Content Area Vocabulary
Use glossary words in a sentence.
atmosphere
axis
observatories
orbits
satellite
telescopes
Before Reading:
Building Academic Vocabulary and Background Knowledge
Before reading a book, it is important to set the stage for your child or student by using pre-reading strategies. This will help them develop their vocabulary, increase their reading comprehension, and make connections across the curriculum.
| Read the title and look at the cover. Lets make predictions about what this book will be about. |
| Take a picture walk by talking about the pictures/photographs in the book. Implant the vocabulary as you take the picture walk. Be sure to talk about the text features such as headings, Table of Contents, glossary, bolded words, captions, charts/diagrams, or Index. |
| Have students read the first page of text with you then have students read the remaining text. |
| Strategy Talk use to assist students while reading. - Get your mouth ready - Look at the picture - Thinkdoes it make sense - Thinkdoes it look right - Thinkdoes it sound right - Chunk it by looking for a part you know |
| Read it again. |
| After reading the book complete the activities below. |
After Reading:
Comprehension and Extension Activity
After reading the book, work on the following questions with your child or students in order to check their level of reading comprehension and content mastery.
| Which space mission was the first to go to the Moon? (Summarize) |
| How does the Hubble Space Telescope take pictures of the Moon? (Asking questions) |
| How does wind and rain affect a surface? (Infer) |
| How does the Moon glow? (Asking questions) |
Extension Activity
The Moon has no weather. There isnt any wind, snow, or rain to change the surface. Using this information, create a hypothesis about your footprint on Earth. Will the impression stay forever? Fill a bin with sand. Step onto the sand to leave your footprint. Keep this bin indoors away from any weather. Now go to the playground or sandbox and make a footprint. After several days look at the different footprints. What changed? Why were there changes in one and not the other?

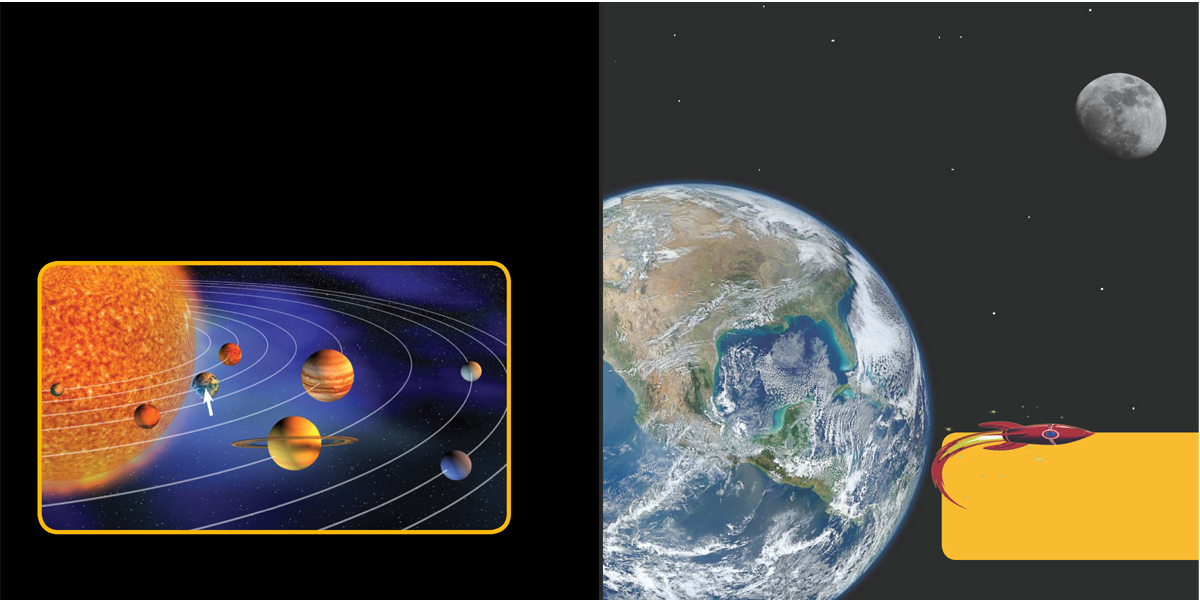
One Moon for Earth
Earth and seven other planets circle the Sun, the star in the center of our solar system. Earth has one natural satellite,our Moon.
From Earth, the Moon appears to glow. But unlike a star, which makes its own light, the Moon only reflects sunlight.
Sun
Earth
The Moon is about onefourth the size of Earth, similar to the difference between a softball and a basketball.
Many scientists think that the Moon formed when a giant meteor crashed into Earth and pieces zinged off into space.
Volcanoes and meteors have made the Moons surface rocky and rough. No volcanoes are active on the Moon today.

