Gardening Answers
CONTENTS
Introduction
Seed companies are well aware of the itchiness that gardeners develop as snow drifts deepen, and they time delivery of their catalogs to coincide with the onset of cabin fever. A common reaction to the glossy pictures and glowing praises of each new variety is to overreact and order more seeds than the entire neighborhood could use. To avoid this, plan your garden carefully.
Decide on the size garden you want. The information contained in this bulletin can be applied to any size area.
Next, determine what vegetables your family enjoys. If just one person enjoys rutabagas, does it make sense to plant an entire row of them?
Also, consider the local climate. Eggplant may be a great delicacy, but are chances for success with this vegetable good in an area with a short growing season?
Table 1 indicates how much seed or how many plants of most popular vegetables are needed to plant a 50-foot row and to produce a seasons supply of each vegetable for one person. Distances between rows are also suggested.
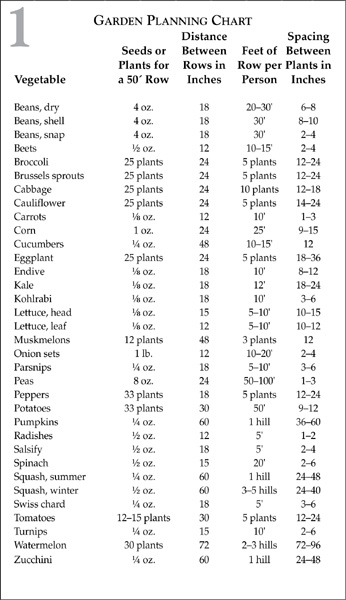
Draw up a plan for your garden on a piece of graph paper. Locate the tallest plants near the northern edge of the garden so that they will not shade shorter neighbors.
The row spacing in Table 1 is the minimum. If your garden soil is rich, the plants will probably be crowded and it would be advisable to increase the distance between rows by about 30 percent.
When making out your garden plan, also consider what type of cultivating equipment you will use. If you plant to use a hoe, rows may be spaced irregularly. If you intend to use a rototiller, plan your rows so the machine will fit between them and wont disturb the plants once they have begun to grow.
Soil Types
Soils are classified by the size of their particles. Generally, they range from coarse to fine or from light to heavy. Here are some soil types:
| sandy | Easliy tilled |
| Sandy loam | Well drained |
| Loam | Warms quickly
Poor nutrient retention |
| Silty loam | Hard to work |
| Clay loam | Slow drainage-great moisture retention |
| Clay | Warms slowly Excellent nutrient retention |
The coarser the soil, the earlier it warms in the spring and the earlier it can be worked. Coarse particles of sand retain less moisture than fine particles of clay. Coarse soils require less spring sunshine to reach a temperature suitable for seed germination.
Delay working the soil until it is dry enough so that a compressed ball of soil will break apart when dropped from the height of your hip. Soil that is worked when too moist forms compact clods and makes root growth difficult.
Soil Analysis
The ideal garden soil is rich in organic matter, well drained, slightly acid, and replenished with plant nutrients. How good is your soil? The amount of nutrients and the level of acidity can be determined by soil tests.
These tests are performed by the Extension Service at little or no charge. Or, you can do your own test, using a kit purchased through the mail, or at better garden and hardware stores.
If you use the Extension Service, contact the nearest office and request specific instructions. In general, these are the guidelines many Extension Service offices recommend:
 Use a trowel to recover small amounts of soil at a depth of about six inches.
Use a trowel to recover small amounts of soil at a depth of about six inches.
 Take several samples from across the garden. Mix these in a bucket to get an accurate indication of average soil conditions.
Take several samples from across the garden. Mix these in a bucket to get an accurate indication of average soil conditions.
 Avoid soil where peas, beans, or other nitrogen-fixing crops have been grown in previous years.
Avoid soil where peas, beans, or other nitrogen-fixing crops have been grown in previous years.
 Dry two or three handfuls of the soil from the bucket at room temperature. Drying with a stove can lead to a false indication of the need for lime. Send a small plastic bag of dry soil to the nearest Extension Service office.
Dry two or three handfuls of the soil from the bucket at room temperature. Drying with a stove can lead to a false indication of the need for lime. Send a small plastic bag of dry soil to the nearest Extension Service office.
Another tip: Do your soil test in the fall. Extension Service offices are often swamped with requests in the spring, causing delays of up to a month. By having the soil test results on hand early, you will be able to purchase the necessary fertilizers during the winter. And, youll be gardening in the first good spring weather, rather than fighting crowds at the local garden supply store.
The acidity or alkalinity of the soil (the pH level) is an important factor. Most plants have a specific pH range within which they thrive and outside of which they perform poorly, if at all. A pH level of 7 represents neutrality, when the soil is neither acid nor alkaline. Levels higher than 7 indicate alkalinity, while numbers below 7 indicate an acid state.
Table 2 indicates the optimum pH range for various popular vegetables.
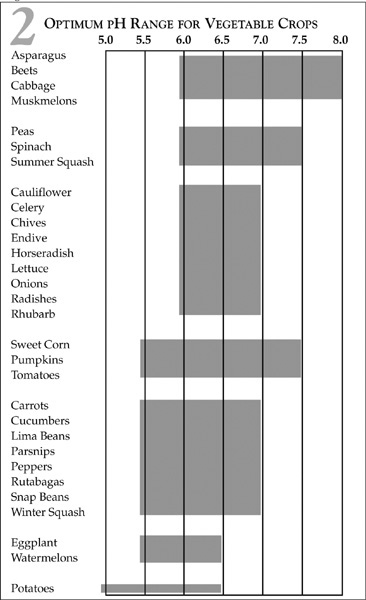
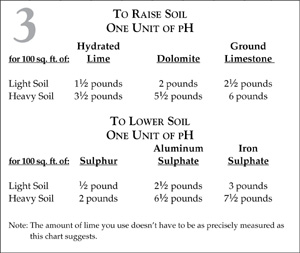
Adjusting Soil pH
Excessive soil acidity is usually corrected by adding lime, in one of three forms: ground limestone (the most commonly used form), burned lime (not recommended), and hydrated lime. The latter two are derived from the first.
Ground limestone is calcium carbonate (CaC3). When burned, the carbon dioxide is driven off, resulting in burned lime (CaO). The volume of the ground limestone is reduced by 44 percent, but its neutralizing value is unimpaired. Hydrated lime is made by adding water to burned limestone.
You may adjust the pH of your soil, if necessary, by applying lime or other materials as suggested in Table 3. Spread the material as evenly as possible and work it into the top three or four inches of soil uniformly. (If you should need to substitute one form of lime for another: 100 pounds of ground limestone equals 74 pounds of hydrated lime.)

Fertilizers
Most fertilizers contain varying amounts of the three essential plant foods: nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. On the label of commercial fertilizer bags, the elements are listed in the order given above. A bag of fertilizer listed as 10-15-20, for example would contain 10 percent nitrogen, 15 percent phosphorus, and 20 percent potassium.
Fertilizers are also available in organic forms, that is, derived from animal, vegetable, or mineral sources. Commercially prepared organic fertilizers tend to be more expensive than chemicals and slower acting, but they provide a more sustained feeding of the plants and generally improve the soil condition.
Fertilizing elements have different effects upon plants. Table 4 indicates what aspect of plant growth is governed by each of the major elements and gives sources for each, and signs of deficiency and excess.




 Use a trowel to recover small amounts of soil at a depth of about six inches.
Use a trowel to recover small amounts of soil at a depth of about six inches.


