Charles River Editors - Umma: The History and Legacy of the Ancient Sumerian City
Here you can read online Charles River Editors - Umma: The History and Legacy of the Ancient Sumerian City full text of the book (entire story) in english for free. Download pdf and epub, get meaning, cover and reviews about this ebook. year: 2020, publisher: Charles River Editors, genre: History. Description of the work, (preface) as well as reviews are available. Best literature library LitArk.com created for fans of good reading and offers a wide selection of genres:
Romance novel
Science fiction
Adventure
Detective
Science
History
Home and family
Prose
Art
Politics
Computer
Non-fiction
Religion
Business
Children
Humor
Choose a favorite category and find really read worthwhile books. Enjoy immersion in the world of imagination, feel the emotions of the characters or learn something new for yourself, make an fascinating discovery.
- Book:Umma: The History and Legacy of the Ancient Sumerian City
- Author:
- Publisher:Charles River Editors
- Genre:
- Year:2020
- Rating:5 / 5
- Favourites:Add to favourites
- Your mark:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Umma: The History and Legacy of the Ancient Sumerian City: summary, description and annotation
We offer to read an annotation, description, summary or preface (depends on what the author of the book "Umma: The History and Legacy of the Ancient Sumerian City" wrote himself). If you haven't found the necessary information about the book — write in the comments, we will try to find it.
Umma: The History and Legacy of the Ancient Sumerian City — read online for free the complete book (whole text) full work