About 238,000 miles (384,500 kilometers) separate the Moon and Earth.
Because the Moon has a thin atmosphere,it has no weather. Without wind or rain to wear away the Moons surface, it does not change.
Without an atmosphere to blanket it, temperatures on the Moon may reach 273 Fahrenheit (134 Celsius) in sunlight and -243 Fahrenheit (-153 Celsius) in darkness.

Moon
Earth
273F (134C)
-243F (-153C)
Moon Motion
Like Earth, the Moon turns on its axis. It also orbits the Earth.
Because the Moon orbits Earth in about 27 days and turns on its axis in the same amount of time, the same side of the Moon faces Earth all the time.
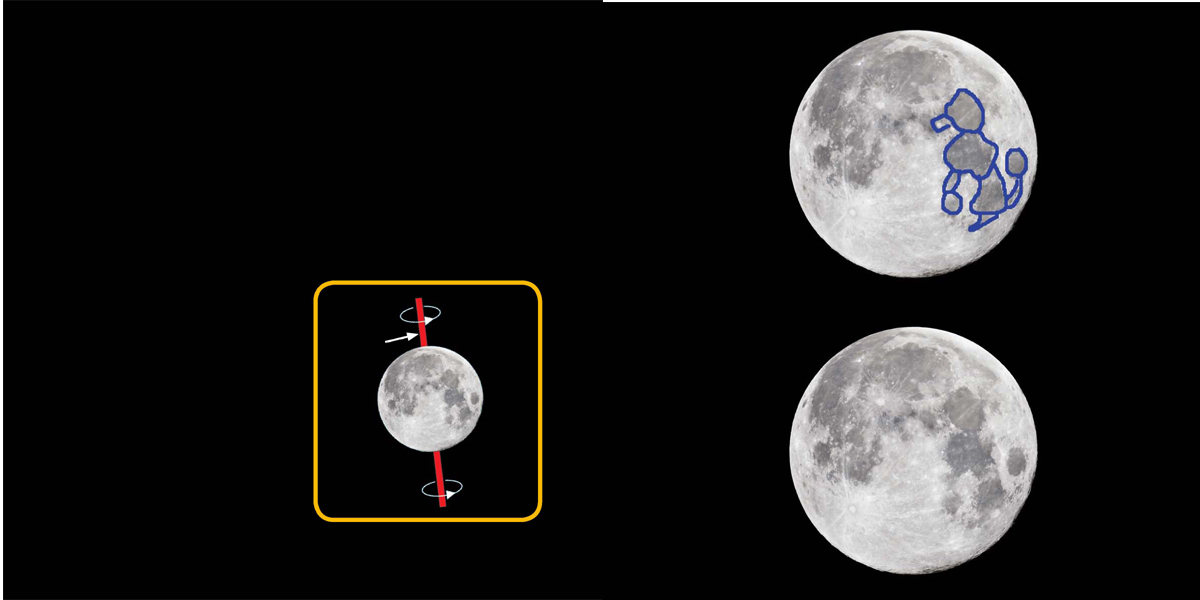

