Ellis, Carol. Leopards (Endangered). Tarrytown, N.Y.: Marshall Cavendish, 2010.
Joubert, Beverly and Dereck. Face to Face with Leopards . Des Moines, Iowa: National Geographic, 2010.
Shiekh-Miller, Jonathan. Big Cats . London, UK: Usborne, 2008.
What Are Big Cats?
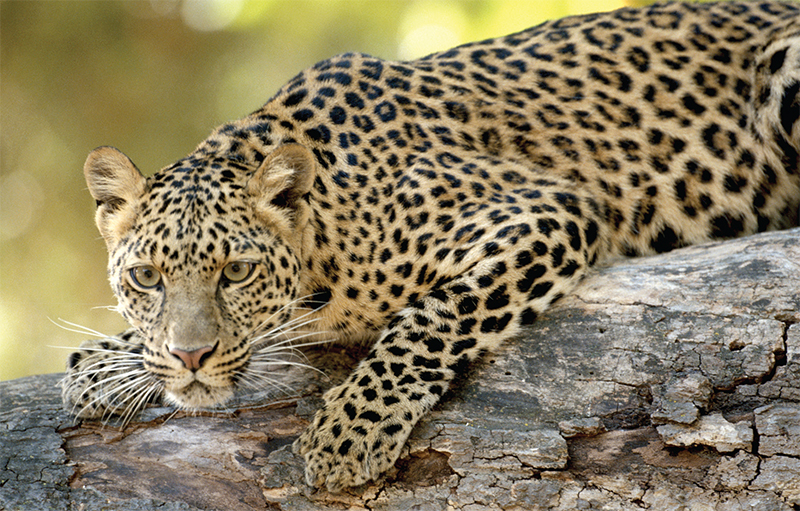
Whats that up in the tree? Its a leopard finding a place to rest in the heat ofthe day. Leopards are far more active at night when its cooler. Thats when theydo most of their hunting.
Mammals
Big cats such as leopards are mammals. Mammals have fur or hair on their body anduse lungs to breathe. Most give birth to live young, and mammal babies feed on milkfrom their mother. Does this description sound familiar? It shouldhumans are alsomammals.
Cats
There are 36 species in the cat family, including the domestic cat you might haveat home! But only a small number are known informally as big cats. One definitionof big cats includes all the species of Panthera or roaring cats. Tigers are thelargest of the roaring cats, followed by lions, jaguars, and leopards. Some scientistsalso describe the cheetah, puma, snow leopard, and clouded leopard as big cats.
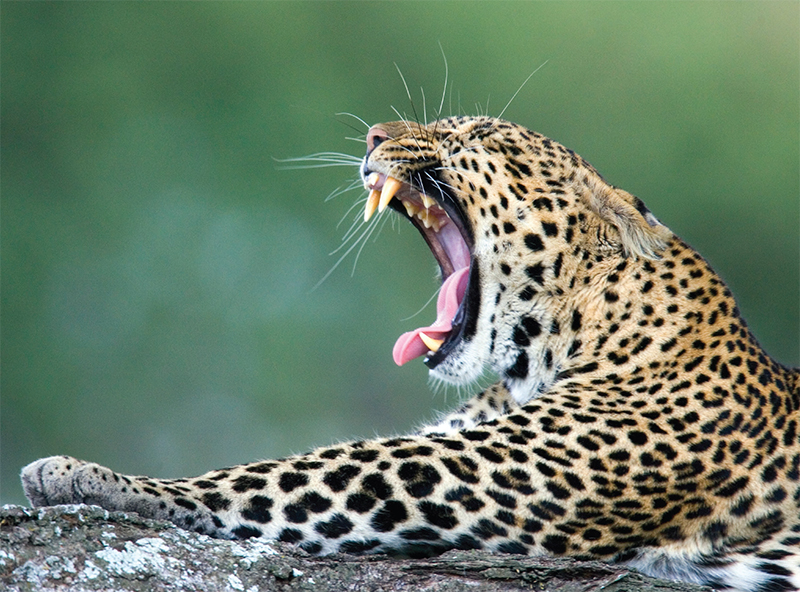
Cats are great hunters, usually searching for food at night because their visionis often a lot better than that of their prey, and because its cooler. All theirsenses are excellent, helped by rotating ears and sensitive vibrissae (whiskers).
