discover the worlds tropical rainforests Tr opical rainfore sts cove r less than 3 perc ent of the planet, yet they contain at least half of all the world s wildlife. T his make s them fascinating and important places. Let s tra v el thr ough these enchanting tr opical worlds b y disco veri ng the huge variety of plants and animals that live ther e.
Where do you find rainfo rests? Camouflaging cre atures and colorful warnings How do plants and animals live? Safety in numbers What does a rainfore st look like ? Finding a mate Why are rainf orests import ant? Growi ng up in the rainfore st Discov er an amazing variety of rainfore st plants Why do rainfore sts need protection? The fight for light Deforestation Plants and their pollinators How do es climate change affect rainfor ests? Plants and their seed spreaders Rainforest r ecov ery The cycle of life How ca n you help? Meet the wonderful animals that live in tr opical rai nforests Make your own m ini rainforest Animal hunters Protecting the place s that are pr ecious
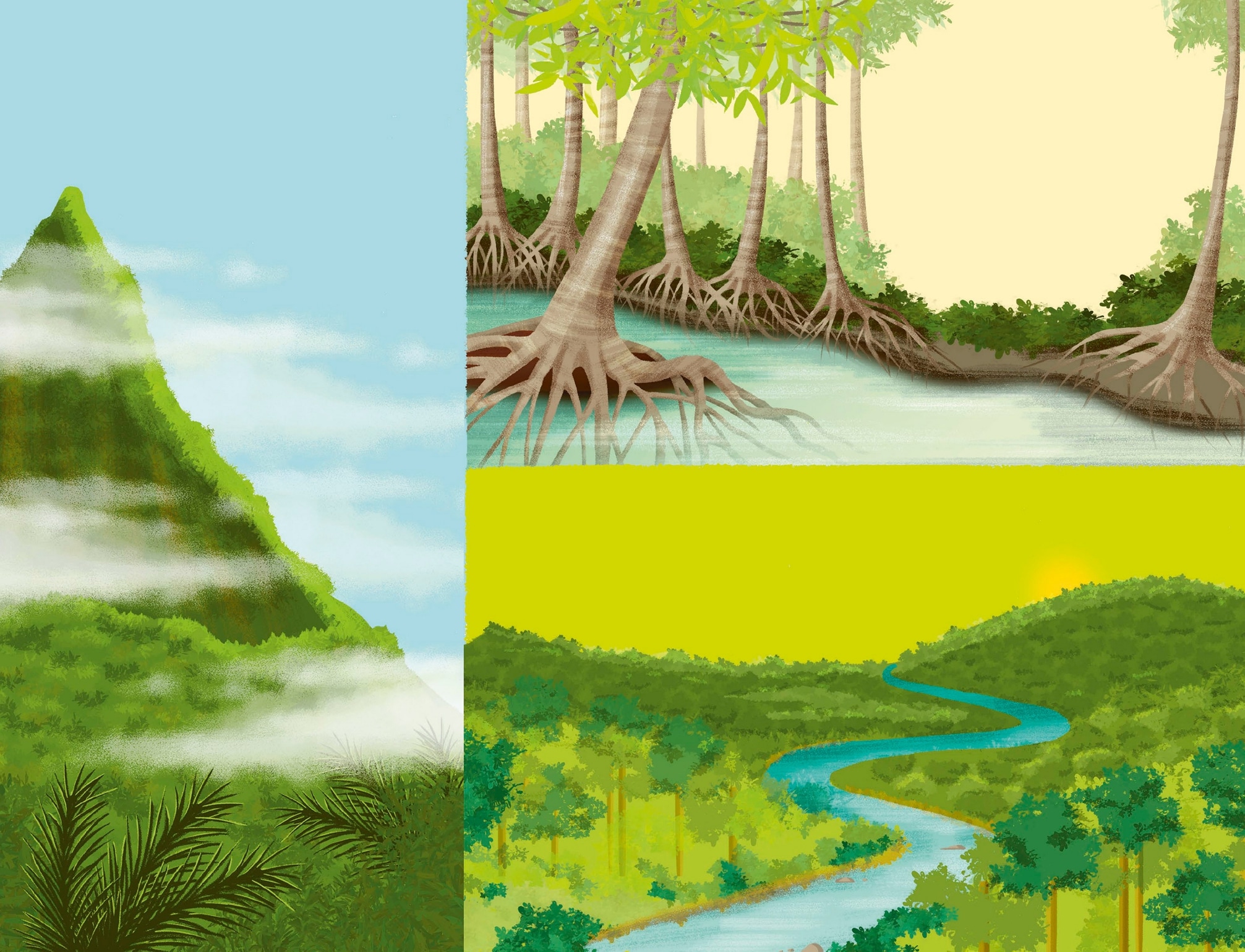