Below is the text of the book, divided by pages. System saving the place of the last page read, allows you to conveniently read the book "Umma: The History and Legacy of the Ancient Sumerian City" online for free, without having to search again every time where you left off. Put a bookmark, and you can go to the page where you finished reading at any time.
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
By Charles River Editors
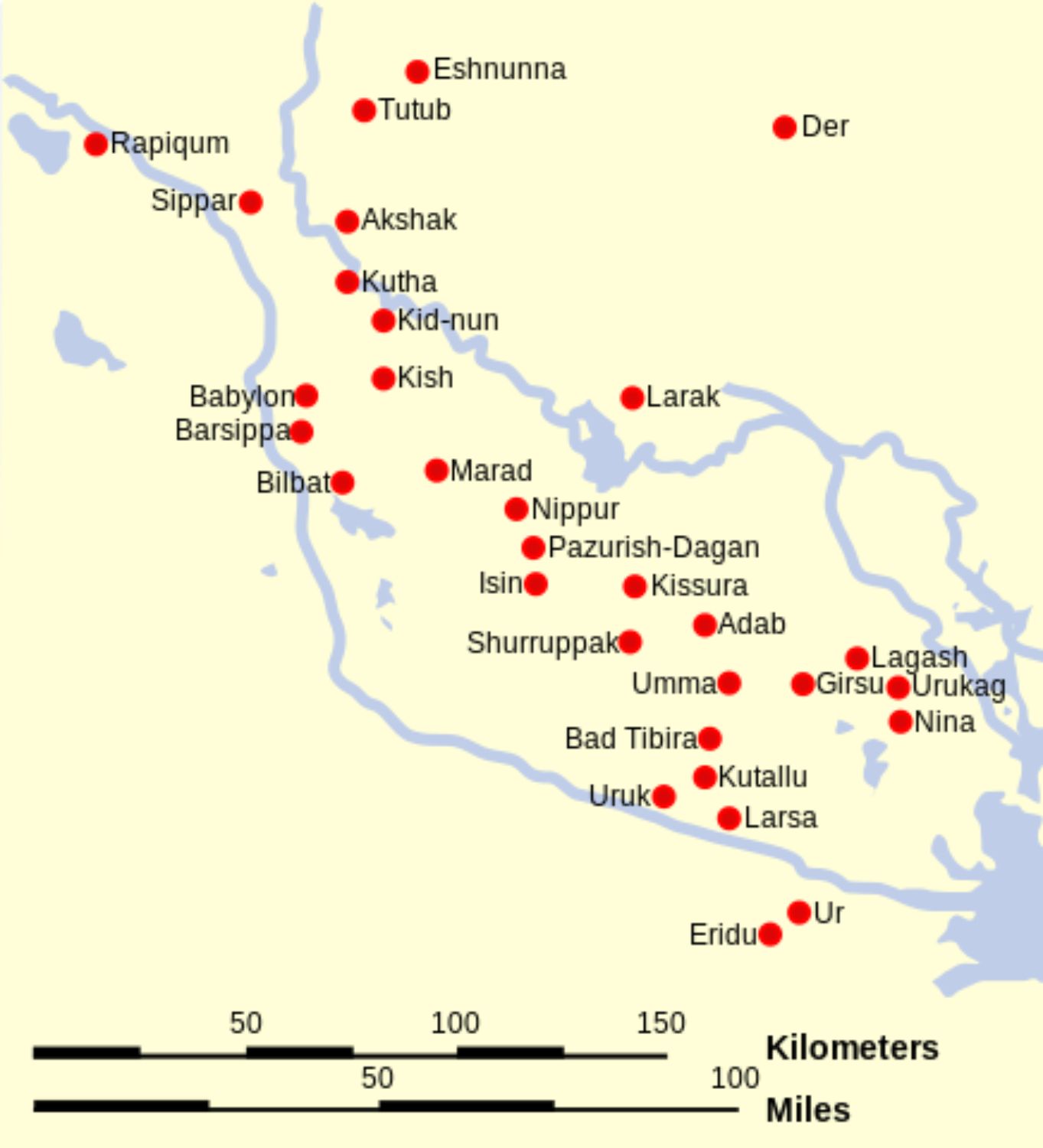
A map of Sumer

Charles River Editors provides superior editing and original writing services across the digital publishing industry, with the expertise to create digital content for publishers across a vast range of subject matter. In addition to providing original digital content for third party publishers, we also republish civilizations greatest literary works, bringing them to new generations of readers via ebooks.
Sign up here to receive updates about free books as we publish them , and visit Our Kindle Author Page to browse todays free promotions and our most recently published Kindle titles.
Sumer
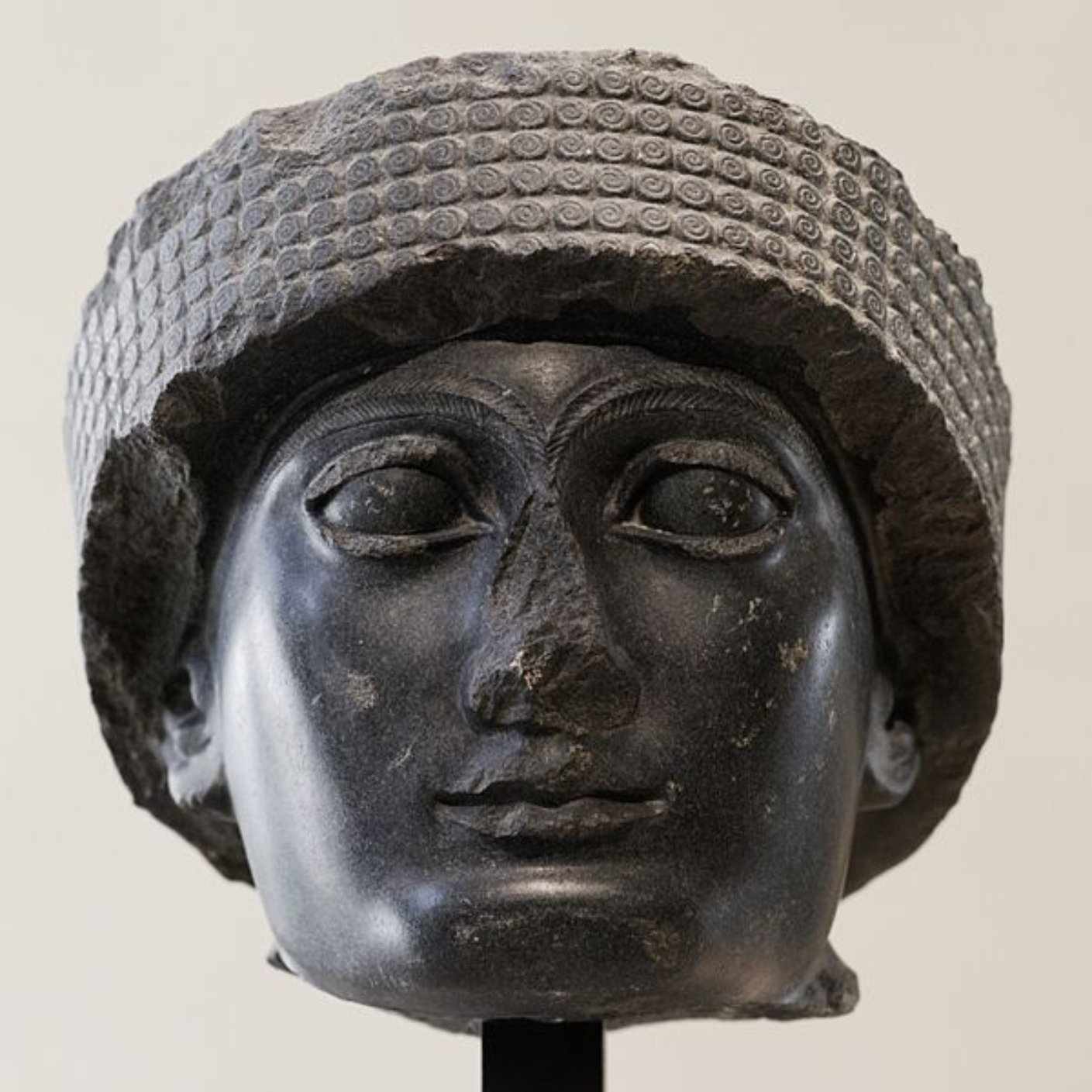

Gudea of Lagash
When American archaeologists discovered a collection of cuneiform tablets in Iraq in the late 19th century, they were confronted with a language and a people who were at the time only scarcely known to even the most knowledgeable scholars of ancient Mesopotamia: the Sumerians. The exploits and achievements of other Mesopotamian peoples, such as the Assyrians and Babylonians, were already known to a large segment of the population through the Old Testament and the nascent field of Near Eastern studies had unraveled the enigma of the Akkadian language that was widely used throughout the region in ancient times, but the discovery of the Sumerian tablets brought to light the existence of the Sumerian culture, which was the oldest of all the Mesopotamian cultures.
