Table of Contents
Guide
Pyramids of Egypt

Shirley Duke

rourkeeducationalmedia.com | 
Scan for Related Titles
and Teacher Resources |
Before & After
Reading Activities | Level: R Word Count: 2,634 Words 100th word: the |
Before Reading:
Building Academic Vocabulary and Background Knowledge
Before reading a book, it is important to tap into what your child or students already know about the topic. This will help them develop their vocabulary, increase their reading comprehension, and make connections across the curriculum.
Look at the cover of the book. What will this book be about?
What do you already know about the topic?
Lets study the Table of Contents. What will you learn about in the books chapters?
What would you like to learn about this topic? Do you think you might learn about it from this book? Why or why not?
Use a reading journal to write about your knowledge of this topic. Record what you already know about the topic and what you hope to learn about the topic.
Read the book.
In your reading journal, record what you learned about the topic and your response to the book.
After reading the book complete the activities below.
Content Area Vocabulary
Read the list. What do these words mean?
archaeologists
civilization
Egyptologists
flax
hieroglyph
mastabas
papyrus
pharaohs
pyramidiums
quarry
scaffolding
silty
stonemasons
tombs
After Reading:
Comprehension and Extension Activity
After reading the book, work on the following questions with your child or students in order to check their level of reading comprehension and content mastery.
1.Explain how the pyramids helped give the pharaohs immortality. (Asking questions)
2.Why do you think pharaohs wanted to create pyramid-shaped tombs? (Infer)
3.Explain the importance of the Nile River in the constructing of the pyramids. (Summarize)
4.Why were narrow air shafts built into the pyramids? (Infer)
5.What techniques and tools used by the ancient Egyptians are still used today? (Asking questions)
Extension Activity
Using a computer, look up the Egyptian hieroglyphic alphabet. Using the book, paint or draw a scene that corresponds with what you learned in the text. Write a sentence or two about your scene using the Egyptian hieroglyphics. Give your picture and the symbols with their letters and sound to a teacher, parent, or classmate to translate.
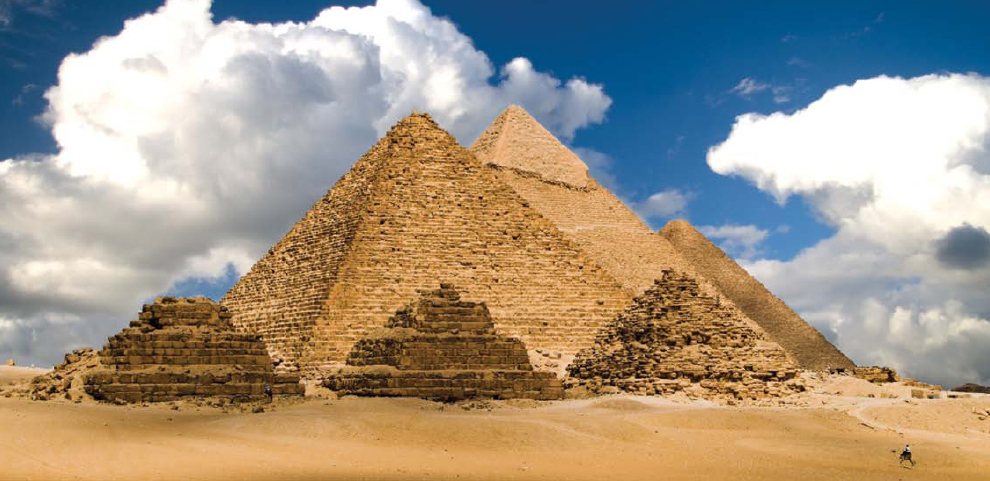

Monumental Pyramids
G reat pyramids line the dry desert on the west side of the Nile River in Egypt. , the rulers of ancient Egypt, built these massive stone structures.
Pyramids were first built about 4,500 years ago. They served as for Egypts pharaohs. The pharaohs believed the pyramids would help them have eternal life.