axis
The axis is an invisible line that cant be seen.
When viewing the full Moon, some say they can see what looks like a poodle in the Moon.
Sometimes only a slice of the Moon can be seen from Earth, while other times the Moon is full. Only the part of the Moon that is lit by the Sun is visible.
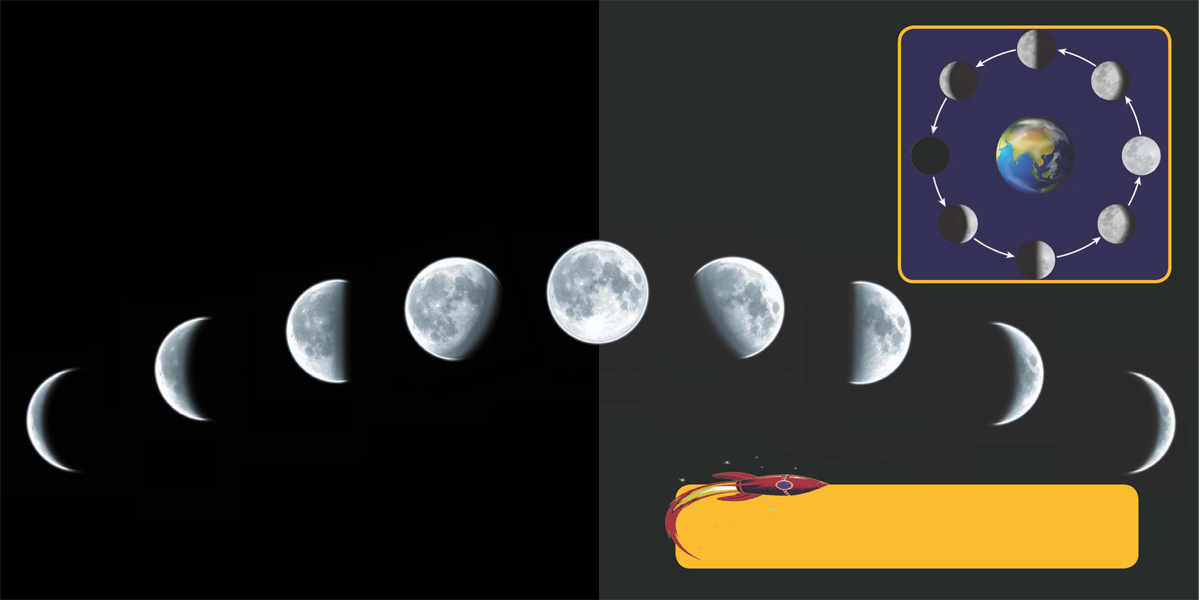

As the Moon orbits Earth, our view of it changes in a regular cycle.
Usually, there is one full Moon in a month. But about every three years, two full Moons will appear in one month. The second one is called a blue Moon.
Fly Me to the Moon
The Moon has always sparked wonder. Telescopes help scientists study the Moon and other objects in space.
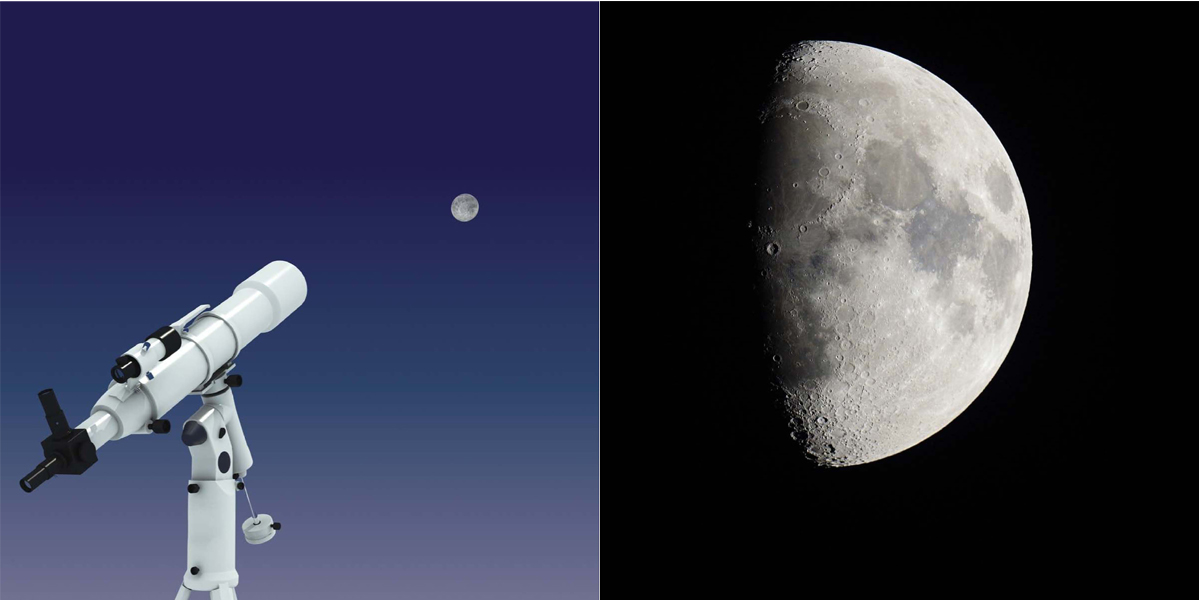

