VIKRAMAN - BUILDING STRUCTURES
Here you can read online VIKRAMAN - BUILDING STRUCTURES full text of the book (entire story) in english for free. Download pdf and epub, get meaning, cover and reviews about this ebook. year: 2021, genre: Children. Description of the work, (preface) as well as reviews are available. Best literature library LitArk.com created for fans of good reading and offers a wide selection of genres:
Romance novel
Science fiction
Adventure
Detective
Science
History
Home and family
Prose
Art
Politics
Computer
Non-fiction
Religion
Business
Children
Humor
Choose a favorite category and find really read worthwhile books. Enjoy immersion in the world of imagination, feel the emotions of the characters or learn something new for yourself, make an fascinating discovery.
BUILDING STRUCTURES: summary, description and annotation
We offer to read an annotation, description, summary or preface (depends on what the author of the book "BUILDING STRUCTURES" wrote himself). If you haven't found the necessary information about the book — write in the comments, we will try to find it.
BUILDING STRUCTURES — read online for free the complete book (whole text) full work
Below is the text of the book, divided by pages. System saving the place of the last page read, allows you to conveniently read the book "BUILDING STRUCTURES" online for free, without having to search again every time where you left off. Put a bookmark, and you can go to the page where you finished reading at any time.
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:

Historic perspective and definition of structure-System of load transferring from various structural elements of building to ground. Principles, Characteristics of loa d and strength in Limit State Method of design, partial safety factor, stress block parameters balance, under and over reinforced beams, analysis and design of singly and doubly reinforced beams, analysis and design of under reinforced flanged beams, clear cover for durability and fire resistance, reinforcement details for beams in flexure
Concrete is a mixture of cement, aggregates, water and admixtures in an adequate proportion. It is a rock like material.
Properties of Fresh Concrete: Concrete should be such that it can be transported, placed, compacted and finished without harmful segregation. The mix should maintain its uniformity and not bleed excessively; these two are collectively called as workability .Bleeding is movement and appearance of water at the surface of freshly-placed concrete, due to settlement of heavier particles. Consistency is a measure of its wetness and fluidity .Measured by the slump test and Workability dependent on water content, fineness of cement, and surface area of aggregates.
Properties of Hardened Concrete: The important properties of concrete are
Compressive strength
Tensile strength
Shear strength
Bond strength
Density
Impermeability
Durability
Ductility
Among these properties, compressive strength of concrete is the most valuable and can be easily tested in laboratory. This is generally measured on concrete cubes or cylinders.
 Many of the properties of concrete can be inferred from compressive strength, using correlation that has been established.
Many of the properties of concrete can be inferred from compressive strength, using correlation that has been established.
Quality of concrete depends on the compressive strength.
Dependent on strength (compressive, tension and flexure), Modulus of elasticity, Durability, Creep and shrinkage
 Concrete is classified under different grades depending upon its characteristic strength.
Concrete is classified under different grades depending upon its characteristic strength.
 Characteristic strength is defined as the strength of material below which not more than 5 percent of the test results are expected to fall.
Characteristic strength is defined as the strength of material below which not more than 5 percent of the test results are expected to fall.
Strength of concrete varies for the same concrete mix, which give different compressive
strength in laboratory tests.
 Variability in strength evidently depends on degree of quality control.
Variability in strength evidently depends on degree of quality control.
 Variability in strength is measured in terms of either the Standard Deviation or the
Variability in strength is measured in terms of either the Standard Deviation or the
Coefficient of Variation (COV), which is the ratio of standard deviation to mean strength(f cm ).
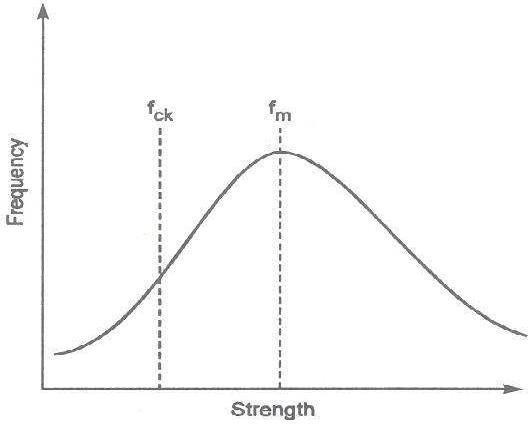
Due to significant variability in strength, it is necessary to ensure that the designer has a reasonable assurance of a certain minimum strength of concrete.
Characteristic strength provides minimum guaranteed strength.
Different methods of design of RCC
Working Stress Method 2.Limit State Method 3.Ultimate Load Method
Probabilistic Method of Design
Working Stress Method:
 The sections of the members of the structure are designed assuming straight linestress-strain relationships ensuring that at service loads the stresses in the steel and
The sections of the members of the structure are designed assuming straight linestress-strain relationships ensuring that at service loads the stresses in the steel and
concrete do not exceed the allowable working stresses.
 The allowable stresses are taken as fixed proportions of the ultimate or yield strength of the materials.
The allowable stresses are taken as fixed proportions of the ultimate or yield strength of the materials.
The B.Ms and forces that act on statically indeterminate structures are
calculated assuming linear elastic behaviour.
 Reinforced concrete sections behave in elastically at high loads. Hence elastic theory cannot give a reliable prediction of the ultimate strength of the members because inelastic strains are not taken into account.
Reinforced concrete sections behave in elastically at high loads. Hence elastic theory cannot give a reliable prediction of the ultimate strength of the members because inelastic strains are not taken into account.
 For structures designed by the working stress method, the exact load factor is unknown
For structures designed by the working stress method, the exact load factor is unknown
and varies from structures to structure.
Ultimate Load Method:
 Sections of members of the structures are designed taking inelastic strains into accountto reach ultimate (maximum) strength when an ultimate load, equal to the sum of each service load multiplied by its respective load factor, is applied to the structure.
Sections of members of the structures are designed taking inelastic strains into accountto reach ultimate (maximum) strength when an ultimate load, equal to the sum of each service load multiplied by its respective load factor, is applied to the structure.
 The beginning moments and forces that act as statically indeterminate structures at theultimate load are calculated assuming non linear elastic behaviour of the structure up to the ultimate load. i.e., redistribution of same actions are taking place due to nonlinear
The beginning moments and forces that act as statically indeterminate structures at theultimate load are calculated assuming non linear elastic behaviour of the structure up to the ultimate load. i.e., redistribution of same actions are taking place due to nonlinear
relationship between actions and deformations.

