About This Book
This book contains more than 600 terms and concepts that most commonly show up on the National Council Licensure Examination for Registered Nurses (NCLEX-RN). The terms are divided into seven major parts: General Concepts, Adult, Obstetrics, Pediatrics (General), Pediatric Disorders, Pediatric Medication, and Mental Health.
This on-the-go, quick review study tool for the NCLEX-RN tests you in the same way that the actual exam doesit goes beyond rote facts and definitions to delve into actual nursing processes. For example, a disease is listed on one side, and then along with the definition of the disease (which you can also find in your course books), the back features causes, symptoms, diagnostics, treatment modalities, and pharmacology.
Each page of this book features two or three terms on the front, with the explanation and application for each on the back. This is a lot of informationdo not try to learn all 600+ concepts in this book at once! The best approach is to study the words in sets of about 12 to 15 words (four or five pages) each day. Following is a suggested program of study:
Review a set of terms in the morning. Say each term aloud. Read the explanations aloud, as well. Try to say each explanation in your own words after reading it several times.
Write the terms down on a sheet of paper, and keep the sheet with you, checking it throughout the day to familiarize yourself with the list.
In the evening, quiz yourself on the terms. Make a check mark next to the terms and processes you define correctly. The next day, review the terms you were unable to define, and study 12 to 15 new words.
Periodically quiz yourself on the terms you have already studied to check that you have learned them thoroughly.
Best of luck on your NCLEX-RN study plan and exam!
Denture Care Procedures
..............................................
Food Sources: Calcium
..............................................
Food Sources: Iron
..............................................
1. Apply gloves.
2. Dentures are fragile; be sure to set a towel (or something soft) over the work area.
3. If the client is able, let him or her remove his or her own dentures.
4. If assistance from the nurse is required, grasp the upper plate at the front teeth and move the dentures up and down to release the suction.
5. Lift the lower plate up on one side at a time.
6. Use warm water to clean dentures.
7. Do not soak dentures for an extended time period.
8. The dentures may have sharp edges; handle carefully.
9. Check the oral cavity (report any abnormalities).
10. Replace the dentures in the clients mouth.
11. If the dentures are to be stored, assure that they are properly labeled with the clients name.
..............................................
Broccoli
Carrots
Cheese
Collard greens
Green beans
Milk
Rhubarb
Spinach
Tofu
Yogurt
..............................................
Dark-green leafy vegetables
Egg yolk
Fortified breads and cereals
Liver
Meats
..............................................
Food Sources: Magnesium
..............................................
Food Sources: Phosphorus
..............................................
Food Sources: Potassium
..............................................
Avocado
Cauliflower
Green leafy vegetables
Legumes (beans and peas)
Milk
Peanut butter
Pork, beef, chicken
Potatoes
Raisins
Rolled cooked oats
White tuna (canned)
Yogurt
..............................................
Fish
Nuts
Organ meats
Pork, beef, chicken
Whole grain breads and cereals
..............................................
Avocado
Bananas
Cantaloupe
Carrots
Fish
Mushrooms
Pork, beef, chicken
Potatoes
Raisins
Spinach
Strawberries
Tomatoes
..............................................
Food Sources: Sodium
..............................................
Laboratory Values, Normal Hematology
..............................................
American cheese
Bacon
Butter
Canned food
Cottage cheese
Cured pork
Hot dogs
Ketchup
Lunch meat
Milk
Mustard
Processed food
Snack food
Soy sauce
Table salt
White and whole wheat bread
..............................................
Red Blood Cell (RBC) Count | 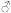 4.76.1 millions/L 4.76.1 millions/L
 4.25.4 millions/mm 4.25.4 millions/mm
|
Hemoglobin (Hgb) | 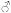 1418 g/dL 1418 g/dL
 1216 g/dL 1216 g/dL
|
Hematocrit (Hct) | 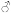 42%52% 42%52%
 37%47% 37%47%
|
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH) | 2731 pg/cell |
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin
Concentration (MCHC) | 3236 g/dL of cells |
Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) | 8090 fL |
White Blood Cell (WBC) Count | 5,00010,000 mm |
Neutrophils | 54%75% |
Monocytes | 2%8% |
Lymphocytes | 25%40% |
Eosinophils | 1%5% |
Basophils | 0%1% |
Bands | 0%5% |
Platelets | 150,000400,000 mm |
..............................................
Laboratory Values, Normal Metabolic
..............................................
Laboratory Values, Normal Renal
..............................................
Albumin | 3.55.0 g/dL |
Alkaline Phosphate | 30120 IU/L |
Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST/SGOT) | 035 IU/L |
Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT/SGPT) | 436 IU/L |
Bilirubin (total) | 0.31 mg/dL |
Calcium | 910 mg/dL |
Carbon Dioxide | 2231 mmol/L |
Chloride | 98106 mEq/L |
Glucose | 70100 mg/dL |
Potassium | 3.55 mEq/L |
Protein (total) | 6.48.3 g/dL |
Sodium | 136145 mEq/L |
..............................................
Serum Blood Test | Normal Value |
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) Level | 825 mg/dL |
Serum Creatinine Level | 0.61.3 mg/dL |
Serum Uric Acid Level | 2.58.0 mg/dL |
Creatinine Clearance | Male: 97 to 137 ml/min. Female: 88 to 128 ml/min. |
..............................................
















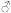 4.76.1 millions/L
4.76.1 millions/L 4.25.4 millions/mm
4.25.4 millions/mm 1418 g/dL
1418 g/dL 1216 g/dL
1216 g/dL 42%52%
42%52% 37%47%
37%47%