The best time to study the Moon is during its first quarter. When the Moon is in its first quarter, the Sun hits it at an angle. It creates shadows on the surface and more detail is visible.
Scientists build large telescopes in mountaintop observatories. The atmosphere is thinner on mountaintops, making it easier to see far away objects in space.
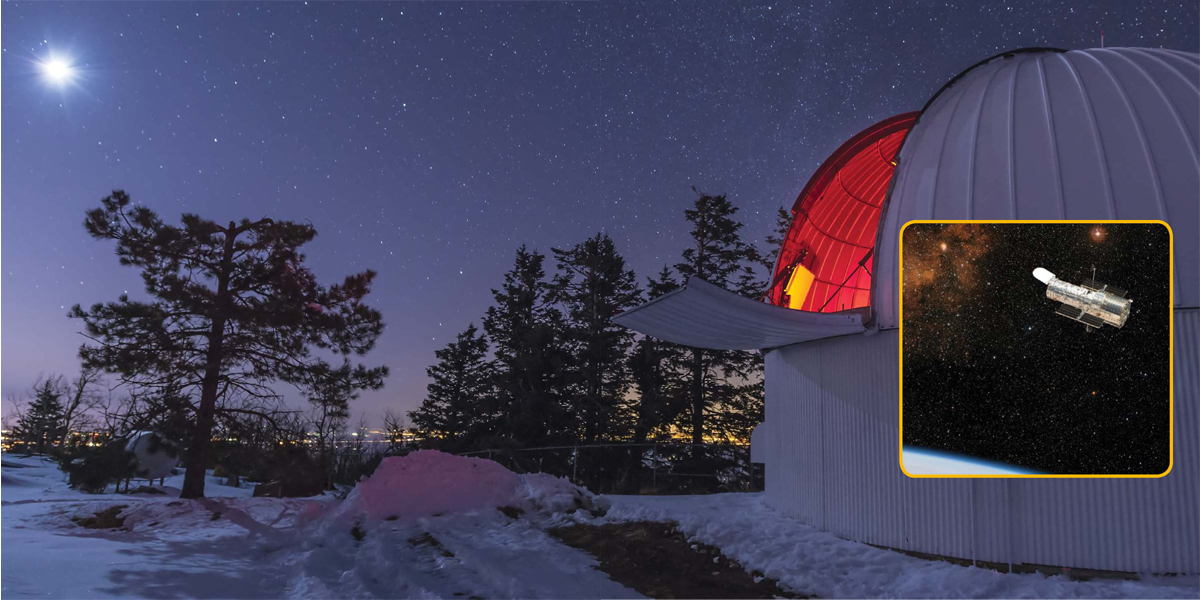

Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope orbits Earth. It has taken many thousands of pictures.
Man-made satellites and spacecraft explore the Moon. Early missions did not carry people.
Satellites in the Moons orbit allow us to take photos of the far side of the Moon. The far side of the Moon always faces away from Earth.

LADEE Satellite

