LENGTH OF HAIR
The hairs of an Amur leopards coat change in length from summer to winter. In summer,they are about 1 inch (2.5 centimeters) long but in winter they grow to 3 inches(nearly 7 centimeters).
Leopards are amazing animals but many subspecies are struggling to survive in thewild.
What Are Leopards?
There are thought to be nine subspecies of leopard, each named after where it isfound: African, Amur, Arabian, Central Asia (Persian), Indian, Javan, Indo-Chinese,Northern Chinese, and Sri Lankan. A recent study has suggested that two more subspeciesexist: the Anatolian leopard in Turkey and the Balochistan leopard in Pakistan andAfghanistan. Clouded leopards are distinct enough to be regarded as separate species,as are snow leopards.
Leopards usually sleep during the day and hunt in the night.
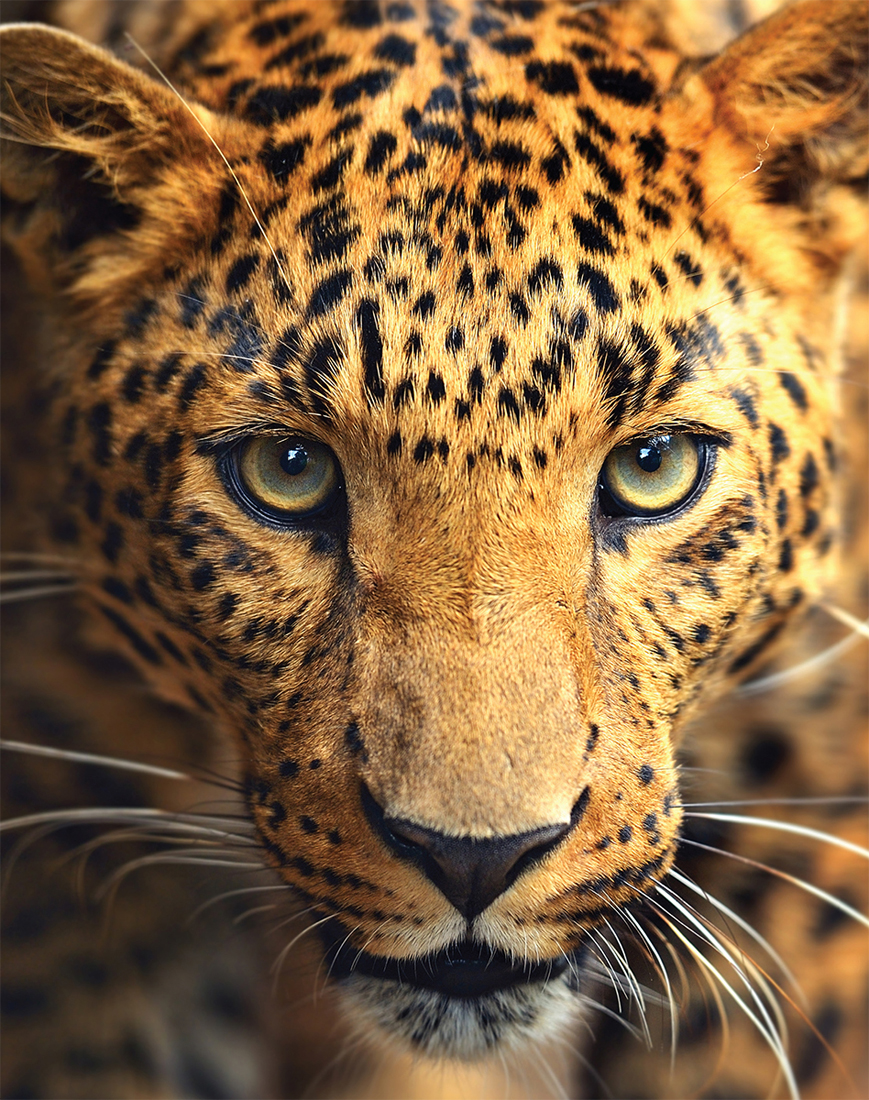
Leopards have large heads with small round ears and whiskers above their mouths.
