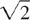Table of Contents
Guide
Page List


Copyright 2021 by Kaplan, Inc., d/b/a Barrons Educational Series Copyright 2019 by Kaplan, Inc., d/b/a Barrons Educational Series under the title
Pre-Algebra: The Easy Way Prior edition Copyright 2012 by Kaplan, Inc., d/b/a Barrons Educational Series under the title
E-Z Pre-Algebra All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means without the written permission of the copyright owner. Published by Kaplan, Inc., d/b/a Barrons Educational Series 750 Third Avenue New York, NY 10017
www.barronseduc.com ISBN: 978-1-5062-8141-4 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 All rights reserved under International and Pan-American Copyright Conventions. By payment of the required fees, you have been granted the non-exclusive, non-transferable right to access and read the text of this eBook on screen. No part of this text may be reproduced, transmitted, downloaded, decompiled, reverse engineered, or stored in or introduced into any information storage and retrieval system, in any form or by any means, whether electronic or mechanical, now known or hereinafter invented, without the express written permission of the publisher.
CONTENTS
Barrons Math 360: Pre-Algebra is designed for self-learners and for those looking for a comprehensive guide to everything pre-algebra.
This book includes a number of helpful tools that will reinforce your knowledge of the topics as you learn. Youll find: What You Will Learn Each chapter begins with a list of the topics covered. This is a useful tool for categorizing the learning process and for devising a study plan. Terms and Definitions Important terms are defined where necessary to help guide you through topics successfully. Examples with Solutions Numerous examples for each topic are included throughout, along with answers to check your progress. Online Practice Questions Access to 50 online multiple-choice questions designed to enhance your understanding and to test your knowledge. Online Practice Questions Access to 50 online multiple-choice questions designed to enhance your understanding and to test your knowledge.
To access, see the card at the front of the book.
BARRONS 360 STUDY TIPS
SET GOALS AND OBJECTIVES
As you use
Barrons Math 360: Pre-Algebra, it is a good idea to set personal goals to chart and direct your learning objectives. A
goal is something that you wish to achieve over a period of time.
Objectives are short-term targets that help you reach a particular goal. For example, suppose that your goal is to learn how to solve different types of equations.
CUSTOMIZE YOUR STUDY
Barrons Math 360: Pre-Algebra does not need to be studied in a linear fashion.
CUSTOMIZE YOUR STUDY
Barrons Math 360: Pre-Algebra does not need to be studied in a linear fashion.
If there is a particular topic that you want to study or reinforce, just turn to that page or chapter, and all the information along with the features mentioned above will be available to you. There are also some things you can do to optimize your study time and ensure you are retaining the important information you want to learn.
Before You Read
Review: Review all chapter headings and subheadings and the information in the What You Will Learn section.
Scan: Glance over any illustrations, tables, or graphs in the chapter youll be reading.
Locate Terms and Definitions: Read any bold or italicized words and study their definitions.
While You Read
Predict: Try to predict the answers to the questions in the Practice Exercises.
While You Read
Predict: Try to predict the answers to the questions in the Practice Exercises.
This will help flag important information to keep an eye out for as you read. Read Aloud: Hearing what is written on the page leads to better comprehension and retention of information. Visualize: Developing a picture in your mind of the information, concepts, or material presented makes it much easier to remember.
Highlighting and Note-taking
Identify Important Facts: Dont excessively highlight. This will have the opposite effect and actually negatively impact your ability to retain the information you need to remember.
Draw It Out: Sketch out pictures, graphs, diagrams, or tables, to help visualize what youre reading.
Draw It Out: Sketch out pictures, graphs, diagrams, or tables, to help visualize what youre reading.
This is particularly helpful with complex topics.
After You Read the Chapter
Talk It Out: Summarize what you have learned from the chapter aloud to a friend or a family member. Explain it as if they are learning it for the first time.
Answer the Questions in the Practice Exercises: Did you need to look them up, or were you able to answer them from memory?
Reinforce: If you found yourself having to look up the answers to the questions, go back and read those portions of the chapter again until you feel confident moving on to the next chapter.
Good luck!
WHAT YOU WILL LEARN
Some basic terms and assumptions of numbers and sets The difference between rational and irrational numbers Properties of real numbers Order of operations SECTIONS IN THIS CHAPTER
In our daily lives we use numbers to count, compare, order, measure, and solve problems.
Numbers are the concept of the amount or quantity in a collection.
The numbers we use the most and are most familiar with are whole numbers, but lets look at some different sets of numbers.

