
EARTH'S COMPANION
EARTH HAS MANY MAN-MADE SATELLITES that travel around it. But the Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. The Moon is also the only place in our solar system, aside from Earth, that astronauts have visited.
Spacecraft and astronauts have visited the Moon to find out more about it. Learn about the amazing missions, the dedicated scientists who plan them, and far-out facts about the Moon.
The Far-Out Guide to the Solar System series provides valuable information about the solar system, its planets, and mankind's quest in exploring them. This series is an excellent resource for young scientists and amateur astronomers.
Bahram Mobasher, PhD, Series Science Consultant
Professor of Physics and Observational Astronomy, University of California, Riverside
About the Author
Award-winning author MARY KAY CARSON has written many nonfiction books for young people and their teachers. In 2009, she received the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Children's Literature Award.

Image Credit: Illustration by AOES Medialab, ESA 2002
Earth's moon is a giant. The Earth and Moon are closer in size than any other moon-and-planet pair in the solar system.
Did you know that the Moon is moving away from us? Every year the Moon moves nearly 4 centimeters (1 inches) farther away from Earth. How do we know this? Scientists measure the distance betweenEarth and the Moon using mirrors put on the Moon by astronauts. You will learn many more far-out facts about the Moon in this book. Just keep reading!
The Moon is Earths only natural satellite. A satellite travels around, or orbits, another space object. Many artificial satellites orbit Earth, sending down TV signals and other information. But only one natural satellite, or moon, circles our planet. Because it is Earths only moon, we call it the Moon. The Moon is unique in the solar system, too. It is the largest moon compared to its planet. While some of Jupiters and one of Saturns moons are bigger, all are tiny compared to their giant planets. The Moons width is about one-quarter of Earths width. That is a huge size for a moon.
FAR-OUT FACT
The Moons shape in the night sky looks as if it changes during the month. These different moon shapes are called phases. Earth goes around the Sun. The Moon orbits Earth. The changing positions of these three objects create the lunar phases. When the Moon is between Earth and the Sun, the shadowed side of the Moon faces us. This is a dark New Moon. When Earth is between the Sun and the Moon, the completely sunlit side faces us. This is a Full Moon. First quarter, third quarter, and other phases are steps along the way from New Moon to Full Moon and back again.
The Moon is an ordinary sight, as well as its own extraordinary world. Humans have studied the Moon for a long time. Ancient people used the changing Moon phases as a calendar. Modern people have peered at the Moon through telescopes and realized it was a world beyond Earth. During the space age, people sent rockets and astronauts to explore our closest neighbor in space.
Twelve astronauts have walked on the Moon. It is the only other world visited by humans. Over the years, more than seventy-five spacecraft have flown by, circled, or landed on the Moon. More robotic spacecraft, or space probes, will be joining them soon. The 2010s are the International Lunar Decade. Moon missions from China, India, Japan, Europe, and the United States are planned.
The Moon has been visited and well mapped. But much is still mysterious about it. Scientists still wonder: What lies underneath its crater-covered crust? What causes moonquakes? How much water ice is on the Moon? We want to know more about our moon, because its history is our history. The Moon affects Earth every day. We will share a changing future, too. Someday, humans may even live on the Moon.

Image Credit: Tom Uhlman
What do you think about when you look at the Moon? Is it a pretty sight, a marker of time, a world to explore, or something else?
FAR-OUT FACT
We call our only moon the Moon, but many call it by its Latin nameLuna. The word to describe moon thingslunarcomes from this name. There are lunar spacecraft, lunar astronauts, lunar rocks, lunar space suits, lunar rovers, and more.
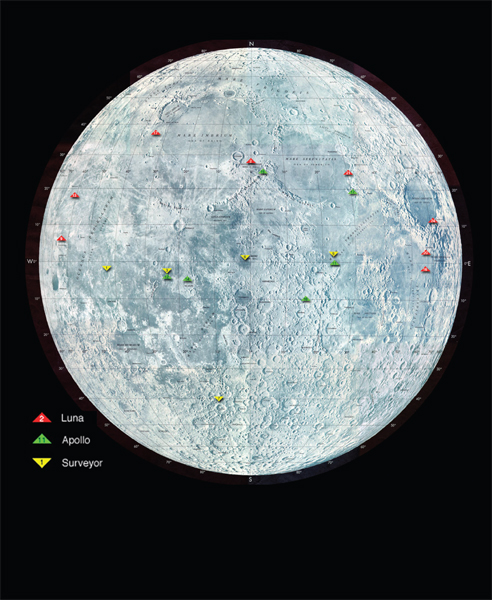

Image Credit: National Space Science Data Center, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
The triangles on this map of the Moon mark the many places where lunar spacecraft have landed. The red triangles are where robotic Russian landers set down from 1959 to 1976. The yellow triangles are where robotic American landers touched down from 1966 to 1968. The six green triangles are where the U.S. astronaut missions landed in 1969 to 1972.

Image Credit: NASA
Only four of our solar systems moons are bigger than Earths moon: Ganymede, Callisto, and Io of Jupiter; and Saturns Titan.
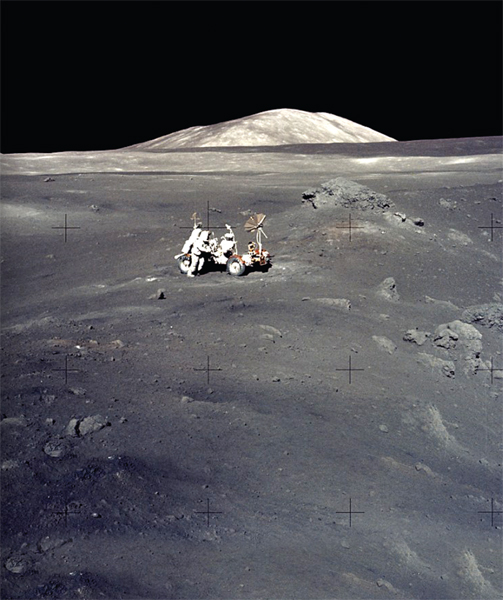

Image Credit: Apollo 17/NASA
Apollo 17 astronaut Harrison Schmitt uses the lunar rover to explore the lifeless, still, gray Moon in 1972.
Astronaut Buzz Aldrin stepped out onto the Moon in 1969. He took a long look around. Then he declared that he saw a magnificent desolation. What did the astronaut mean? The Moon is a still, empty, lonelyor desolateworld. Not a single weed or bug lives there. The lunar landscape looks like a black-and-white movie. Nearly every pebble, rock, and boulder is a shade of gray. The daytime sky is inky black. There is no air on the Moon. No breeze blows the dust blanketing its bare ground.
The Moon is also a magnificent sight, as Aldrin said. Millions of craters cover its surface. Space rocks slamming into the Moon created these bowl-shaped dents.

Image Credit: NASA/JPL/USGS
This is the near side of the Moon, the side always turned toward Earth. You can see the dark maria, the lighter highlands, and the bright rays surrounding the 85-kilometer- (52-mile-) wide Tycho crater near the bottom.
Meteoroids, asteroids, and comets have left craters of all sizes on the Moon. They range from tiny dimples in the dust to holes bigger than Texas. Some recent craters are surrounded by streaky rays. The rays are bright material splashed out at impact. The largest moon craters are ringed in rims as tall as mountains. Highlands like these look light-colored from Earth. The areas of the Moon that look dark from Earth are called maria (seas). The dark maria were once oceans of lava. They cooled into flat plains of rock billions of years ago.
Next page























