UNDERSTAND BANKS AND FINANCIAL MARKETS
An Introduction to the International World of Money & Finance

Published by Michiel van den Broek at Smashwords
Copyright 2014 Michiel van den Broek
http://www.financialtraininghub.com.
Smashwords Edition, License Notes ISBN: 9781311158314
This ebook is licensed for your personal enjoyment only. This ebook may not be re-sold or given away to other people. If you would like to share this book with another person, please purchase an additional copy for each recipient. If you are reading this book and did not purchase it, or it was not purchased for your use only, then please return to Smashwords.com and purchase your own copy. Thank you for respecting the hard work of this author.
****
Table of Content
*******
There is something big happening in the world of finance that impacts our economies and welfare. Most of us do not realize the extent of whats going on. But its not so complicated: Finance is not rocket science. After working in finance from 1990, I train people who work in the finance industry and specialized so as to explain complex finance since 2005.
Starting in the '80s, banks have become huge financial supermarkets offering a wide range of different services and products. Employees in these large banks have developed specialized expertise in the area in which they decide to make a career. Along with rapid developments in information technology this has resulted in large IT departments staffed by people without any particular financial and banking knowledge.
You may like banks or not, but banks have been and still are very important to our modern society as key intermediators in the facilitation of economic development. The global financial crisis of 2008 became a turning point in the banking industry. We use banks almost every day, for example to make payments. But what do you really know about banks? How was it possible that banks caused a major financial market and economic crisis?
After a short introduction about money, I will explain i n Part I the core activities of banks. In Part II, I will introduce you to the standard bank types, explain the root of the 2008 global financial crisis and the Basel Agreements that is now the basis of Central Bank regulation. 'What happens on Financial Markets' in Part III will learn you why products are traded and how product are priced. This is followed by Part IV about trade organization: the dealing room, public- and over-the-counter trading.
After reading this booklet you will understand the fundamentals of world of a finance. Also it supports p
articipants of my other training programmes and workshops.
*******
A simplified description of a bank is a money shop. To generalize: for meat you need a butcher, for medicine a pharmacy, for money you contact a bank. Money is important for our economy as oil is for the engine of a car. This part is an introduction that will explain the basics of types, source and control of money.
Central banks are the money managers of our economy: they can create and destroy two types of money: cash and central bank money. With cash you are familiar. Cash represents only a very small fraction of the money in our economy. The use of cash is decreasing rapidly as result digital payments tools, such as cards, internet and mobile phones. Central bank money is digital cash that banks use to make payments through the accounts that banks hold with the Central Bank. This type of Central bank money is only available to licensed banks.
The third money type is not created by Central Banks, but by banks. This third money source is bank credit. Credit is used to pay for products and services using payment accounts registered by banks. Banks net-settle payments and receipts with other banks. The net settlement as result of credit money is done with digital central bank money. Banks only need a fraction of central bank money to be able to facilitate the credit they have created. Central banks can influence the amount of credit money by regulating banks. For example, banks can be obliged to have liquidity reserves that can't be used for credit to customers.
Since most money used today is credit, banks can influence the level of economic activities. For example, banks will decrease the amount of credit money if they are pessimistic due to negative economic expectations.
Money Creation explained in a short video: click Types of Money ; or copy in your browser: http://www.positivemoney.org/how-money-works/banking-101-video-course/how-is-money-really-made-by-banks-banking-101-part-3/
Money is the lubricant of our economic engine. The Central Bank is the money manager. Banks are hubs in the management and distribution of money and produce approximately 90% of the money in the form of credit. The next section describes in more detail what banks do.
*******
There are four core bank activities:
Transformation
Intermediation
3. Payments
4. Proprietary Trading
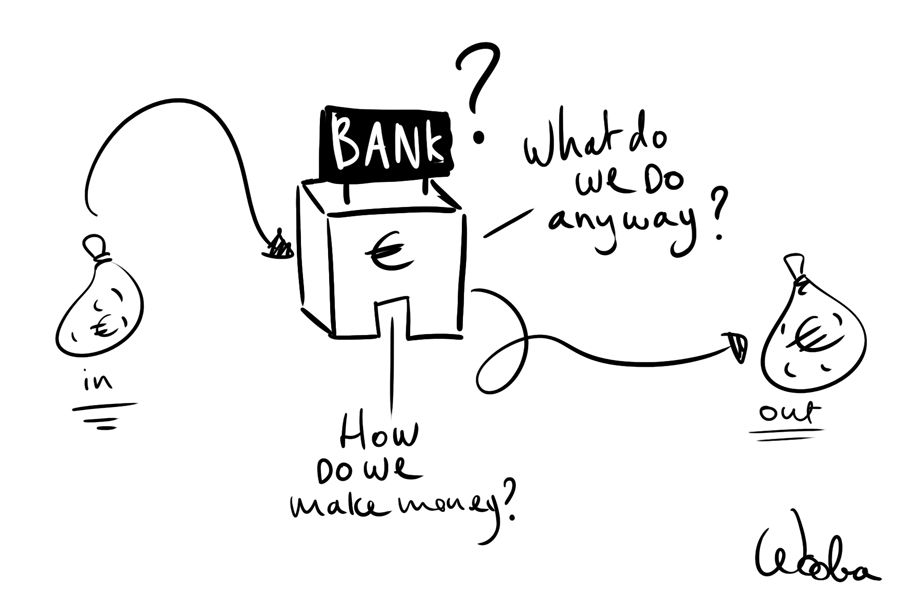
In the following sections I will explain these four core activities and how these activities can generate bank income.