DEFINITIONS
All whole numbers greater than zero; also called natural numbers: {1, 2, 3, 4, }.
Whole numbersThe set of counting numbers plus zero: {0, 1, 2, 3, }.
IntegersThe set of numbers consisting of the counting numbers {1, 2, 3, 4, }, their opposites {1, 2, 3, 4, }, and zero.
Rational numbersAny number that can be expressed as a ratio in the form
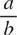
where
a and
b are integers and
b 0. Rational numbers include all counting, whole, and integer numbers.
They also include all fractions and decimal numbers, which terminate or have a repeating string of digits. Decimal numberA fractional number written using base-ten notation; a mixed decimal number has a whole number part as well (e.g., 0.32 is a decimal number and 3.5 is a mixed decimal number). FractionA number that represents part of a whole, part of a set, or a quotient in the form 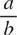 , which can be read as a divided by b. Irrational numberA real number that cannot be represented as an exact ratio of two integers; the decimal form of the number never terminates and never has a repeating string of digits (e.g., ,
, which can be read as a divided by b. Irrational numberA real number that cannot be represented as an exact ratio of two integers; the decimal form of the number never terminates and never has a repeating string of digits (e.g., , 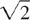















 Copyright 2021 by Kaplan, Inc., d/b/a Barrons Educational Series Copyright 2019 by Kaplan, Inc., d/b/a Barrons Educational Series under the title Pre-Algebra: The Easy Way Prior edition Copyright 2012 by Kaplan, Inc., d/b/a Barrons Educational Series under the title E-Z Pre-Algebra All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means without the written permission of the copyright owner. Published by Kaplan, Inc., d/b/a Barrons Educational Series 750 Third Avenue New York, NY 10017 www.barronseduc.com ISBN: 978-1-5062-8141-4 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 All rights reserved under International and Pan-American Copyright Conventions. By payment of the required fees, you have been granted the non-exclusive, non-transferable right to access and read the text of this eBook on screen. No part of this text may be reproduced, transmitted, downloaded, decompiled, reverse engineered, or stored in or introduced into any information storage and retrieval system, in any form or by any means, whether electronic or mechanical, now known or hereinafter invented, without the express written permission of the publisher.
Copyright 2021 by Kaplan, Inc., d/b/a Barrons Educational Series Copyright 2019 by Kaplan, Inc., d/b/a Barrons Educational Series under the title Pre-Algebra: The Easy Way Prior edition Copyright 2012 by Kaplan, Inc., d/b/a Barrons Educational Series under the title E-Z Pre-Algebra All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means without the written permission of the copyright owner. Published by Kaplan, Inc., d/b/a Barrons Educational Series 750 Third Avenue New York, NY 10017 www.barronseduc.com ISBN: 978-1-5062-8141-4 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 All rights reserved under International and Pan-American Copyright Conventions. By payment of the required fees, you have been granted the non-exclusive, non-transferable right to access and read the text of this eBook on screen. No part of this text may be reproduced, transmitted, downloaded, decompiled, reverse engineered, or stored in or introduced into any information storage and retrieval system, in any form or by any means, whether electronic or mechanical, now known or hereinafter invented, without the express written permission of the publisher.  DEFINITIONS
DEFINITIONS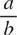 where a and b are integers and b 0. Rational numbers include all counting, whole, and integer numbers.
where a and b are integers and b 0. Rational numbers include all counting, whole, and integer numbers.