Copyright
STERLING PAPERBACKS
An imprint of
Sterling Publishers (P) Ltd.
A-59, Okhla Industrial Area, Phase-II,
New Delhi-110020.
Tel: 26387070, 26386209; Fax: 91-11-26383788
E-mail: sterlingpublishers@airtelbroadband.in
ghai@nde.vsnl.net.in
www.sterlingpublishers.com
5 Steps to
Control High Blood Sugar
2007, Dr. Anjali Arora
ISBN 978-81-207-3243-8
All rights are reserved.
No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval
system or transmitted, in any form or by any means, mechanical,
photocopying, recording or otherwise, without prior written
permission of the authors.
The author and publisher specifically disclaim any liability,
loss or risk, whatsoever, personal or otherwise, which is
incurred as a consequence, directly or indirectly of
the use and application of any of the contents of this book.
The author wishes to thank all academicians, scientists and writers
who have been a source of inspiration.
Title


D iabetes or high blood sugar is a disease that occurs if there is a disorder in certain body functions that utilise carbohydrates, fats and proteins in the food to produce energy. Lack of a hormone called insulin or inadequate production of insulin by the pancreas results in this disease. Insulin regulates the amount of sugar in the blood. An imbalance in the amount of insulin produced can lead to the onset of diabetes mellitus.
01. Test Yourself For Diabetes

Yes | No | Hunger and Thirst |
You are often very thirsty.
|
You feel hungry all the time.
|

Yes | No | Health Problems
|
You have an itchy skin or skin problems.
|
You often develop boils.
|
Your injuries take a long time to heal.
|
| You often get leg pain and cramps. |
Yes | No | Urinary Problems
|
You have to pass urine often in the day.
|
You get up at night to pass urine.
|
| You frequently develop urinary infections. |

Yes | No | General Symptoms
|
There is numbness or a tingling sensation in your feet or hands.
|
You have lost weight recently without making an effort.
|
You feel tired and weak.
|
| You are very nauseous. |

Yes | No | Other Risk Factors
|
You have a family history of diabetes.
|
You are overweight.
|
The more times you answer yes to the above statements, the greater you are at the risk of developing diabetes mellitus.
02. Understand Diabetes Mellitus
01. What Is Diabetes?
Diabetes mellitus means honey sweet. Diabetes occurs due to the inability of the body to convert food into energy. It is a condition where we have high blood sugar (glucose) levels in our body. It is a chronic disease, which can be managed well through proper guidance.
02. The Insulin Factor
Normally our body converts the food we eat into sugar or glucose, which is used for the production of energy. This is done by the pancreas, an organ lying near the stomach. The pancreas makes a hormone called insulin, which attaches itself to the receptors on the cell wall, thereby allowing glucose
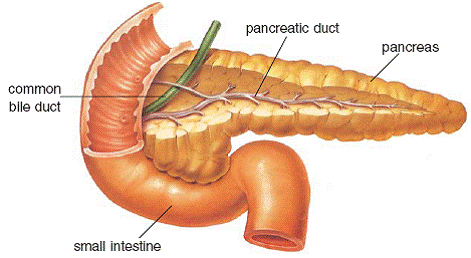
to enter the cells. It acts as the key, unlocking the receptors for glucose to enter the cells. The cells then metabolise the glucose to give energy to the body.
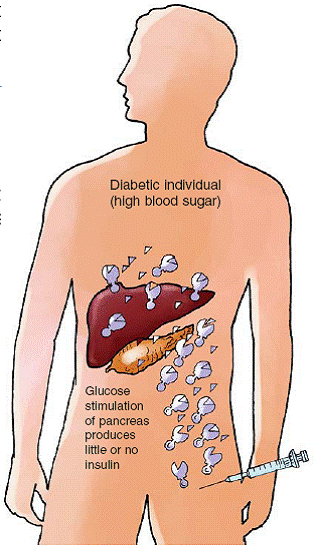
03. Insulin Resistance
The pancreas makes enough insulin, but due to certain factors, the insulin is not effective in transferring glucose from the blood into the cells of the body. Such a disorder is referred to as insulin resistance.
Factors involved can be:
- The number of receptors on each cell becomes lower than normal.
- Insulin is not able to attach itself to the receptor.
- Insulin produced may be defective.
With the passage of time, the capacity of the pancreas to produce insulin declines.
04. Types Of Diabetes
Type I Diabetes
Type I diabetes is a severe form of disease. It is an auto-immune disease, which mostly develops in childhood or in adults under 30 years of age. (Auto-immune is when the bodys immune system starts destroying itself) Juvenile diabetes develops in childhood and must be treated with insulin. It accounts for 5-10% of diabetics in the world. Inside the pancreas are cell clusters known as the

islets of langerhans. There are several type of islet cells including alpha cells and beta cells. Insulin is produced by beta cells. On increase of sugar in the blood, these cells manufacture insulin and then release it into the blood stream. The role of these cells is to monitor levels of blood sugar. In people withType I diabetes, beta cells are attacked by the immune system and are destroyed slowly. What exactly causes the immune system to get affected is still based on a number of theories. The unfortunate part is that, though this slow destruction takes place over a number of years (5-7), the symptoms of diabetes mellitus do not surface until about 80% of these beta cells are destroyed. Eventually, insulin production comes to a halt as no beta cells remain.