Contents
Guide

The author and publisher have provided this e-book to you for your personal use only. You may not make this e-book publicly available in any way. Copyright infringement is against the law. If you believe the copy of this e-book you are reading infringes on the authors copyright, please notify the publisher at: us.macmillanusa.com/piracy.
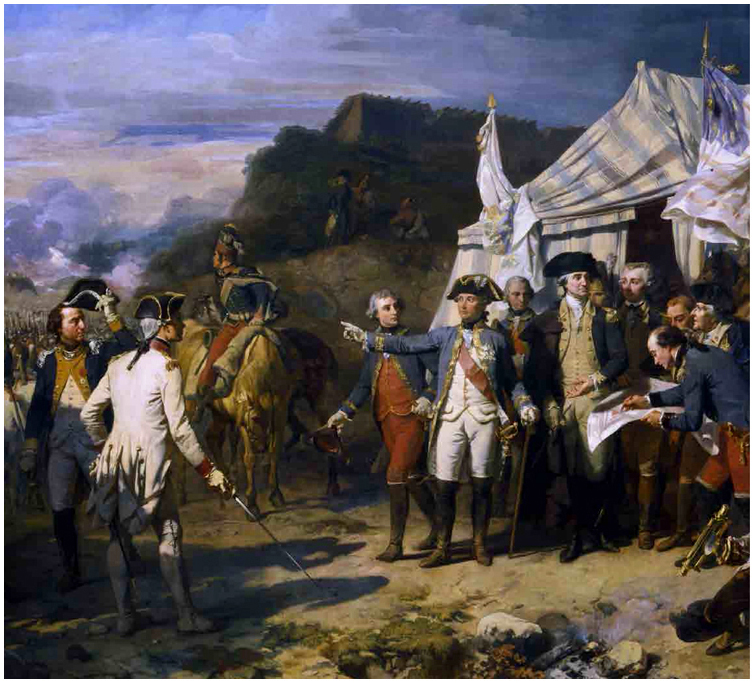

Sige de Yorktown (1836) by Auguste Couder. Generals Rochambeau and Washington giving their last orders before the assault on Yorktown in 1781. The future American president stands in the centre of the group of officers, with French surveyors and engineers to the right.
North America became a battleground for European colonial ambitions during the 17th and 18th centuries, with Britain and France fighting a series of bloody wars against each other, and against the native peoples. But it was the War of Independence that came to redefine the political identity of the continent, with the Declaration of Independence of 4 July 1776 announcing the creation of a new nation: the United States of America.
American Colonies/French and Indian War 16221774
V IRGINIA C OLONY , 1622
The commercial success of tobacco cultivation at Jamestown resulted in the rapid expansion of the English plantations into surrounding Indian territory, provoking a large-scale attack and the massacre of 350 colonists by the Powhatan tribe.
K ALINGO (K ALINAGO ), 1626
Upon arriving at the British island of St Kitts, French settlers found the native Caribs resisting, with 4000 of the Kalingo tribe in arms. The French joined forces with the British to butcher them.
P EQUOT W AR , 163438
The expanding Massachusetts colony ground into the expanding Pequot tribe with bloody results. After the murder of an English trader by some of the tribe, indemnity negotiations broke down. Further incidents led to colonial punitive expeditions burning villages. Indian counterattacks led to the co-operation of Connecticut with Massachusetts against a Pequot-Narragansett alliance. An amphibious assault upon two Pequot stockaded towns devastated the tribe, making the English dominant in New England.
I ROQUOIS W ARS , 164098
These were struggles between the Great Lakes tribes for control of the trade for European goods. The Iroquois Confederation combined the powerful Cayuga, Mohawk, Oneida, Onondaga and Seneca tribes into a formidable body. The Iroquois desired control of the trade routes with the English settlements in New York and to increase their power and numbers decimated by multiple epidemics. The initial attacks were upon native rivals in the fur trade, which expanded to a full-scale attack upon the Hurons, through whose lands the trade went. Using European-supplied weapons, the Iroquois defeated the Hurons and went on to fight the Susquehannocks, who resisted successfully with weapons purchased from the Swedish along the Hudson and with the support of the English in Maryland and Delaware. Surrounded by hostile tribes, the Iroquois finally ceased their expansion.
K IEFTS W AR , 164345
The Dutch Governor Willem Kieft turned a theft of pigs on Staten Island into warfare with previously friendly tribes. Reprisals on both sides led to widespread slaughter, ending when the Dutch imported English mercenaries and negotiated.
