1.1 Introduction
The theory of Special Relativity formulated by Albert Einstein in 1905 [] is, without doubt, one of the great intellectual achievements of the twentieth century. Our everyday experience is about objects moving at speeds much smaller than the speed of light in vacuo,
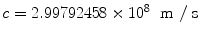
. Newtonian mechanics was developed to describe phenomena at typical speeds
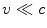
and fails when speeds are not negligible in comparison with
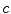
. This situation is not infrequent; for example, it is relatively easy to accelerate electrons to speeds
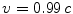
in accelerators. However, as their velocities become closer and closer to
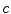
, it becomes harder and harder to accelerate these electrons further. As we will see, it is believed that the speed of light
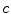
is a barrier that particles and physical signals cannot break.
The theory of Special Relativity was a one mans work which incorporated previous ideas and contributions (especially those of Poincar), but in a way that nobody was able to fully grasp before Einstein.
In our exposition of Special Relativity we will omit gravity from the picture and we will assume that inertial frames extend to spatial infinity. Special Relativity is a theory for a world in which gravity is switched off; the relativistic theory of gravity, General Relativity, contains Special Relativity as the limit for vanishing gravitational fields, and was created by Einstein in 1915. We will not consider General Relativity and gravity in this book, except for some considerations at the end of it.
1.2 The Principle of Relativity
Physical phenomena are normally described with respect to a given reference frame, which consists of a set of spatial axes and a set of synchronized clocks with respect to which one measures positions and time intervals. Newtons second law is valid in all inertial frames, which are defined by Newtons first law. According to this law, an inertial frame is one in which a free body (i.e., a body not subject to forces) is not accelerating. Any system moving with constant velocity with respect to an inertial frame is also an inertial frame.
The Principle of Newtonian (or Galilean ) Relativity states that
the laws of mechanics are invariant under change of inertial frame.
In other words, the outcome of a physical experiment performed in two different inertial frames must be the same; no experiment can detect a difference between the two frames. This statement applies not only to kinematics, but to any kind of (non-gravitational) physics. Therefore, there is no absolute motion through space, and there is no preferred inertial frame .
In pre-relativistic physics, the transformation from one inertial frame to another ( change of frame ) is given by the Galilei transformation . For simplicity, consider the motion of two inertial frames
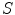
and
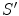
such that the
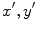
, and
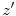
Cartesian axes of
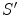
are parallel to the
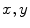
, and
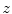
axes of
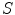
, respectively, and such that the system
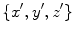
moves along the
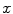
-axis with constant velocity
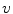
( standard configuration ), as in Fig.. We adopt the convention that the velocity
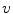
is positive if the system
is moving away from
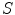
.
Fig. 1.1
Two inertial frames
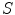
and
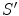
in standard configuration
Suppose that you synchronize clocks in the two inertial frames in such a way that the time indicated by a clock in
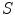












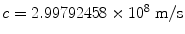 . Newtonian mechanics was developed to describe phenomena at typical speeds
. Newtonian mechanics was developed to describe phenomena at typical speeds 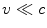 and fails when speeds are not negligible in comparison with
and fails when speeds are not negligible in comparison with 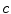 . This situation is not infrequent; for example, it is relatively easy to accelerate electrons to speeds
. This situation is not infrequent; for example, it is relatively easy to accelerate electrons to speeds 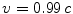 in accelerators. However, as their velocities become closer and closer to
in accelerators. However, as their velocities become closer and closer to 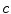 , it becomes harder and harder to accelerate these electrons further.
, it becomes harder and harder to accelerate these electrons further.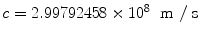 . Newtonian mechanics was developed to describe phenomena at typical speeds
. Newtonian mechanics was developed to describe phenomena at typical speeds 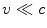 and fails when speeds are not negligible in comparison with
and fails when speeds are not negligible in comparison with 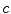 . This situation is not infrequent; for example, it is relatively easy to accelerate electrons to speeds
. This situation is not infrequent; for example, it is relatively easy to accelerate electrons to speeds 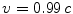 in accelerators. However, as their velocities become closer and closer to
in accelerators. However, as their velocities become closer and closer to 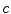 , it becomes harder and harder to accelerate these electrons further. As we will see, it is believed that the speed of light
, it becomes harder and harder to accelerate these electrons further. As we will see, it is believed that the speed of light 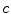 is a barrier that particles and physical signals cannot break.
is a barrier that particles and physical signals cannot break. and
and 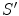 such that the
such that the 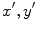 , and
, and 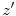 Cartesian axes of
Cartesian axes of 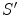 are parallel to the
are parallel to the 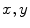 , and
, and 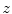 axes of
axes of 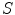 , respectively, and such that the system
, respectively, and such that the system 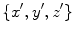 moves along the
moves along the 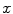 -axis with constant velocity
-axis with constant velocity 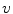 ( standard configuration ), as in Fig.. We adopt the convention that the velocity
( standard configuration ), as in Fig.. We adopt the convention that the velocity 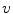 is positive if the system
is positive if the system 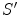 is moving away from
is moving away from 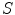 .
. 
 and
and  in standard configuration
in standard configuration