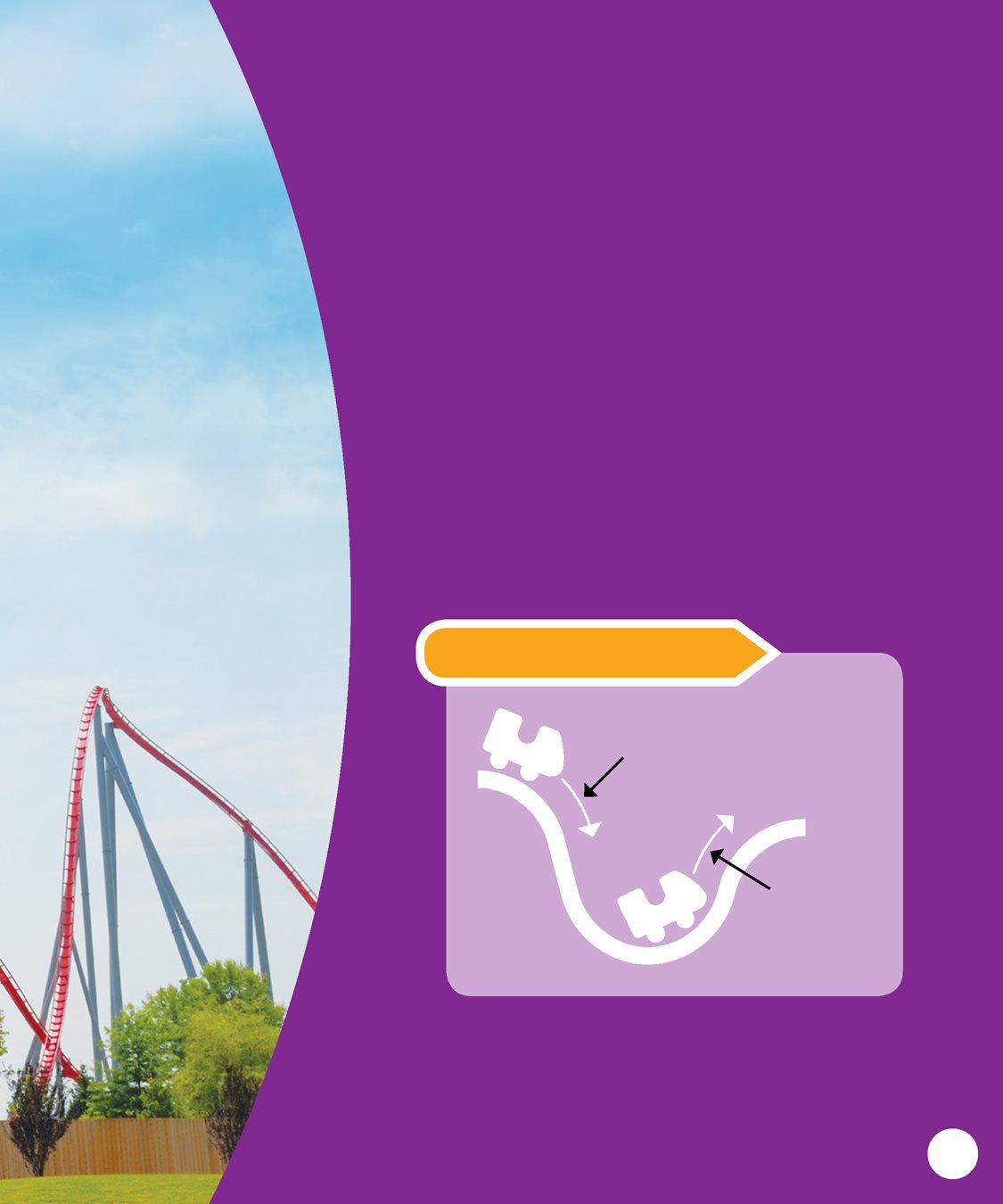
By starting high, the car has the
energy it needs to move. This is
called potential energy .