Although the Sumerians continue to get second or even third billing compared to the Babylonians and Assyrians, perhaps because they never built an empire as great as the Assyrians or established a city as enduring and great as Babylon, they were the people who provided the template of civilization that all later Mesopotamians built upon. The Sumerians are credited with being the first people to invent writing, libraries, cities, and schools in Mesopotamia (Ziskind 1972, 34), and many would argue that they were the first people to create and do those things anywhere in world.
For a people so great it is unfortunate that their accomplishments and contributions, not only to Mesopotamian civilization but to civilization in general, largely go unnoticed by the majority of the public. Perhaps the Sumerians were victims of their own success; they gradually entered the historical record, established a fine civilization, and then slowly submerged into the cultural patchwork of their surroundings. They also never suffered a great and sudden collapse like other peoples of the ancient Near East, such as the Hittites, Assyrians and Neo-Babylonians did. A close examination of Sumerian culture and chronology reveals that the Sumerians set the cultural tone in Mesopotamia for several centuries in the realms of politics/governments, arts, literature, and religion.
Even today, the world owes the Sumerians a tremendous amount. When Western Europe was still in the Stone Age, it was the Sumerians who invented writing and the wheel, divided time into minutes and seconds, tamed nature, and built gigantic cities. They embraced culture and the arts, and their caravans crossed the desert, opening up the first trade routes. Their myths and legends inspired various origin stories, and their memory lives on in the Old Testament. They wrote the history of the birth of mankind. The heritage of the Sumerian civilization and their successors is everywhere.