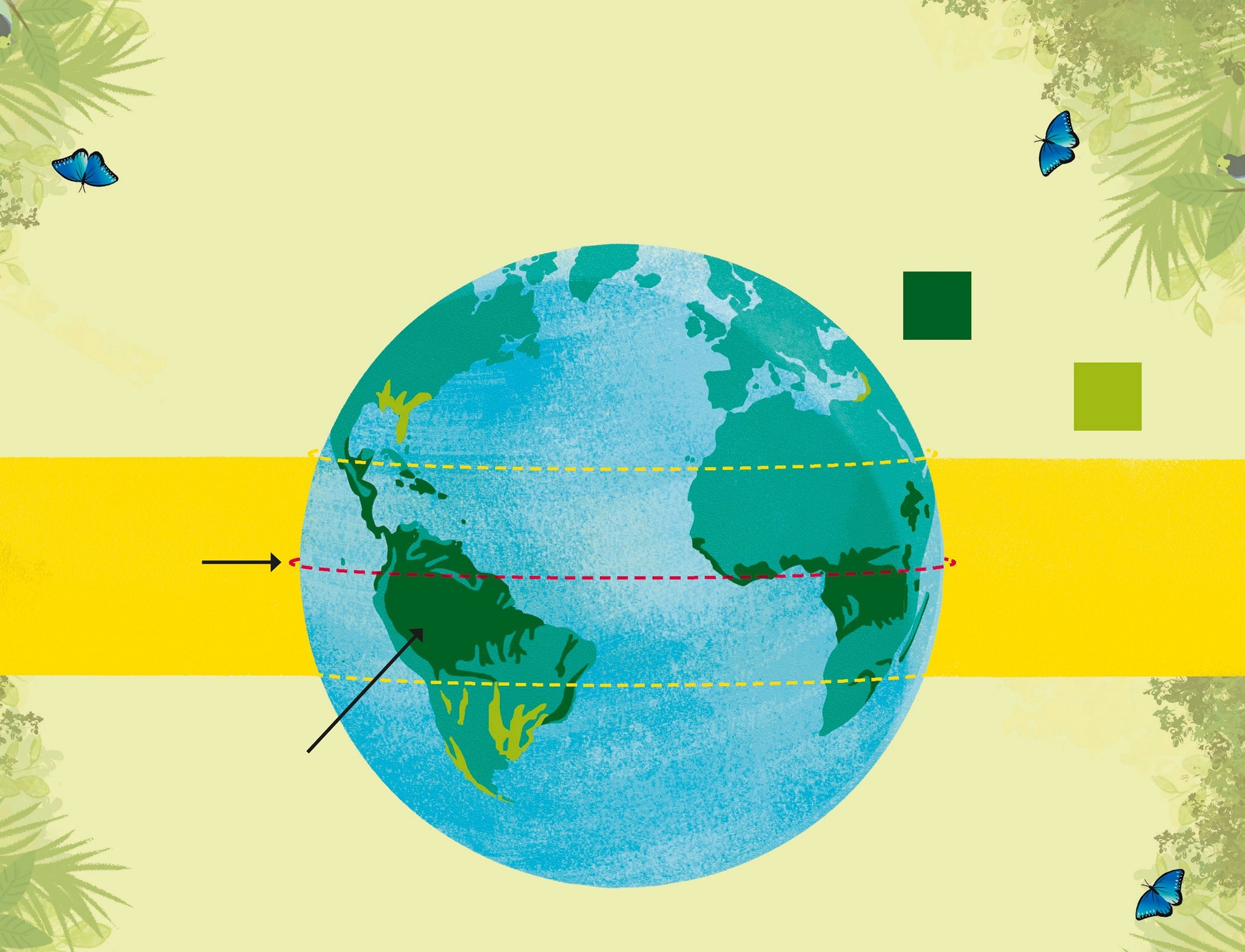
Where do you find rainforests? The equator is an imaginary line that runs aro und the middle of the Earth lik e a belt. Tropical rainforests are fou nd in places near the Equator , where it is warm year -r ound, and wet fo r most of the year . The area betw een the yellow lines is called the tropical zone. A tropi cal rainfore st will get at least 79 in (2 m) of rain ev ery year . But sometimes, this amount can be more than 394 in (10 m). The temperature is normall y 7293F (2234C). Above and below the Equator , the temperature is cooler , but you can still find rainfore sts gro wing in areas wher e ther e is a lot of rain. T hese rainfore sts are called temperate rainforests. The Amazon is the largest tro pical rainfore st and has one of the world s longest rivers running thro ugh it. The equator tropical rainforests: temperate rainforests:
There are different types of tropical rainforests. Most trop ical rainfore sts gro w in low areas of land wher e rive rs flow . T hese are the rainfore sts that most people think of when they hear the w or d jungle . Some tro pical fore sts are called cloud fores ts . They gro w on mountains and hills among damp, low clouds. Tr opical f orests g rowing near the sea are called mangro ve f orests . Here mangr ove t rees gr o w with their r oots sunk deep into the salty water .
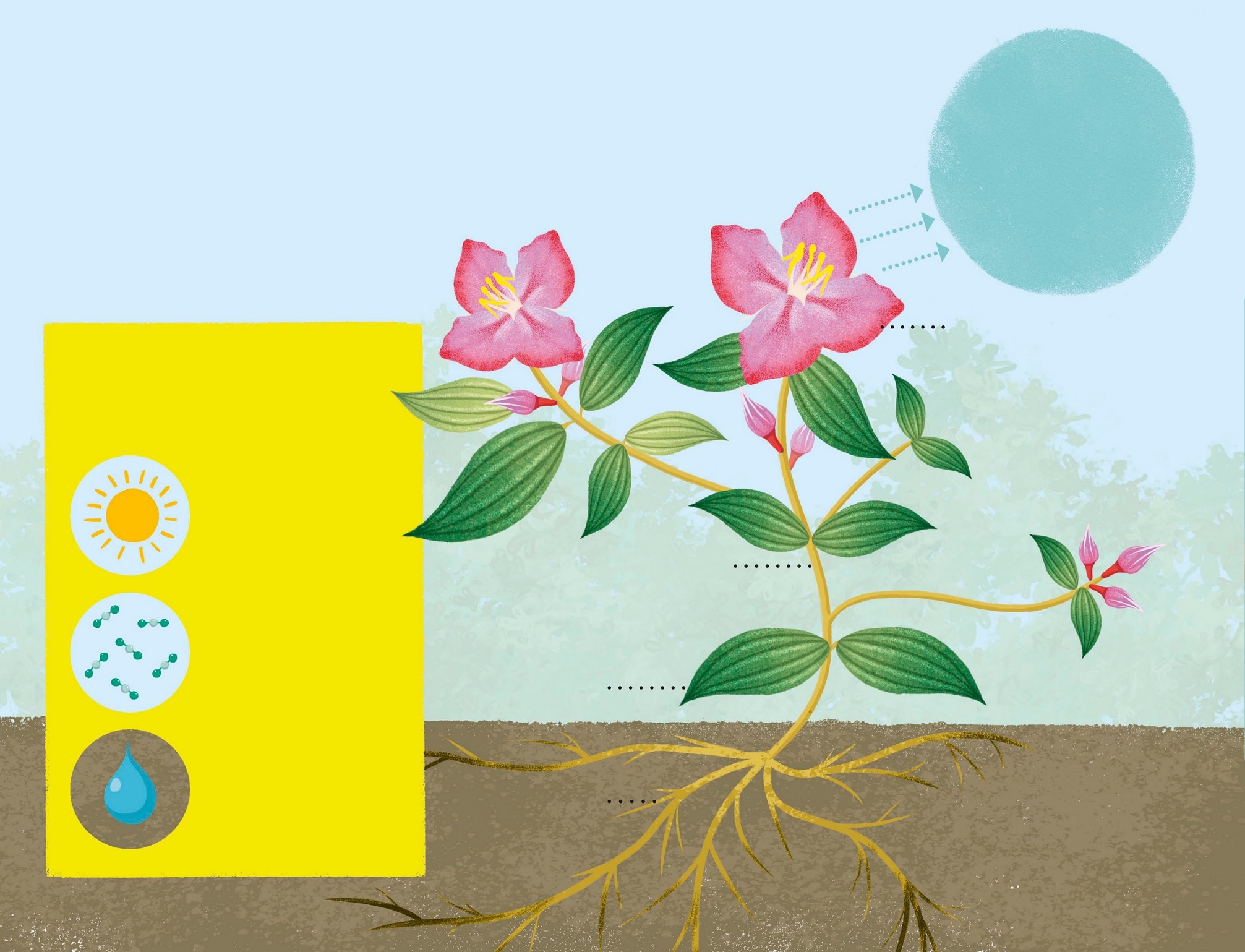
How do plants and animals live? An enormous variety of plants and animals live in tr opical rainfore sts. All these living things need food to give them energy to surv ive, but plants and animals get their food in differ ent way s. A plant s leaves act like food factories. T hey make the f ood using thr ee things: Plants are able to make their own food. Light from the sun carbon dioxide from the air water from the ground While plants are making f ood, they release oxygen into the air . T his is a gas that all animals need to breathe. On some plants, the seeds are found in fruits. The roots take up water and nutrients fro m the soil. The stem carries water to the leave