Medium Tanks of Germany in the World War II
(Extended edition)
Unique modern and old world war technology
William S. Carson
All rights reserved
William S. Carson, 2017
Fotos by:
Gina Smith
Tanya Dolski
Sam Sanderson
Bill Carson
This is an extended edition. In it, I added a few little-known models of medium tanks.
This book is devoted to the models of medium tanks used by Wehrmacht during World War II. Outside you will learn the history of the creation of medium tanks, their tactical and technical characteristics. I also included various upgrades and experimental models of medium tanks.
The book is intended for those who are interested in military armored vehicles.
Content:
Medium Tank "Grosstraktor"
Medium Tank E-50
Medium Tank Pz.Kpfw.III
Medium Tank PzKpfw IV
Medium Tank E-75
Family of tanks Pz.Kpfw.V "Panther"
Medium Tank "Panther II"
Unfortunately, my native language is Spanish, so I apologize in advance for all the errors and inaccuracies that you see in the text.
Introduction
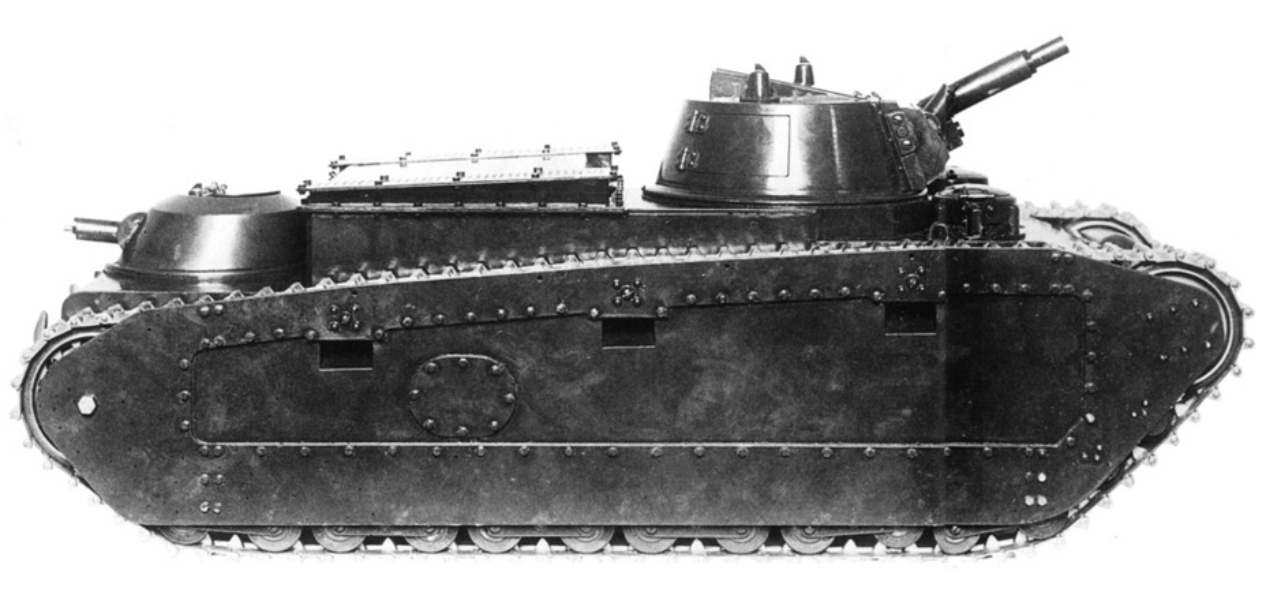
Model Armeewagen 20 development Krupp. Tower and housing in the original configuration
German tank building in the eyes of an inexperienced reader looks like something from the snuffbox. It may seem that a decade and a half after the end of the First World War, German industry suddenly came to life and immediately gave out first-class examples of armored vehicles. Miracles do not happen: besides German engineering engineers like Volmer and Merker, who worked abroad, Germany had its own tank program. It developed in secret, and its result was the appearance of tanks of a very strange construction. One of these machines was Grosstraktor, the middle tank, which became the personification of the German tank building of the 1920s. It was the first step on the way to the creation of Pz.Kpfw.IV - the most widespread German tank of the Second World War.
