PYTHON AND HADOOP
BASICS
PROGRAMMING FOR BEGINNERS
J KING
PYTHON
BASICS
PROGRAMMING FOR BEGINNERS
J KING
PYTHON INTRODUCTION
Python is a programming language that is general purpose, dynamic , high level, and interpreted. To develop applications, it supports Object-Oriented programming approach. Learning is simple and easy, and provides lots of high-level data structures.
Python is yet a powerful and versatile scripting language that is easy to learn, making it attractive for application development.
With its interpreted nature, Python's syntax and dynamic typing make it an ideal language for scripting and quick application development.
Python supports multiple styles of programming including object-oriented, imperative, and functional or procedural styles.
Python is not intended to operate in a given area, such as web programming. This is why it is known as the language of multipurpose programming because it can be used with web, enterprise, 3D CAD etc.
We don't have to use data types to declare variable because it's typed dynamically so that we can write a=10 to assign an integer value in an integer variable.
Python Features
Python makes the development and debugging fast because the compilation step is not included in the development of Python, and the edit-test-debug cycle is very fast.
Compared with other programming languages Python is easy to learn. Its syntax is direct and much the same as the English language. The semicolon or curly-bracket is not used, and the indentation defines the block of code. It is the recommended language for beginners in the programming.
Using a few lines of code Python can perform complex tasks. A simple example, you simply type print("Hello World) to the hello world program. It'll take one line to execute, while Java or C will take multiple lines.
Python History and Versions
Guido Van Rossum at CWI in The Netherlands began implementing Python in December 1989.
Guido Van Rossum published the code (labeled version 0.9.0) to alt.sources in February 1991.
Python 1.0 was released in 1994, with new features such as lambda, map, filter, and reduce.
Python 2.0 has added new features such as list understandings and garbage collection systems.
Python 3.0 (also called "Py3 K") was released on December 3, 2008. It had been designed to correct the language's fundamental flaw.
Python Version List
Python Version | Released Date |
Python 1.0 | January 1994 |
Python 1.5 | December 31, 1997 |
Python 1.6 | September 5, 2000 |
Python 2.0 | October 16, 2000 |
Python 2.1 | April 17, 2001 |
Python 2.2 | December 21, 2001 |
Python 2.3 | July 29, 2003 |
Python 2.4 | November 30, 2004 |
Python 2.5 | September 19, 2006 |
Python 2.6 | October 1, 2008 |
Python 2.7 | July 3, 2010 |
Python 3.0 | December 3, 2008 |
Python 3.1 | June 27, 2009 |
Python 3.2 | February 20, 2011 |
Python 3.3 | September 29, 2012 |
Python 3.4 | March 16, 2014 |
Python 3.5 | September 13, 2015 |
Python 3.6 | December 23, 2016 |
Python 3.7 | June 27, 2018 |
Python 3.8 | October 14, 2019 |
To download the latest Python release, please visit the link https:/www.python.org/downloads/
First Python Program
In this section, we 're going to discuss Python 's basic syntax, and run a simple program to print Hello World on the console.
Python provides us with two modes of running a program:
- Using Interactive interpreter prompt
- Using a script file
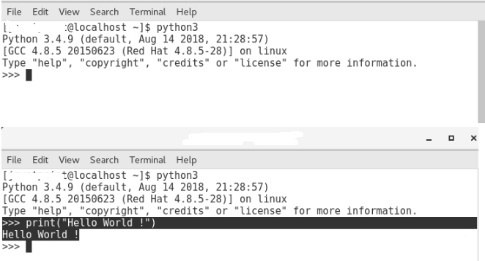
Interactive interpreter prompt
Python gives us the functionality to execute the Python statement at the interactive prompt one by one. In the case where we are concerned about the output of every line of our Python programme.
Open the terminal (or command prompt) and type python (python3, if you have both Python2 and Python3 installed on your system) .
It will open the following prompt where we can execute the statement in Python and check its impact on the console.
Using a script file
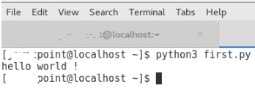
The interpreters prompt is good at running the individual code statements. We can't write the code on the terminal anytime .
Our code must be written into a file that can be executed later. To do this, open a notepad editor, create a file named first.py (Python used the.py extension) and write the following code into it.
print ( "hello world" ); #here, we have used print() function to print the message on the console.
Run the following command on the terminal
$ python3 first.py
Python Variables
Variable is a name used to refer to the location of a memory. Also known as an identifier and used for holding value.
In Python, we don't need to specify the variable type, because Python is an inferior language and is smart enough to get the type of variable.
Variable names can be a group of letters and digits, but must start with a letter or an underscore.
Using lowercase letters for name of the variable is recommended. Rahul and rahul are both two different variables.
Identifier Naming
Variables - example of identifiers .To identify the literals used in the program an Identifier is used. The rules for naming an identifier are set out below.
The variable must have an alphabet or underscore (_) as its first character.
All characters except the first character can be lower-case(a-z), upper-case (A-Z), underscore, or digit (0-9) alphabets.
The name of the identifier shall not contain any white space or any special character!, (@,#,%,^, &, *).
The name of the identifier must not be similar to any keyword set in the language.
Identifier names are case sensitive; my name, for example, and MyName is not identical.
Declaring Variable and Assigning Values
Python does not bind us to declare a variable before we use it in the app. It enables us to create a variable in the time required.
In Python we do not need to declare explicitly variable. That variable is declared automatically when we assign any value to the variable.
The operator equal (=) is used to assign value to a variable.
Object References
When we declare a variable it's necessary to understand how the Python interpreter works. The process of treating variables differs slightly from many other programming languages.
Python is a highly object-oriented programming language; therefore, each data item belongs to a specific class type. Consider example below.