A 30 foot (10 meter) wall surrounded the Step Pyramid and buildings around it in Saqqara. The buildings included temples, chapels, and courtyards.
Through the years, pyramids were built in different ways. They were made of huge slabs of stone and brick. Granite and limestone were cut from a and moved down the Nile River.
The bricks were made from river mud, straw, and sand. The workers pressed the mixture into wooden molds. They sat in the heat until they hardened. The pyramid was then covered with other types of stone.
Pyramid stones fitted together closely. Erosion through the years wore down the stones so the blocks now appear to have separations.
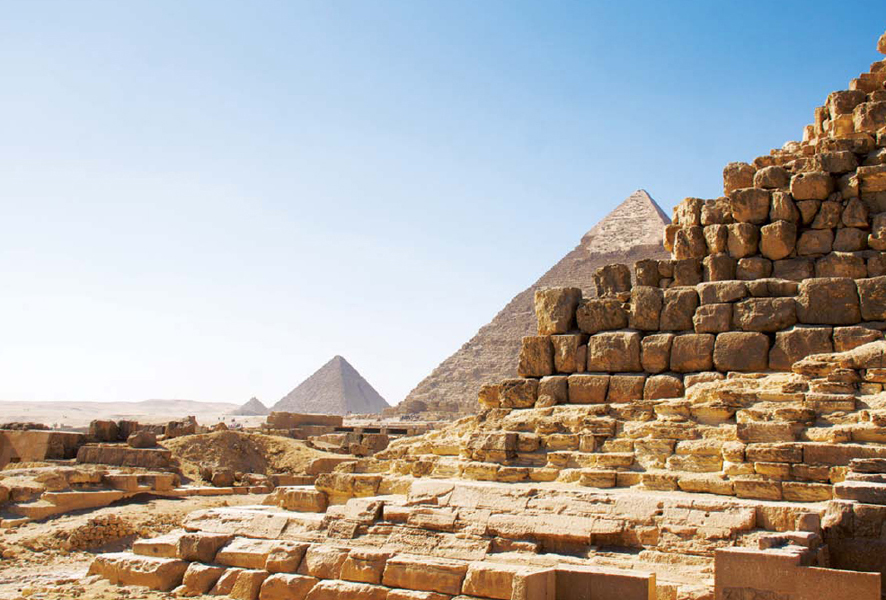