By the beginning of the Second World War, the armored tanks of the Third Reich included light tanks Pz Kpfw I, Pz Kpfw II, Czech tanks Pz Kpfw 35 (t), Pz Kpfw 38 (t), medium tanks Pz Kpfw III and Pz Kpfw IV, and armored personnel carriers.
The armament of the tanks consisted mainly of small-caliber guns and machine guns, which enabled them to create at close distances the fire zone necessary to defeat and demoralize the enemy's manpower, and the high speed of the tanks was the main factor of a rapid and deep breakthrough into the enemy territory.
The experience of military operations in Poland and Western Europe revealed the low combat qualities of 37- and 50-mm German short-barrel cannons, whose shells in most combat collisions could not penetrate the armor of French heavy tanks. In this regard, the 1940 Pz Kpfw III tank was equipped with more powerful 50-mm cannon. It was also found out that the armored protection and the reserve of the German tanks are insufficient.
Preparing for the attack on the USSR, the Third Reich was striving for a quantitative increase in its tank fleet. An important role in its increase was played by the Czech factories seized by Germany, which in the first half of 1941 provided one-fifth of the tanks that were supplied to the German army. As of June 1, 1941, the German Armed Forces and its satellites numbered 4,188 tanks and 377 assault guns. The operation was intended for 3,712 tanks and automatic control systems, of which the average Pz Kpfw III tanks were 2348 and Pz Kpfw IV - 438.
The shortcomings in the organizational and technical equipment of the tank troops of the Third Reich did not manifest themselves before the attack on the Soviet Union after violent clashes with the new Soviet T-34 and KV tanks, which were few (KV-504 tanks) at the beginning of the war as part of the Red Army. During the first months of bloody battles units of German light tanks Pz Kpfw I and Pz Kpfw II quickly lost their staff.
At the end of 1941 in Germany, the production of all light tanks that did not meet the requirements for fighting new Soviet tanks was stopped. Irrevocable losses of German tanks from June to November 1941 amounted to 2,251 units, of which 348 medium tanks Pz Kpfw IV. At that time, the Pz Kpfw IV was the best German tanks. However, not only the cannons of the new Soviet T-34 and KV tanks penetrated their armor, but also the T-26 and BT light tank guns, as well as the 45mm Soviet anti-tank guns (the so-called "sorokopyatki").
The appearance of T-34 tanks in combat necessitated a radical change in the design of German tanks, as well as their tactical application. If previously the main task of the tank divisions of the Wehrmacht was the suppression of the infantry and artillery of the enemy, now the main task was to defeat the enemy tanks at maximum range. To do this, it was intended to rearm all medium tanks with 75-mm long-barreled cannons.
Despite the modernization of the medium-sized tanks Pz Kpfw III and Pz Kpfw IV, aimed at increasing their firepower and armor protection, in terms of their main indicators, they continued to yield to the new Soviet tanks. Therefore, the Pz Kpfw III tank, which was the base of the tank units in 1940-1942, was not produced since June 1943, and various samples of special tanks and automatic control systems were created on its basis. The average Pz Kpfw IV tank, repeatedly modernized, remained in production until the end of the war.