Features
Most leopards are yellow to light brown with black spots, known as rosettes. Thereare some leopards that have black coats, but these are not as common. Leopards legsare short in comparison to their body.
The average height and weight of leopards varies between subspecies and depends inpart on the amount and type of prey available. Mountain and desert leopards tendto be smaller than leopards living in woodlands or grasslands. Most females tendto grow to 5.56.25 feet (1.71.9 meters) in length; males measure 5.257.5 feet(1.62.3 meters). Females typically weigh 37.5128 pounds (1758 kilograms), andmales are usually 68143 pounds (3165 kilograms).
WHATS IN A NAME?
The leopard gets its name from the Greek word leopardus , which is a mixture of leon (lion) and pardus (panther).
How Are Leopards Classified?
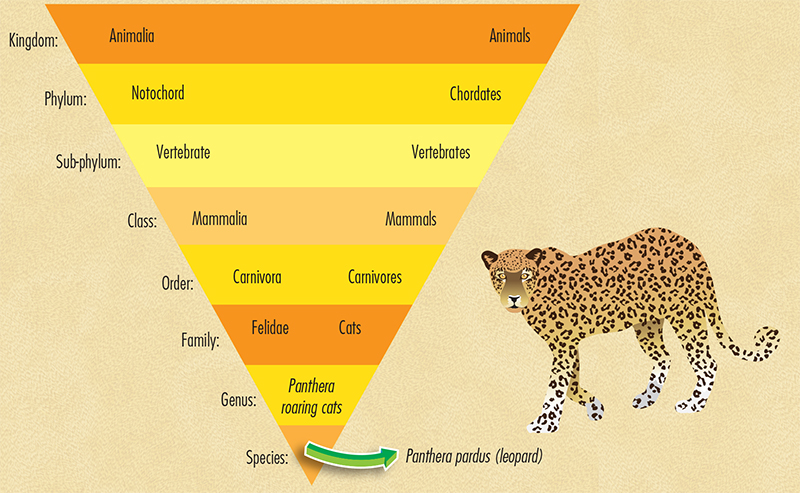
Classification is the way that humans try to make sense of the world. Grouping livingthings together by the characteristics that they share allows us to identify themand understand why they live where they do and behave how they do.
Classification groups
In classification, animals are split into various groups. The standard groups areKingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, and Species. Sometimes, further classificationinvolves adding more groups such as a subspecies. Each of the standard groups containsfewer and fewer members. For example, there are far more animals to be found in theclass Mammalia (mammals), than animals in the family Felidae (cats). Animals aregiven an internationally recognized two-part Latin name. This helps to avoid confusionif animals are known by different common names in different countries. The leopardsLatin name is Panthera pardus , for example.
Evolution of cats
While the first cat-like mammals appeared 60 million years ago, it is thought thatthe first true cats appeared about 25 million years ago. One was Proailurus, meaningearly cat, which was an animal the size of a large domestic cat. The family Felidaeincludes modern wild cats such as leopards and other big cats as well as domesticcats. Members of this family are called felids.
This feline family tree shows estimated dates of when new lines evolved.
AMUR LEOPARD
The Amur leopard is the worlds most endangered cat. In the first successful snow-trackcensus since 2007, between 43 and 45 adult Amur leopards were counted. This is anincrease on the previous estimate of 35 leopards.
Classification disagreements
The genus Panthera is still being changed and added to today. Scientists disagreeover which species are most closely related to each other.
Clouded leopards are a different genus from leopards Neofelis rather than Panthera and have differences in teeth and skull shape. Snow leopards were once thought tobe very different from leopards and had their own genus. However, they have now beenreturned to the Panthera genus after it was discovered that they are most closelyrelated to tigers. They are still very different from leopards though.
There are also issues over the number of subspecies with some scientists claimingseven rather than nine. Others suggest 15 subspecies or even more. Changes are suggestedas new methods of determining species emerge. Scientists are now using genetics towork out differences.
This diagram shows how the leopard is classified.
CARL LINNAEUS
Carl Linnaeus included the leopard in his book Systema Naturae in 1758. The bookintroduced the first modern way of classifying animals. This makes the leopard oneof the first animals to be named within the modern system of classification.