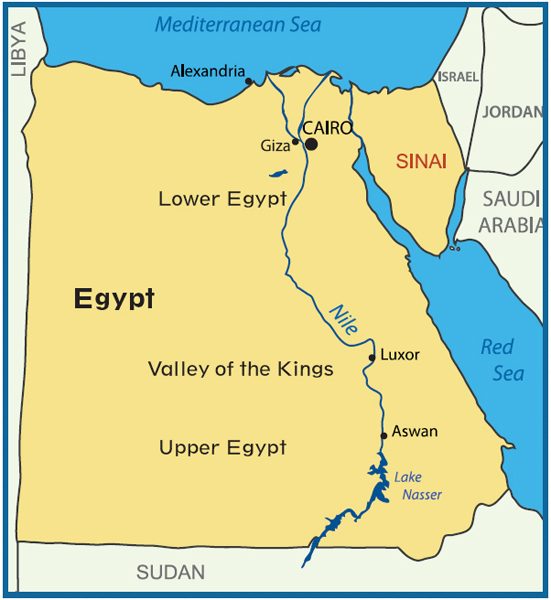
The Nile River is the longest river in the world. It supplied the ancient Egyptians with transportation, food, building materials, and water.
About 80 pyramids still exist in Egypt. The three best-known pyramids are at Giza, near modern-day Cairo. The largest of the three was built for the pharaoh Khufu.
The pyramids at Giza were built so the pharaohs could watch from their palaces as they rose. The construction took many years and each pharaoh hoped to live long enough to see his pyramid finished. The cost of these giant tombs was enormous.
The pharaohs gave grand names to the pyramids. Khufu named his Great Pyramid Khufu is one belonging to the horizon.
Brain Builder!
Khufus Great Pyramid rose to a height of about 45 stories (481 feet; 147 meters). The base measured 755 feet (230 meters) along each side. It was the tallest structure in the world for more than 4,000 years until the Eiffel Tower was built in Paris, France. The Great Pyramid was one of the seven wonders of the ancient world and the only ancient wonder still standing today.
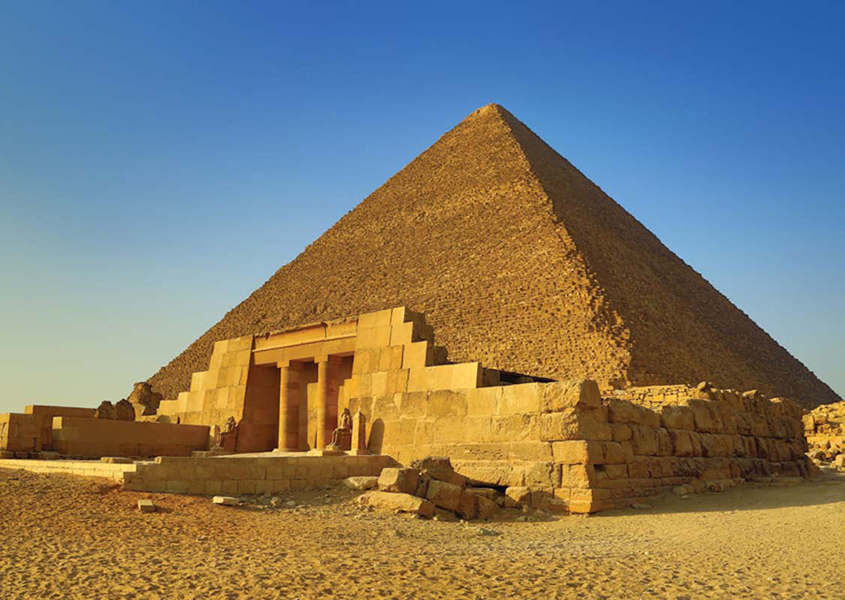

The mastaba, or tomb, of Seshemnefer IV includes a group of rooms, worship area, and burial chamber. It sits in front of the Great Pyramid at Giza and is the most visited mastaba. Seshemnefer oversaw the two seats of the House of Life and was keeper of the king's secrets.
A pyramid contains a burial chamber for the pharaoh. Some also include a chamber for the queen. A series of tunnels connects other rooms and galleries. Narrow shafts allow air inside.
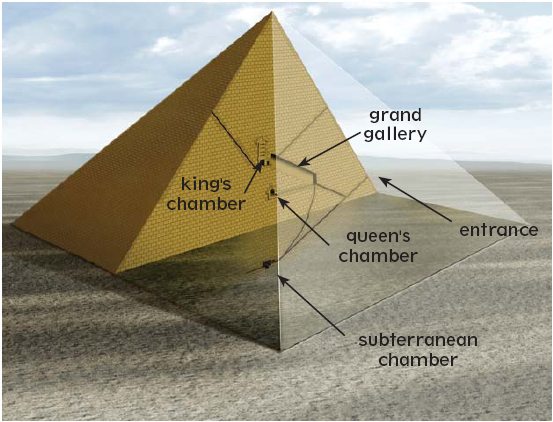
The interior of the Great Pyramid of Giza has three chambers. It is the only Egyptian pyramid known to have both ascending and descending passages.
Brain Builder!
Pharaohs were buried with everything they might need, including food, drinks, pottery, jewelry, furniture, and other treasures. A boat was often buried next to the pyramid for the pharaoh to use in the afterlife.
The Egyptians also preserved the pharaoh's intestines, stomach, lungs, and liver for the afterlife. They did not save the brain, because they believed it was worthless.

Canopic jars were used to store and preserve the internal organs. Each jar featured the head of an Egyptian god.
Tales of treasures buried with the pharaohs tempted tomb robbers. To keep thieves out of the tombs, huge stones weighing up to three tons were set in the passages and at the entrances.


