s. The leav es absorb energy from the sun to help make food. The flow ers make seeds, which can grow in to new plants. Melastome plant In eve ry r ainfore st there ar e thousands of diff er ent types of plants, which pro vide food and shelter for animals.
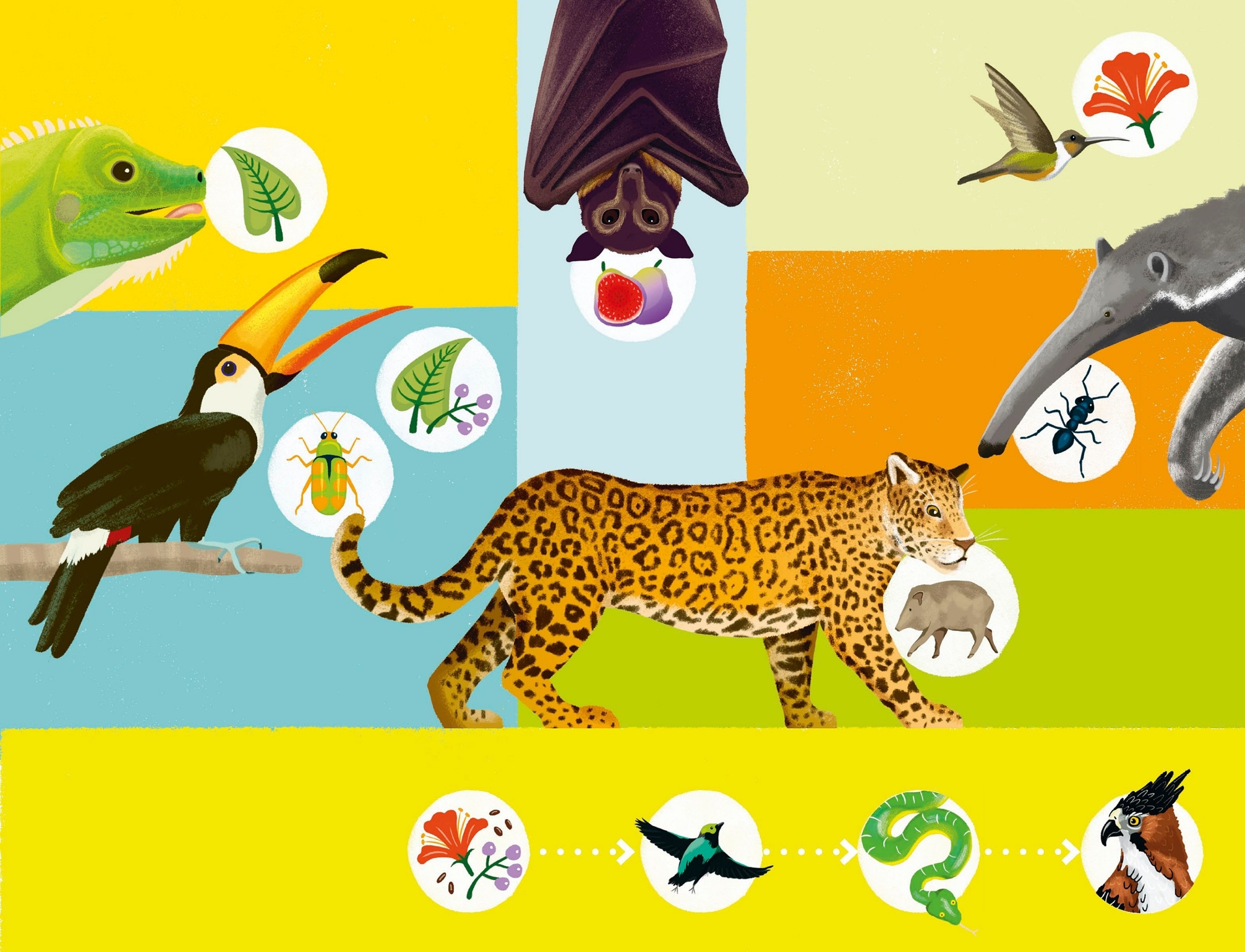
Animals get their food from eating other living things. Iguana An herbivore is an animal that eats only plants. To ucan An omnivore is an animal that eats both plants and other animals. In a rainf or est, animals and plants need each other to survi ve. One way that plants and animals are connected is throu gh food chains. A Frugivore is an animal that mainly eats fruits. Bat A nectivore is an animal that mainly eats nectar , a sweet liquid made by the flo w ers of plants. Hummingbird An insectivore is an animal that mainl y eats insects. Anteater A carnivore is an animal that mainly eats other animals. Jaguar Seeds and berries get eaten by the bird . The bird gets eaten by the snake . The snake is eaten by the eagle.

what does a rainforest look like? Tr opical ra inforest s such as the A mazon contain some of the world s tallest trees. A t the very top, the sun shines brightly onto their leav es. But as we tra vel do wn toward the rainfore st floor , it gets darke r because mor e tr ee lea v es, branches, and other plants block out the sunlight. forest floor: Covere d in fallen leave s, the dark and damp fore st floor is the perfect habitat for insects, as well as insect-eating animals such as anteaters. understory: Leafy bushes and small tr ees mak e up this dark and hot ar ea, where fr ogs hide and birds find fo od. canopy: More wildlif e lives here than in all the other layers. In the canopy there ar e thick tr ee branches, leaves dappled with sunlight, and a refr eshing br eeze. Emergent layer: A t the top of the trees ther e is little shelter fr om the wind and rain. But some monk eys like t o hang out here, swinging betwe en the branches. Some animals that live in the emergent layer will neve r set foot on the fore st floor , but they may trave l to the understory to find food.
