MySQL for Beginner s |
(1 st Edition) |
By Ganesh Bagaria |


About the Author
Ganesh Bagaria was born on December 15, 1997 in Nawalgarh City, Rajasthan, India. He is a student, authon,owner of http://worldfreeapps.com website. This is his first book.
Ganesh has made website http://worldfreeapps.com for downloading apps and games for Android, Iphone, Windows Phone, for downloading Songs and for Playing Online Games for free.
You can connect to Ganesh Bagaria via Twitter at https://twitter.com/@ganeshbagaria , via LinkedIn https://in.linkedin.com/in/ganeshbagaria .
This is Ganesh Bagarias first book so sorry for any mistakes.
Contents
Introduction 1
Part 1: Creating Databases, Tables 3
- Create Database
- Create Table
- Set Primary Key in Table Creation
- Set Foreign Key in Table Creation
- Set default value in create table
Part 2: Accessing Databases 7
Part 3: Inserting data into Table 8
- Insert data into Table
- Insert Null Values
Part 4: Altering Table 10
- Add Column, Primary Key
- Delete Column, Primary Key, Row, Table, Database
- Modify Table
Part 5: Select Queries 14
- Format of Select Query
- Select Queries
Part 6: MySQL Functions 20
- String Functions
- Numeric Functions
Part 7: MySQL Join 26
- MySQL Join
- Different MySQL Joins
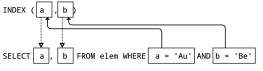
Part 8: MySQL Create Index 29
- Create Index
- Create Unique Index
- Delete Index
Part 9: MySQL Auto Increment a field 31
- Add Auto Increment in a field in Table
Part 10: MySQL View 32
- Create View
- Replace View
- Drop View
Part 11: MySQL Reference 34
Part 12: About MySQL 38
Introduction
MySQL is (as of July 2013) the world's second most[a] widely used relational database management system (RDBMS) and most widely used open-source RDBMS. It is named after co-founder Michael Widenius's daughter, My. The SQL acronym stands for Structured Query Language.
The MySQL development project has made its source code available under the terms of the GNU General Public License, as well as under a variety of proprietary agreements. MySQL was owned and sponsored by a single for-profit firm, the Swedish company MySQL AB, now owned by Oracle Corporation. For proprietary use, several paid editions are available, and offer additional functionality.
MySQL is a popular choice of database for use in web applications, and is a central component of the widel y used LAMP open source web application software stack (and other 'AMP' stacks). LAMP is an acronym for "Linux, Apache, MySQL, Perl/PHP/Python." Free-software-open source projects that require a full-featured database management system often use MySQL.
Applications which use MySQL databases include: TYPO3, MODx, Joomla, WordPress, phpBB, MyBB, Drupal and other software. MySQL is also used i n many high-profile, large-scale
websites, including Google (though not for searches), Facebook, Twitter, Flickr, and YouTube.
MySQL ships with no GUI tools to administer MySQL databases or manage data contained within the databases. Users may use the included command line tools, or use MySQL "front-ends", desktop software and web applications that create and manage MySQL databases, build database structures, back up data, inspect status, and work with data records. The official set of MySQL front-end tools, MySQL Workbench is actively developed by Oracle, and is freely available for use.
MySQL works on many system platforms, including AIX, BSDi, FreeBSD, HP-UX, eComStation, i5/OS, IRIX, Linux, OS X, Microsoft Windows, NetBSD, Novell NetWare, OpenBSD, OpenSolaris, OS/2 Warp, QNX, Oracle Solaris, Symbian, SunOS, SCO OpenServer, SCO UnixWare, Sanos and Tru64. A port of MySQL to OpenVMS also exists.
Part: 1
Creating Databases, Tables
____________________________________________________________
In this Part
- Create Database
- Create Table
- Set Primary Key in Table Creation
- Set Foreign Key in Table Creation
- Set default value in create table
; (Semicolon ) is a necessary symbol at end of all MySQL Structure.
Create Database:
Create a database in MySQL
Th e CREATE DATABAS E statement is used to create a database.
Syntax : - Create database ;
Example : - Create database mywebsite;
Create table:
Create tables in MySQL
Th e CREATE TABL E statement is used to create a table in a database.
Tables are organized into rows and columns; and each table must have a name.
- Create table query
Syntax : - Create table
((size),(size),)
The column name parameters specify the names of the columns of the table.
The data type parameter specifies what type of data the column can hold (e.g. varchar, integer, decimal, date, etc.).
The size parameter specifies the maximum length of the column of the table.
Example : - Create table worldfreeapps (Sr integer(5),Appstore char(20),Song char(20),Game char(30));
- Set not null value on default position in table create
Th e NOT NUL L constraint enforces a column t o NO T accep t NUL L values.
Th e NOT NUL L constraint enforces a field to always contain a value. This means that you cannot insert a new record, or update a record without adding a value to this field.
Example : - Create table worldfreeapps (Sr integer(5)not null,Appstore char(20)not null,Song char(20));
- Set default value in Create table
Th e DEFAUL T constraint is used to insert a default value into a column.
The default value will be added to all new records, if no other value is specified.
Example : - Create table worldfreeapps (Sr integer(5)default,Appstore char(20),Song char(20));
- Check default condition in table create
Th e CHEC K constraint is used to limit the value range that can be placed in a column.
If you define a CHEC K constraint on a single column it allows only certain values for this column.
If you define a CHEC K constraint on a table it can limit the values in certain columns based on values in other columns in the row.
Example : - Create table worldfreeapps (Sr integer (5)check(Sr>2),Appstore char(20),Song char(20));
- Set Primary Key in table creation
Th e PRIMARY KE Y constraint uniquely identifies each record in a database table.
Primary keys must contai n UNIQU E values.
A primary key column cannot contai n NUL L values.
Most tables should have a primary key, and each table can have only ONE primary key.
Example : - Create table worldfreeapps (Sr integer(5)primary key,Appstore char(20),Song char(20));
Or
Example : - Create table worldfreeapps (Sr integer(5),Appstore char(20),Song char (20), primary key (Sr));
- Set Foreign Key in table creation
A FOREIGN KE Y in one table points to a PRIMARY KEY in another table.
Example : - Create table worldfreeapps (Sr integer(5),Appstore char(20),Song char(20),Game char(20), foreign key (Sr) references world(Sr));