Rome
(753 BCAD 476)
- 753 BC Rome is founded.
- 509 BC Rome is now a Republic and citizens elect their leaders.
- 450 BC Romans write down their laws for the first time in the Laws of the Twelve Tables.
- 312 BC Rome builds its first major road.
- 146 BC Rome defeats its major rival, the city of Carthage. The Romans tear down every building in Carthage.
- 47 BC Julius Caesar becomes dictator of Rome.
- 44 BC Political rivals kill Caesar; Civil wars begin.
- 27 BC The civil wars end the Republic. Augustus Caesar becomes the first emperor of the Roman Empire.
- AD 64 A fire destroys much of Rome.
THE SENATE
The Roman Senate was the empires governing body. Senators made important decisions about the Roman empire. These decisions included declaring war, managing funds for public use, and meeting with ambassadors from all over the empire. At various times, there were between 300 and 900 senators.
- AD 79 The volcano Mount Vesuvius destroys the Roman city of Pompeii.
- AD 80 The Roman Colosseum opens.
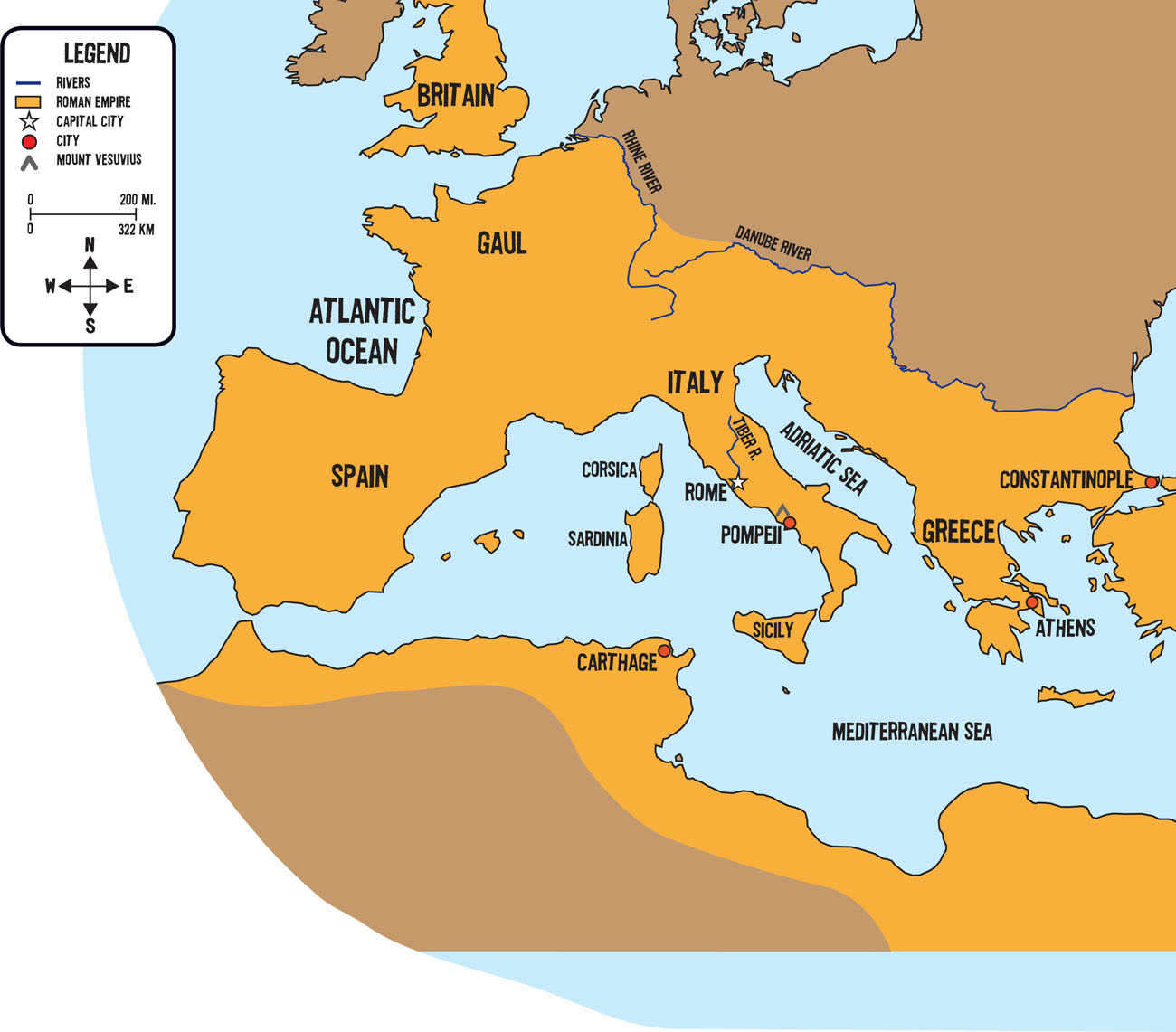
- AD 324 Constantinople founded as Eastern capital.
- AD 391 Christianity becomes the religion of Rome.
- AD 476 The fall of Rome. Last western emperor overthrown.