Medium tank as a priority
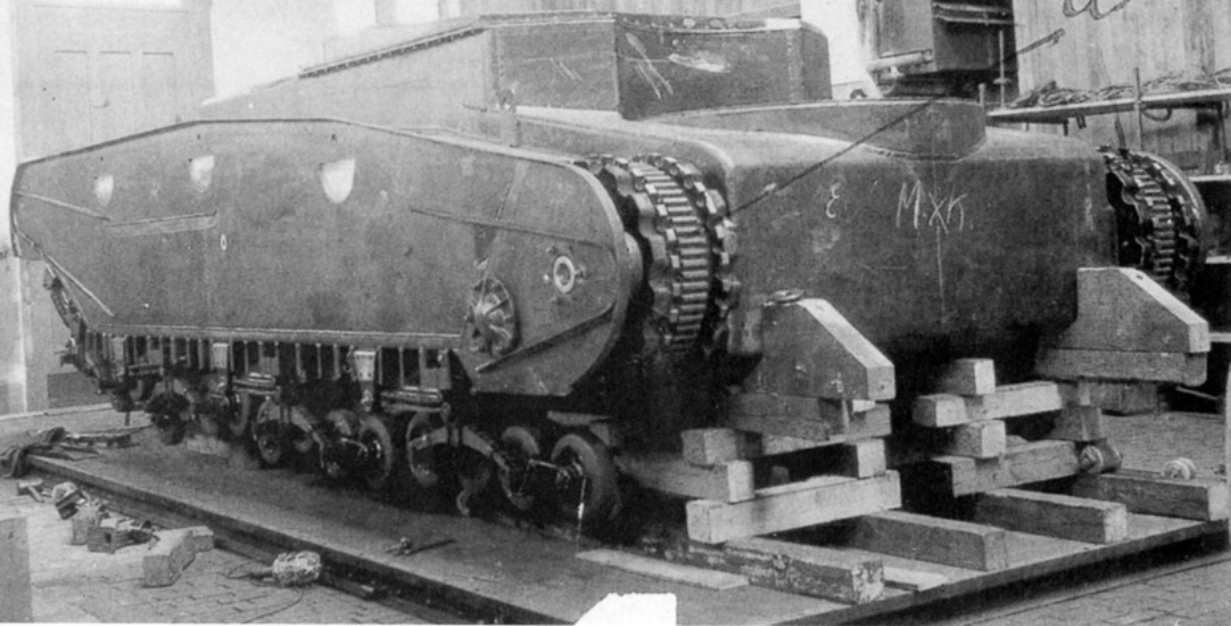
Assembling the Daimler-Benz tank at the Rheinmetall plant in Unterls. The chassis design is clearly visible
The end of the First World War was accompanied by a real collapse of the German tank industry. It's not even that the terms of the Treaty of Versailles directly forbade Germany to develop and produce tanks, as well as other armored vehicles. The German command itself exerted considerable effort to defeat its own tank-building. Somehow it is difficult to characterize what happened to this industry of German industry towards the end of 1918.
Attempts of Joseph Volmer to return work to normal channel were only partially successful. Establishing the production of the light tank LK-II went with great difficulty and was accompanied by opposition from the German military. Some of them still kept on dreaming about steel monsters like the 120-ton K-Wagen. One can safely say that the German generals have signed their own illiteracy and the highest level of incompetence. With such "successes," it should not be surprising that the work began in the end with a clean slate.
The beginning of work on a new German tank was preceded by a careful study of the development of tank building abroad. It became clear that the German tank-building greatly lagged behind in development. This was especially true for medium and heavy tanks. While the Germans were trying to adapt their designs to their needs, they were sent to the dustbin of history.
The idea of a "fiery hedgehog" turned out to be a dead end, the French came first to such a decision. As a result, they had FCM 2C, the best heavy tank of the First World War, though it was late for it. The machine was a landmark, and it was on it that the Germans turned their attention. The concept of the tank, which had a gun and machine-gun turret, the German military took as a basis for developing a specification for its own tank.
At the same time they refused the heavy car. It would be too expensive, and the lesson with organizing the production of the A7V, which was released in only 20 copies, was learned by the Germans. It did not appear at first in the German plans and the light tank. In recognizing the average weight category, the Germans were not the only ones who were not alone: in the 1920s, the British tanks achieved the greatest successes in the middle class. Some points of the German specification for the middle tank clearly had English roots.