The prime core activity for most banks is transformation. Transformation involves borrowing money from customers with surplus funds and lending money to other customers with a need for funds. Or to explain it differently: to trade money.
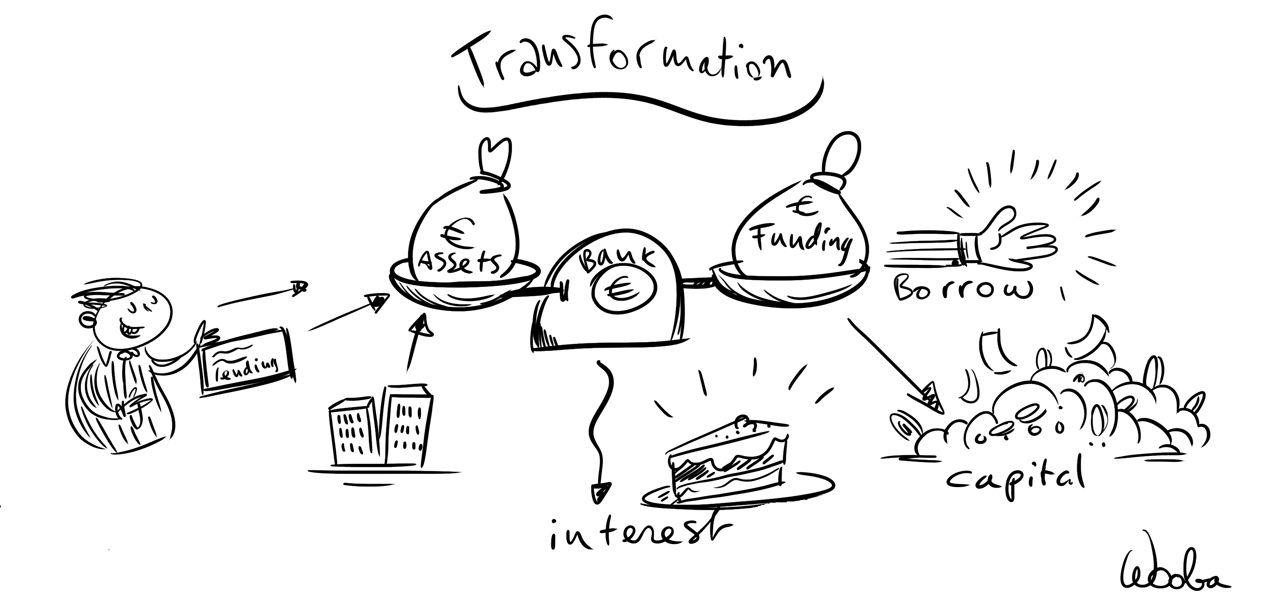
To borrow, or buy money, the bank has to pay a p rice, deposit interest rate on savings account or the rate on its own bond issues or borrowings. An exception is money borrowed from holders of payment (current) accounts: most banks do not pay interest on such accounts. The bank then on-lends, or sells the money it has raised to customers that will pay interest to the bank. The level of interest is influenced by several factors, such as competition, monetary policy, economic development, creditworthiness of the borrower and political factors.
Transformation generates income if the received interest rate is higher than the paid interest: this is the Net Interest Margin Income. For many bank this is the main source of income, sometimes up to approx. 70% of total bank income.
The next section is about intermediation, the second most important core activity of most banks.
Intermediation summarizes all bank activities that provide a range of financial services to clients. The banks income sources may be known as: fees, commissions, service charges and spreads.
The four major Intermediation activities are:
a. Brokerage
b. Asset Management
c. Mergers & Acquisitions / Underwriting
d. Custody
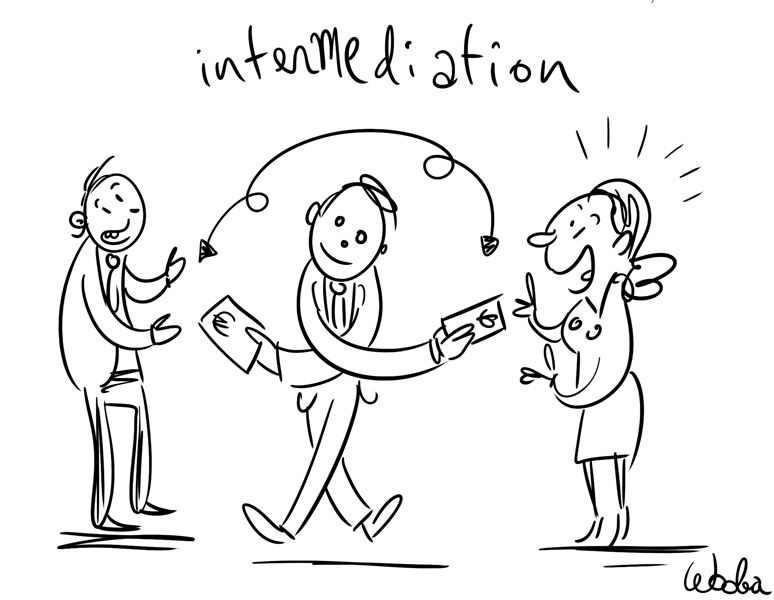
The above financial services will be explained in following paragraphs.
(a) Intermediation: Brokerage
An example of brokerage is that a bank client wants to buy or sell financial products, such as commercial paper, bonds, shares, foreign currencies or derivatives. Examples of derivatives are options, swaps and share index investments. The bank will intermediate by executing transactions on the financial markets to best match the needs of its deposit and borrowing clients.