L ONG S AULT , 1660
The Iroquois stormed this unprepared French fort at a strategic portage on the Ottawa River. Joined by some 200 friendly Hurons, Adam Dollard and 54 French unsuccessfully resisted a powerful Iroquois force coming down the river.
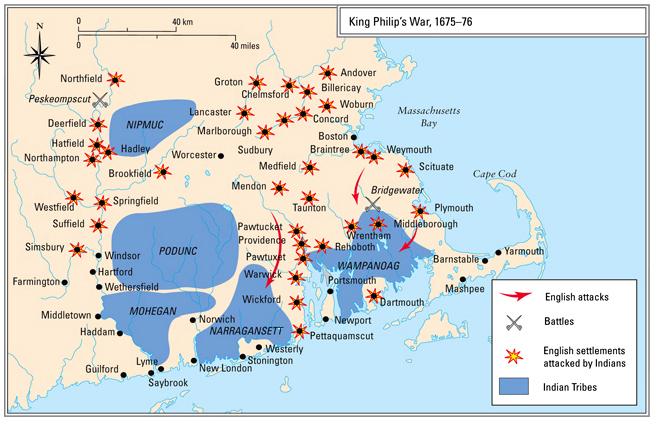
K ING P HILIPS W AR , 167576
In terms of proportional casualties, this conflict remains North Americas bloodiest Indian war. Alliance with the Pilgrims and subsequent Puritan settlements in and around Boston had made the Wampanoag tribe the most powerful in New England, but upon assuming leadership, Metacom, christened King Philip by the Pilgrims, realized that English expansion would include his tribes lands. Colonial efforts to disarm his tribe exasperated Metacoms fears and prompted his alliance with the Nipmuck and Narragansett tribes. The Wampanoags began killing English spies and raiding outlying farms, while the Massachusetts Bay Colony raised a militia and established new tribal alliances, slaughters taking place on both sides. By the time a powerful colonial force had reduced the last of Metacoms strongholds and set Metacoms head on a pike, at least 2500 colonists plus an unknown, but larger number of Indians had perished.
B ACONS R EBELLION , 1676
Virginia Governor Berkeleys policy of Indian conciliation provoked a strong reaction by planter Nathaniel Bacon, who led colonial attacks upon the Susquehannocks and Pamunkey tribes. Bacon lost support when he burned the capital at Jamestown.
L ACHINE M ASSACRE , 5 A UGUST 1689
With England suddenly at war with France, the allied Iroquois sacked this French village with 1500 warriors under cover of a hailstorm. The villages three blockhouses could not prevent the death or capture of 114 inhabitants.
L EISLERS R EBELLION , 1689
After the Glorious Revolution, protestant Jacob Leisler seized power in New York, seeking royal authorization for his measures against Catholics and Indians. Leislers plan backfired and he was hanged after the return of British government and his enemies to power.
P ORT R OYAL , 19 M AY 1690
This French bastion and naval base in Acadia became a target of the English colonists in King Williams War. Sir William Phips led a Massachusetts regiment by sea against the town, which Governor Meneval surrendered.
A PALACHEE M ASSACRE , 2526 J ANUARY 1704
During the War of the Spanish Succession, Governor James Moore of British Carolina attacked the allied Apalachee tribe in Florida with colonists and native allies. The 1000 surviving Apalachees were taken as slaves back to Carolina.
D EERFIELD , 29 F EBRUARY 1704
The French and allied Indians attacked this western Massachusetts town, killing 41 villagers and taking 112 for ransom to Canada. The attackers scaled the ungarrisoned towns stockades at night and captured the villages houses individually.
C ARYS R EBELLION , 170711
Thomas Cary, governor of Carolina, disputed the claim of Edward Hyde to be his appointed successor. Sporadic fighting between associated religious factions ended when Royal Marines entered the capital, with Cary eventually acquitted of treason charges.
B LOODY C REEK , 1711
Acadian French and Abenaki Indians successfully ambushed 70 Massachusetts militia in three boats moving up the Annapolis River. The ambush killed 16 in the first boat and wounded nine of the others, capturing the surrendering survivors.
Q UEBEC E XPEDITION , 1711
Buoyed by success in Nova Scotia, the Massachusetts colony sent 12,000 sailors and soldiers under Sir Hovenden Walker against French Canada. Eight transports in the Gulf of St. Lawrence grounded with 900 dead, Walker abandoning the campaign.
N ICHOLSON E XPEDITION , 22 A UGUST 1711
Col Francis Nicholson led 2000 militia overland from Albany against French Canada, intending to rendezvous with Sir Hovenden Walkers forces sailing up the St. Lawrence. The troops from three colonies turned back when Walker retreated.

