 Ultimate strength design makes more efficient use of high strength reinforcement and smaller beam depths can be used without compression steel.
Ultimate strength design makes more efficient use of high strength reinforcement and smaller beam depths can be used without compression steel.
 Ultimate strength design allows the designer to assess the ductility of the structure in the post-elastic range.
Ultimate strength design allows the designer to assess the ductility of the structure in the post-elastic range.
the sections are designed based on ultimate strength design, there is a danger thatalthough the load factor is adequate. The cracking and the deflections at the service
loads may be excessive.

 Cracking may be excessive if the steel stresses are high or if the bars are badly distributed.
Cracking may be excessive if the steel stresses are high or if the bars are badly distributed.
Deflections may be critical if the shallow sections, which are possible in USD, are used
and the stresses are high.To ensure a satisfactory design, the crack widths and deflections at service loads mustbe checked to make sure that this lies within reasonable limiting values, as per functional requirements of the structure. This is done by use of elastic theory.
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
Similar books «BUILDING STRUCTURES»
Look at similar books to BUILDING STRUCTURES. We have selected literature similar in name and meaning in the hope of providing readers with more options to find new, interesting, not yet read works.
Discussion, reviews of the book BUILDING STRUCTURES and just readers' own opinions. Leave your comments, write what you think about the work, its meaning or the main characters. Specify what exactly you liked and what you didn't like, and why you think so.