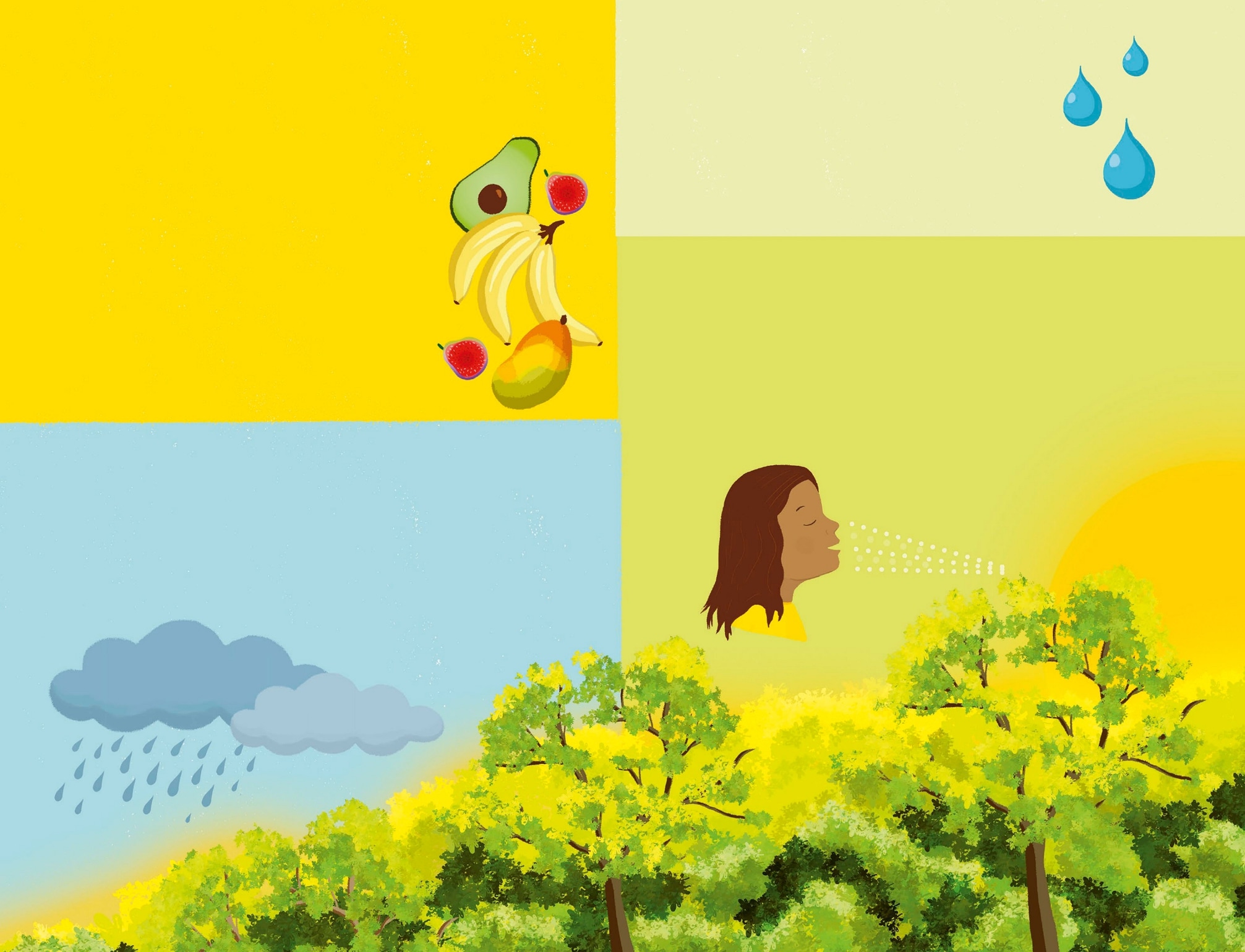
Why are rainforests so wet? The air in a rainfore st feels we t and sticky because trees and plants r elease water that they dont need. T his moisture rises when it is heated by the sun. High up in the air , the moisture f orms clouds that re lease rainwater back into the rainfore st below . Plants release water into the air . The water in the air rises and forms clouds. The clouds release rainwater back into the fore st. The river: Streams and riv ers flow thro ugh lowland rainfor ests. In these waters we find alligatorlik e reptiles called caimans, and fish such as piranhas.
Why are rainforests important? Rainforests give us food. More than 3,000 types of fruit can be found in rainfor ests, including wild v ersions of bananas, oranges, and mangoes. Ev en a fa v orite tr eat, chocolate, comes from cacao trees that gro w in rainfor ests. Rainforests create the air we breathe. Rainfores ts are know n as the lungs of the planet because their plants create o xygen that all animals, including humans, need to breathe. Rainforests stop floods. T r ee r oots suck up rainwater . Without trees, water could wash the soil away into rivers and block them, which would cause flooding. Rainforests create rainwater. The moisture r eleased into the air b y rainfore st plants and trees rises up to f orm clouds. T hese clouds can trave l to places that would otherwise be very dry, where they r elease rainwater .