As the car drops, the potential
energy changes to kinetic
energy . This energy comes
from the rides drop. It also
comes from the pull of
gravity . Its what makes
the ride fast. TAKE A LOOK! potential
energy high kinetic
energy high CHAPTER 2
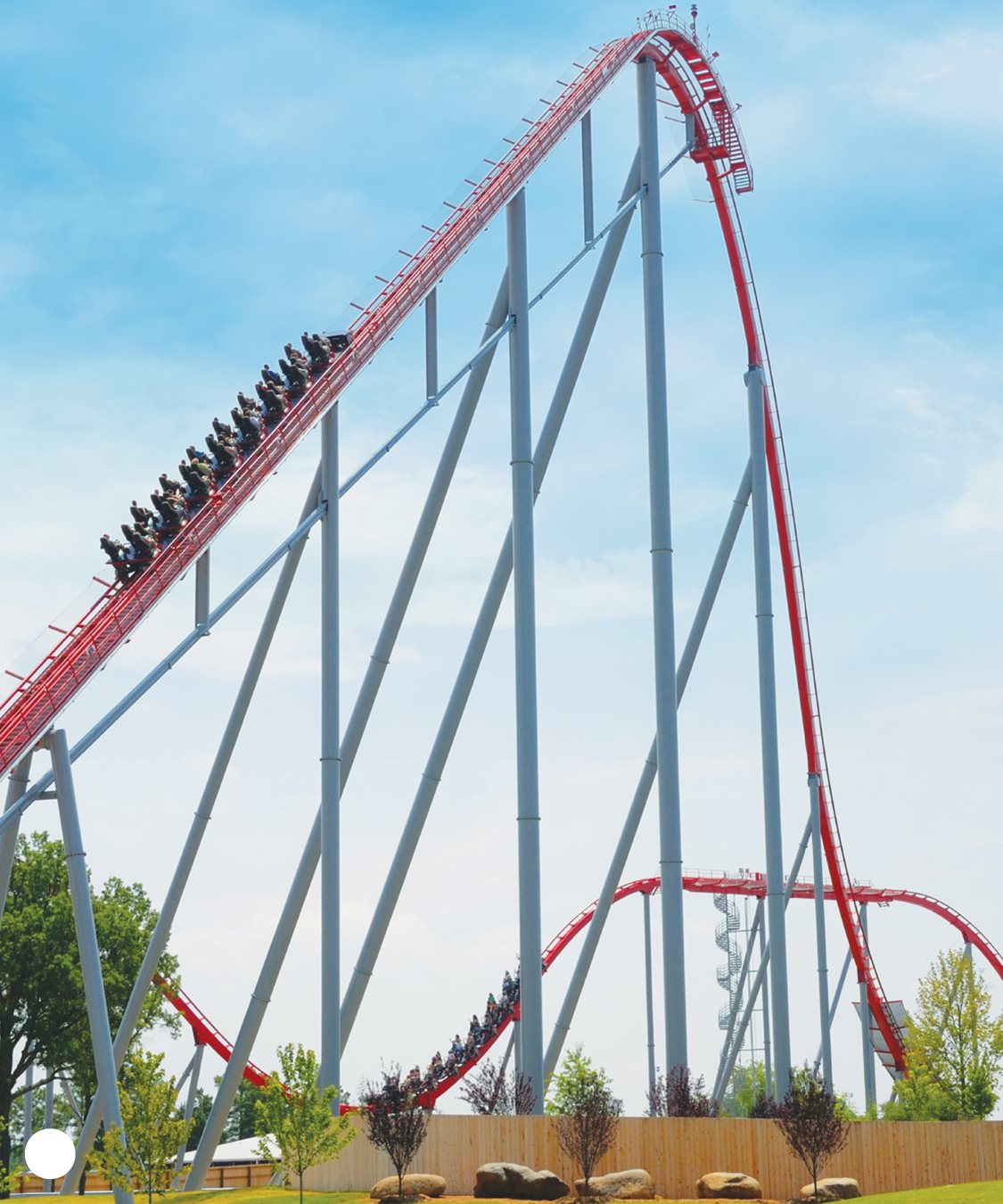
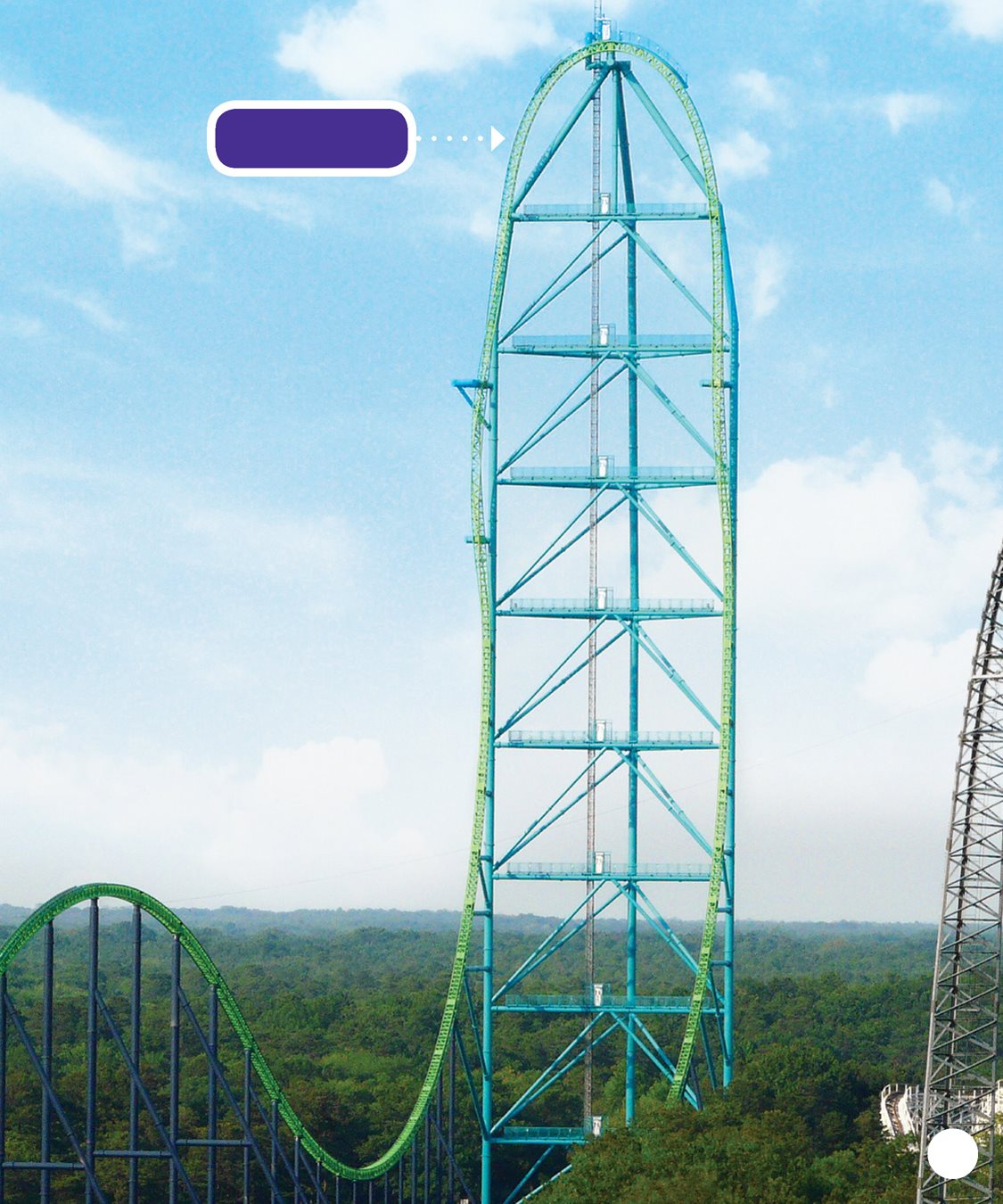
The Kingda Ka is the fastest
coaster in North America.
It reaches miles per hour
( kilometers per hour )
in 3.5 seconds! It is also the
tallest roller coaster in the
world. At its tallest point it
is feet ( meters ) high! DID YOU KNOW? Some rides use a launch system
to start the cars.
The launch builds
up and stores a lot of energy.
When the energy
is released, the
cars zoom forward. CHAPTER 2
Kingda Ka CHAPTER 2
Roller coasters run on incredibly
powerful motors. A cars engine usually delivers
about horsepower .
