Bustos Molina - Kinetic Simulations of Ion Transport in Fusion Devices
Here you can read online Bustos Molina - Kinetic Simulations of Ion Transport in Fusion Devices full text of the book (entire story) in english for free. Download pdf and epub, get meaning, cover and reviews about this ebook. City: Cham;Heidelberg, year: 2013, publisher: Springer International Publishing, genre: Children. Description of the work, (preface) as well as reviews are available. Best literature library LitArk.com created for fans of good reading and offers a wide selection of genres:
Romance novel
Science fiction
Adventure
Detective
Science
History
Home and family
Prose
Art
Politics
Computer
Non-fiction
Religion
Business
Children
Humor
Choose a favorite category and find really read worthwhile books. Enjoy immersion in the world of imagination, feel the emotions of the characters or learn something new for yourself, make an fascinating discovery.
- Book:Kinetic Simulations of Ion Transport in Fusion Devices
- Author:
- Publisher:Springer International Publishing
- Genre:
- Year:2013
- City:Cham;Heidelberg
- Rating:4 / 5
- Favourites:Add to favourites
- Your mark:
- 80
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Kinetic Simulations of Ion Transport in Fusion Devices: summary, description and annotation
We offer to read an annotation, description, summary or preface (depends on what the author of the book "Kinetic Simulations of Ion Transport in Fusion Devices" wrote himself). If you haven't found the necessary information about the book — write in the comments, we will try to find it.
Kinetic Simulations of Ion Transport in Fusion Devices — read online for free the complete book (whole text) full work
Below is the text of the book, divided by pages. System saving the place of the last page read, allows you to conveniently read the book "Kinetic Simulations of Ion Transport in Fusion Devices" online for free, without having to search again every time where you left off. Put a bookmark, and you can go to the page where you finished reading at any time.
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
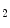 and other greenhouse effect gasses coming from energy activities have deep impact on the environment, leading to the rising climate change that produces global warming among other effects. The development of alternative energy sources becomes necessary for the modern society. Fusion energy is a good candidate to supply a large fraction of the world energy consumption, with the added advantage of being respectful with the environment because radioactive fusion waste has lifetimes much shorter than fission long term radioactive waste. The future fusion reactors are intrinsically safe, and nuclear catastrophes like Chernobyl or Fukushima cannot happen. Thus, research and investments in fusion energy can play a crucial role in the sustainable development.
and other greenhouse effect gasses coming from energy activities have deep impact on the environment, leading to the rising climate change that produces global warming among other effects. The development of alternative energy sources becomes necessary for the modern society. Fusion energy is a good candidate to supply a large fraction of the world energy consumption, with the added advantage of being respectful with the environment because radioactive fusion waste has lifetimes much shorter than fission long term radioactive waste. The future fusion reactors are intrinsically safe, and nuclear catastrophes like Chernobyl or Fukushima cannot happen. Thus, research and investments in fusion energy can play a crucial role in the sustainable development.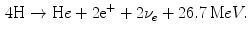
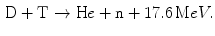
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
Similar books «Kinetic Simulations of Ion Transport in Fusion Devices»
Look at similar books to Kinetic Simulations of Ion Transport in Fusion Devices. We have selected literature similar in name and meaning in the hope of providing readers with more options to find new, interesting, not yet read works.
Discussion, reviews of the book Kinetic Simulations of Ion Transport in Fusion Devices and just readers' own opinions. Leave your comments, write what you think about the work, its meaning or the main characters. Specify what exactly you liked and what you didn't like, and why you think so.