There were many great cities in the ancient Near East that influenced the course of history. Babylon and Jerusalem are two of the better known, but Nineveh, Damascus, Ur, Uruk, Memphis, Thebes, and Sidon were just a few of the great cities where science and literature were created, theologies proposed, and empires born. There are numerous reasons why these cities became prominent, many of which were related to the fortuitous circumstances of environment and politics, but for every one of the great cities, there were many more that flourished and then had their prestige overshadowed by the growth of their larger neighbors. These cities often played important roles in the historical processes of the region for a time, but due to numerous circumstances their influence proved to be ephemeral.
One of the most interesting of these early ephemeral cities was Umma. Located in the southern region of Mesopotamia known as Sumer, Umma became a prominent Sumerian city in the early 3 rd millennium BCE, and while Uruk was the most important Sumerian city during that era, Umma was close behind in influence and power and for a time seemed poised to become the most important place in Sumer. A powerful dynasty arose in Umma that expanded its influence across southern Mesopotamia, uniting the Sumerian cities under one government, but the central position that Umma enjoyed proved to be temporary because Semitic conquerors from the north forced Umma and the other cities to accept their rule.
Umma continued to exist and even prosper, and it eventually became a somewhat important city again under the Neo-Sumerian Third Dynasty of Ur in the late 3 rd millennium BCE. It was not until the 6 th century BCE that Umma went unmentioned in the historical record during the Neo-Babylonian Period. By then the city was a shadow of its former self, but some of the earliest known Mesopotamian historiographical inscriptions were recorded in Umma, the god of its city became an important deity in the Mesopotamian pantheon, and its merchants became well-known for introducing a type of silver standard for trade. Thus, even as Umma was forgotten even as far back as ancient times, it continues to fascinate modern historians and archaeologists.
Umma: The History and Legacy of the Ancient Sumerian City examines the origins of the settlement, and what life may have been like there. Along with pictures of important people, places, and events, you will learn about Umma like never before.
The word Mesopotamia highlights the central theme of life in the Fertile Crescent, coming from the ancient Greek for land between two rivers.
The people who settled in Mesopotamia were inextricably connected to their environmental context. In central and southern Mesopotamia the low hills and fertile plains were juxtaposed with swamps, jungles, and countless streams where the Tigris and Euphrates drained into the Persian Gulf most of which have disappeared over the course of time. Mesopotamia had few natural resources; no stone, wood, or precious metals could be found in southern Iraq. There was only water, and a rich alluvial soil with which a hardworking people could transform a land of scarcity into a land of plenty.
The Mesopotamian civilizations are amongst the worlds oldest, with archaeological evidence stretching back beyond 6000 BCE into the Neolithic. As hunter-gatherers discovered ways to farm and store their food for weeks and months at a time, instead of being itinerant they decided to colonize lands along the fertile banks of the Tigris and Euphrates. During the Ubaid Period (ca. 6500 3800 BCE), the earliest settlements were established in southern Mesopotamia. Many of the smaller villages were clustered in relatively close proximity to one another due to the nature of irrigation on the alluvial plain. The large cities would have had a number of smaller satellite towns in their hinterland. The archaeological remains of the latter have largely disappeared over time, so it is large sites like Eridu that archaeologists must look at to build a picture of life in ancient Mesopotamia.
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
Similar books «Umma: The History and Legacy of the Ancient Sumerian City»
Look at similar books to Umma: The History and Legacy of the Ancient Sumerian City. We have selected literature similar in name and meaning in the hope of providing readers with more options to find new, interesting, not yet read works.
Discussion, reviews of the book Umma: The History and Legacy of the Ancient Sumerian City and just readers' own opinions. Leave your comments, write what you think about the work, its meaning or the main characters. Specify what exactly you liked and what you didn't like, and why you think so.



