But roller coasters can
produce nearly 21,000
horsepower! Who makes roller coasters?
Lets find out. DID YOU KNOW? A roller coaster needs
brakes so it can slow down
and stop when the ride
ends. The brakes are built
into the track. CHAPTER 2
CHAPTER 2
CHAPTER
BUILDING
ROLLER
COASTERS
Designers build roller
coasters.
They look
for new ways to make
the rides faster and
more fun. CHAPTER 3
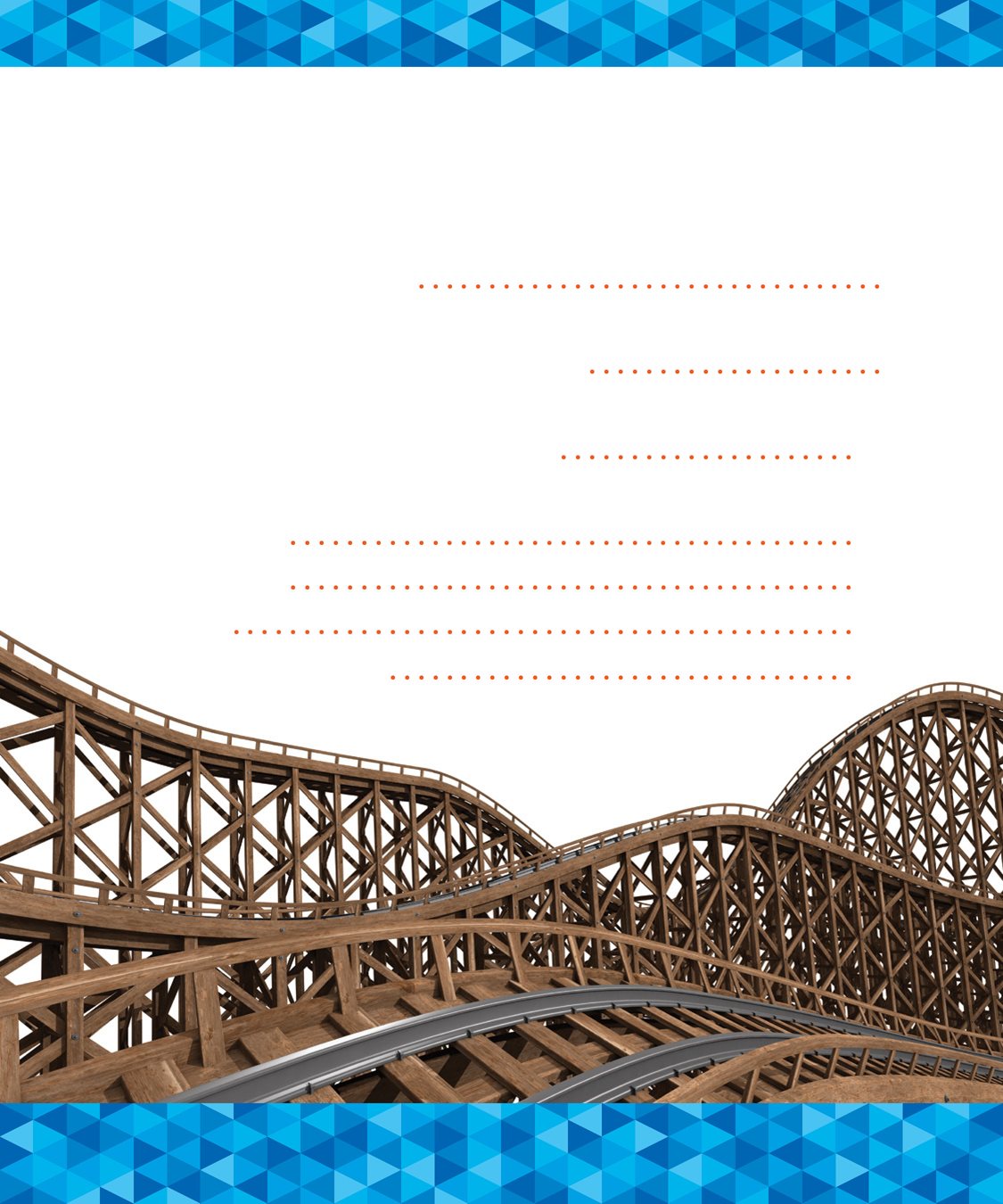
Newer rides are made of
steel. They are the fastest
and tallest rides. They have
more drops and loops. CHAPTER 3
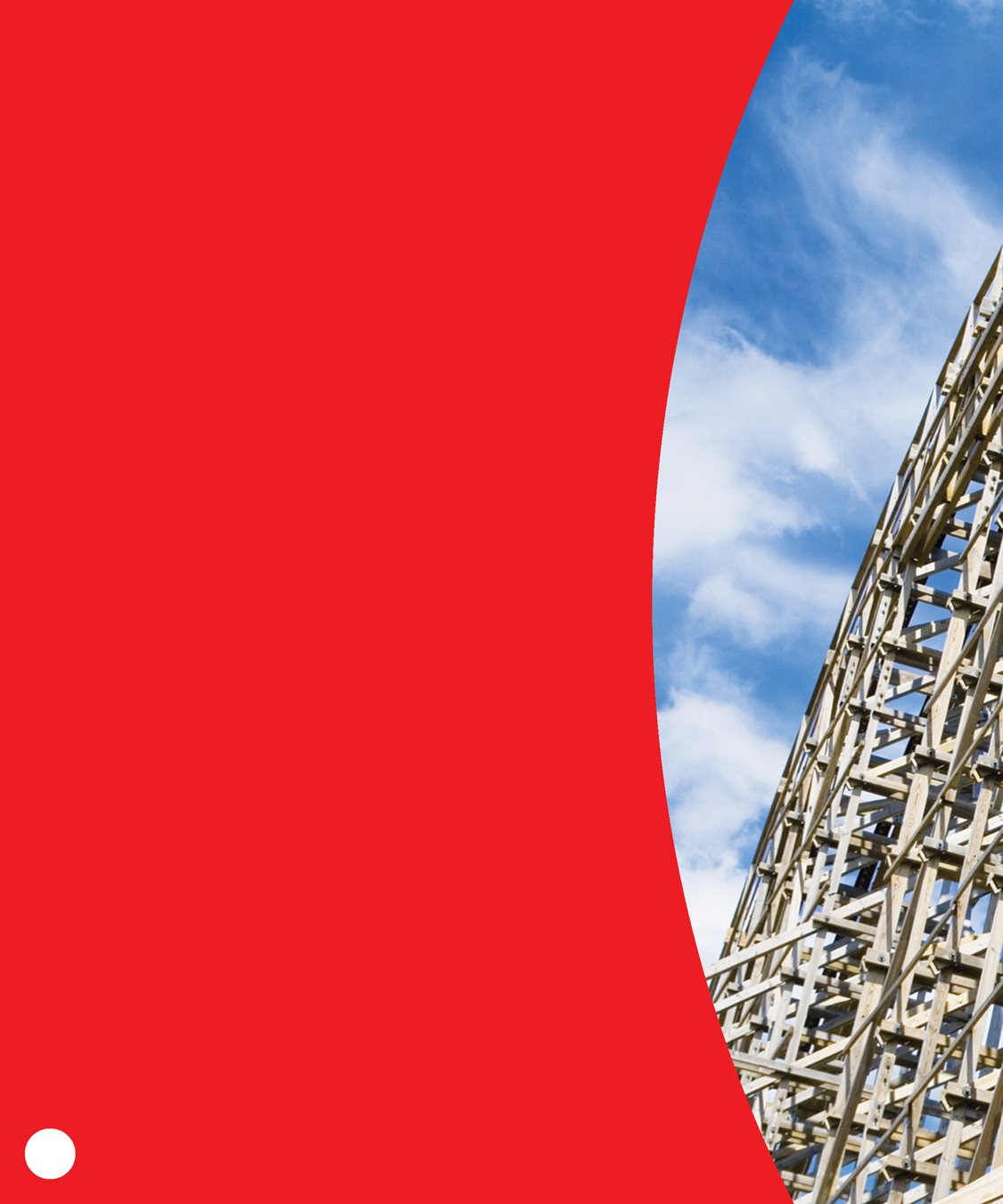
Wooden coasters are
often older and louder.
They are not as tall