
OUR VERY OWN EARTH
EARTH IS THE ONLY PLANET in our solar system that is suitable for life. It has liquid water, oxygen, and enough gravity to hold its own atmosphere. But did you know that Earth is always changing?
Scientists have used spacecraft and satellites to learn more about our planet. They can better predict natural disasters like hurricanes, and monitor volcano eruptions and climate change. Learn about the amazing missions, the dedicated scientists who plan them, and lots of far-out facts about our home planet.
The Far-Out Guide to the Solar System series provides valuable information about the solar system, its planets, and mankind's quest in exploring them. This series is an excellent resource for young scientists and amateur astronomers.
Bahram Mobasher, PhD, Series Science Consultant
Professor of Physics and Observational Astronomy, University of California, Riverside
About the Author
Award-winning author MARY KAY CARSON has written many nonfiction books for young people and their teachers. In 2009, she received the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Children's Literature Award.

Image Credit: NASA/JPL
Earth is the third planet from the Sun. (Note that the planets distances are not shown to scale.)
Did you know that Earths day is getting longer? The day grows longer by about one to two thousandths of a second about every hundred years. Whats causing our days to stretch? Earths spin is slowing. One spin is one day, so a slower spin makes a day last longer. How do we know this? Scientists use atomic clocks to compare the time to day length. You will learn lots more far-out facts about Earth in this book. Just keep reading!
Earth is the fifth largest planet in our solar system and the third closest to the Sun. But Earth is first when we talk about life. It is the only known place where life thrives. The more we explore and learn about other planets, the more we realize how special Earth is.

Image Credit: Tom Uhlman/www.tomuphoto.com
Earth's land, water, air, and life are all connected to each other.
Earths distance from the Sun makes it the right temperature for liquid watersomething all known forms of life need. Earths neighbor Venus is closer to the Sun. It has a thicker layer of air than Earth. This makes it so hot that its water boiled away long ago. Earths other neighbor, Mars, is chilly. It has little air and is farther away from the Sun than Earth. Its water is frozen.
Earths size helps make it livable, too. Our planet is big enough to have the gravity needed to hold onto its layer of surrounding air, or atmosphere. Much of the air around smaller worlds floated off into space long ago. An atmosphere gives living things air to breathe. It also blocks the Suns harmful rays.
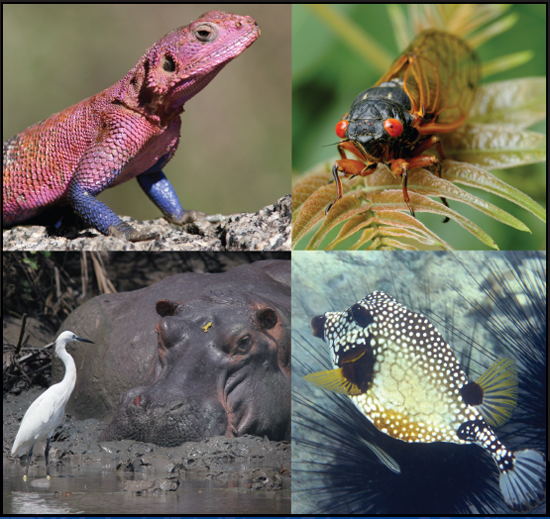

Image Credit: Tom Uhlman/www.tomuphoto.com
Earth is the only known place where life swims, hops, sprouts, runs, flies, and grows.
FAR-OUT FACT
Earth is a system made up of different parts, called spheres. The outermost sphere is the atmosphere. This is Earths air. Then there is the watery hydrosphere. It is the layer of ocean, rivers, lakes, and ice sheets that covers much of Earths surface. The lithosphere is made of rocks, land, and underground earth. The biosphere is the living layer. It is where Earths life-forms live within the other spheres.
Earths unique environment is possible because of our planets air, water, rocks, and life. Earth is a system created by these combined parts working together. Each part affects the others. For example, pollution in the air can mix with rain. When the rain fills up streams, it becomes water pollution. Lifeespecially human lifealso affects Earth. People have made Earth a different planet than it was centuries ago. The world population has doubled since the 1950s. Earths environment is changing as people fill up its land and use up its forests, water, minerals, and other resources.
Scientists studying Earth are tracking these changes. They are measuring air and water pollution, studying weather and storms, and watching how well different plants and animals are surviving. Scientists want to know how these changes are affecting our planet. Are they upsetting Earths balance? Can the planets complex system continue without problems? The answers they find will affect us all.

Image Credit: NASA
The Apollo 8 astronauts were the first humans to see Earth from deep space in 1968.
Sometimes a different view really changes how you see something. Think of looking at a rock with a magnifier. You may see tiny mineral grains or other details. Now imagine zooming out and seeing our rocky world from space. People shrink and streets disappear. Mountains become bumps on chunks of land surrounded by lots of blue ocean water.
The Apollo 8 astronauts were the first people to see Earth like this. The astronauts were on their way to orbit the Moon in 1968. They looked back at Earth in aweand took photographs. Seeing our planet alone against the darkness of space changed the way many humans viewed it. People saw Earth as a wholeone system with shared air, land, water, and life.
Apollo 8s mission was during a decade when scientists were chasing the dream of landing astronauts on the Moon. (They succeeded in 1969 with Apollo 11.) But some scientists had a different dream. They wanted to use space technology to look at our own planet. A view from space makes it possible to track changes all around the globe. The secret to getting that view is satellites.
A satellite is a machine launched into space that circles Earth. The first satellite went into Earth orbit in 1957. Today, nearly 3,000 satellites circle our planet. They help us predict weather, make phone calls, watch television, guide airplanes and ships, and spy on enemies. Satellites are also amazing tools forEarth scientists. Taking pictures from up above is the best way to keep track of shrinking forests, melting ice caps, or growing deserts.
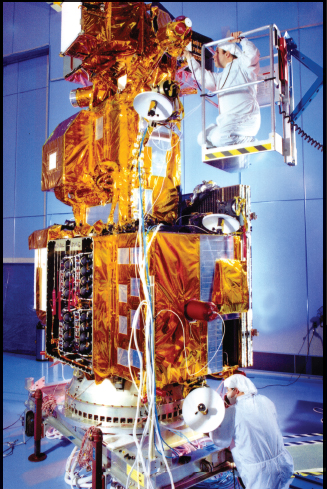
Image Credit: NASA
Engineers work on Landsat 7 before launch. The satellite went into orbit around Earth on April 15, 1999.
FAR-OUT FACT
In 1955, two nations announced plans to be the first to launch a satellite. The Soviet Union and the United States both competed in the space race to prove that their form of government was superior. And both nations wanted spy satellites capable of looking in on their enemieseach other. The United States lost the space race. The Soviet Union successfully launched Sputnik in October 1957. The United States launched its first satellite, Explorer 1, about four months later. It was not a friendly competition. Satellites have a less than peaceful past! But they have become a powerful tool for scientists.
Next page




















