JГјrgen H Gross - Mass Spectrometry
Here you can read online JГјrgen H Gross - Mass Spectrometry full text of the book (entire story) in english for free. Download pdf and epub, get meaning, cover and reviews about this ebook. year: 0, publisher: Springer International Publishing, Cham, genre: Art. Description of the work, (preface) as well as reviews are available. Best literature library LitArk.com created for fans of good reading and offers a wide selection of genres:
Romance novel
Science fiction
Adventure
Detective
Science
History
Home and family
Prose
Art
Politics
Computer
Non-fiction
Religion
Business
Children
Humor
Choose a favorite category and find really read worthwhile books. Enjoy immersion in the world of imagination, feel the emotions of the characters or learn something new for yourself, make an fascinating discovery.
- Book:Mass Spectrometry
- Author:
- Publisher:Springer International Publishing, Cham
- Genre:
- Year:0
- Rating:3 / 5
- Favourites:Add to favourites
- Your mark:
- 60
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Mass Spectrometry: summary, description and annotation
We offer to read an annotation, description, summary or preface (depends on what the author of the book "Mass Spectrometry" wrote himself). If you haven't found the necessary information about the book — write in the comments, we will try to find it.
Mass Spectrometry — read online for free the complete book (whole text) full work
Below is the text of the book, divided by pages. System saving the place of the last page read, allows you to conveniently read the book "Mass Spectrometry" online for free, without having to search again every time where you left off. Put a bookmark, and you can go to the page where you finished reading at any time.
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
- The relevance of mass spectrometry
- Mass spectrometry Basic concepts
- How mass spectra are displayed and communicated
- The performance features of mass spectrometry
- Basic terminology and conventions in data presentation
- Aims and scope and general organization of this textbook
Key application and field of application | Explanation |
|---|---|
Elemental and isotopic analysis Physics Radiochemistry Geochemistry | Elemental identification and isotopic abundance measurement of both short-lived and stable species in physics and radiochemistry (nuclear waste), in geochemistry and more recently in the life sciences. |
Organic and bio-organic analysis Organic chemistry Polymer chemistry Biochemistry and medicine | Identification and structural characterization of molecules from small to very large as provided either by chemistry, physiological processes, or polymer chemistry. |
Structure elucidation Organic chemistry Polymer chemistry Biochemistry and medicine | Mass spectrometric experiments can be arranged consecutively to study mass-selected ions in tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS or MS2). Eventually products are subjected to a third level (MS3) and so forth (MSn). |
Characterization of ionic species and chemical reactions Physical chemistry Thermochemistry | Tandem MS provides an elegant means for the study of unimolecular or bimolecular reactions of gas phase ions and for the determination of ion energetics. |
Coupling to separation techniques Quality control Environmental analysis Complex mixture analysis Forensics Petroleum chemistry Food chemistry | MS can be coupled to separation methods such as gas chromatography (GC) and liquid chromatography (LC). In hyphenation, i.e., as GC-MS or LC-MS, MS delivers high selectivity and low detection limits for the analysis of trace compounds in complicated matrices or the deconvolution of complex mixtures. |
Mass spectral imaging Biomedical studies Pharmaceutical developments Material sciences | Mass spectra can be obtained from micrometer-sized areas on surfaces, translating the lateral distribution of compounds on surfaces (microelectronics, slices of tissue) into images, which in turn can be correlated to optical images. |
Miniaturization Field portable MS Space missions Military applications | Mass spectrometers can be very small. Portable instruments allow for environmental on-site analysis, detection systems for explosives and warfare chemicals, and last but not least for many space missions. |

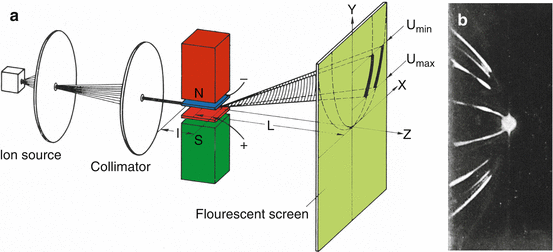
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
Similar books «Mass Spectrometry»
Look at similar books to Mass Spectrometry. We have selected literature similar in name and meaning in the hope of providing readers with more options to find new, interesting, not yet read works.
Discussion, reviews of the book Mass Spectrometry and just readers' own opinions. Leave your comments, write what you think about the work, its meaning or the main characters. Specify what exactly you liked and what you didn't like, and why you think so.