THE COLOSSEUM
Construction on the Colosseum was completed in AD 80. The arena stood 171 feet (52 meters) high. Seventy-six public entries led to 48 sections of seating. Spectators were given tickets showing their exact section, row, and seat number.
ROMAN EMPIRE BY THE NUMBERS, AD 250
300 MILLION number of people in the world
65 MILLION number of people living under the Roman Empire
1,000,000 number of people living in the city of Rome
500,000 number of slaves living in the city of Rome
number of senators
number of emperors who ruled Rome
Filthy Streets
Two thousand years ago, the Roman Empire ruled all the lands that bordered the Mediterranean Sea. The ancient Romans had many tools that helped make their lives easier. But there were also parts of Roman life that were dirty, gross, or even deadly.
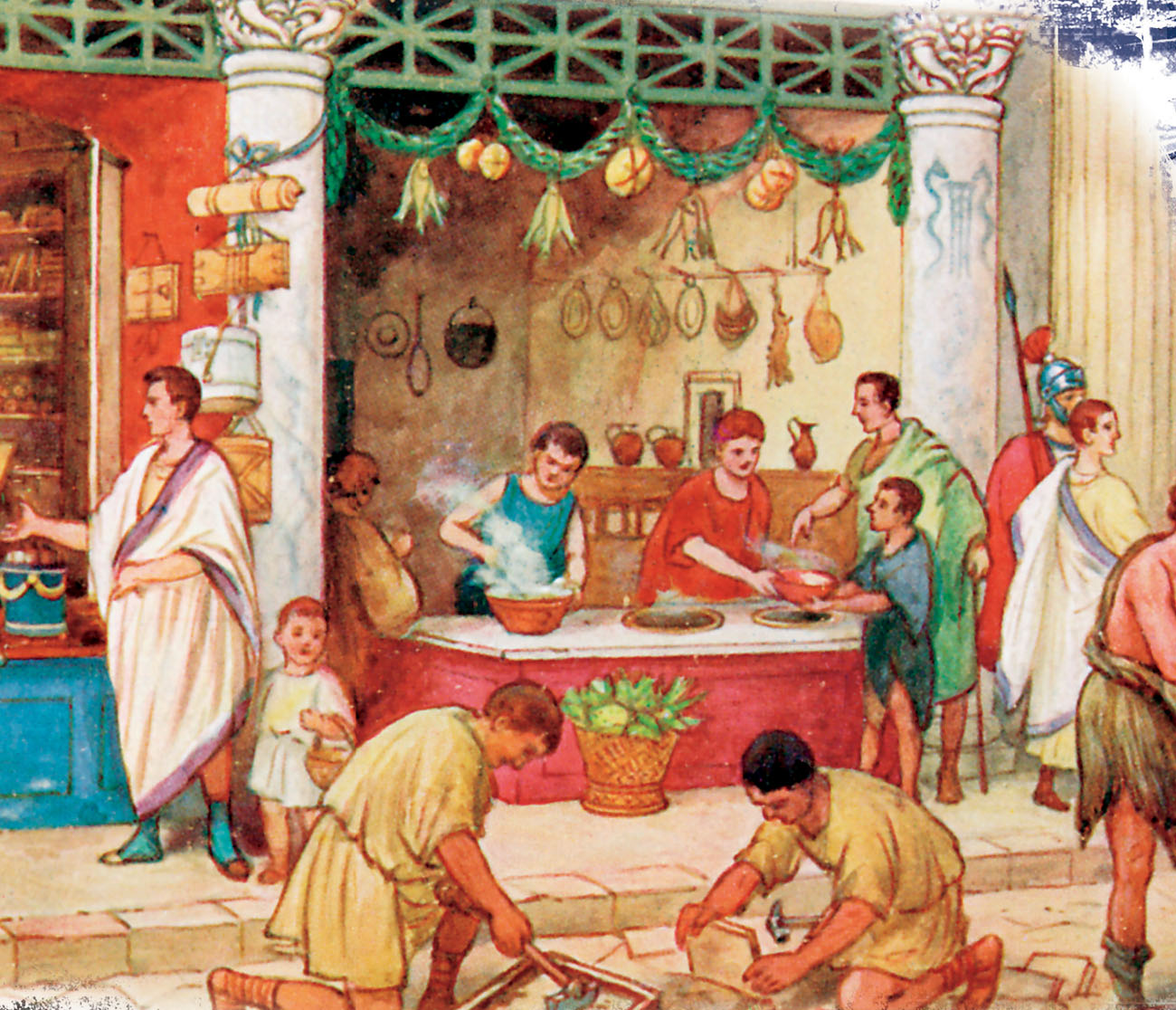
The Romans grew rich off their empire. Gold, silver, and other treasures flowed into the city. There were large public buildings and many expensive homes. There was also a sports arena and two racetracks.
But Rome was not all gold and riches. Garbage filled the streets in the poorer parts of the city. There was also plenty of human and animal waste. Only the very rich had running water. Human waste piled up outside apartment buildings. Animals lived on the streets, dropping waste as they moved about.
Shops lined the streets of ancient Rome.
FOUL FACT
People killed their animals on the street. The animal remains were tossed in the sewer.
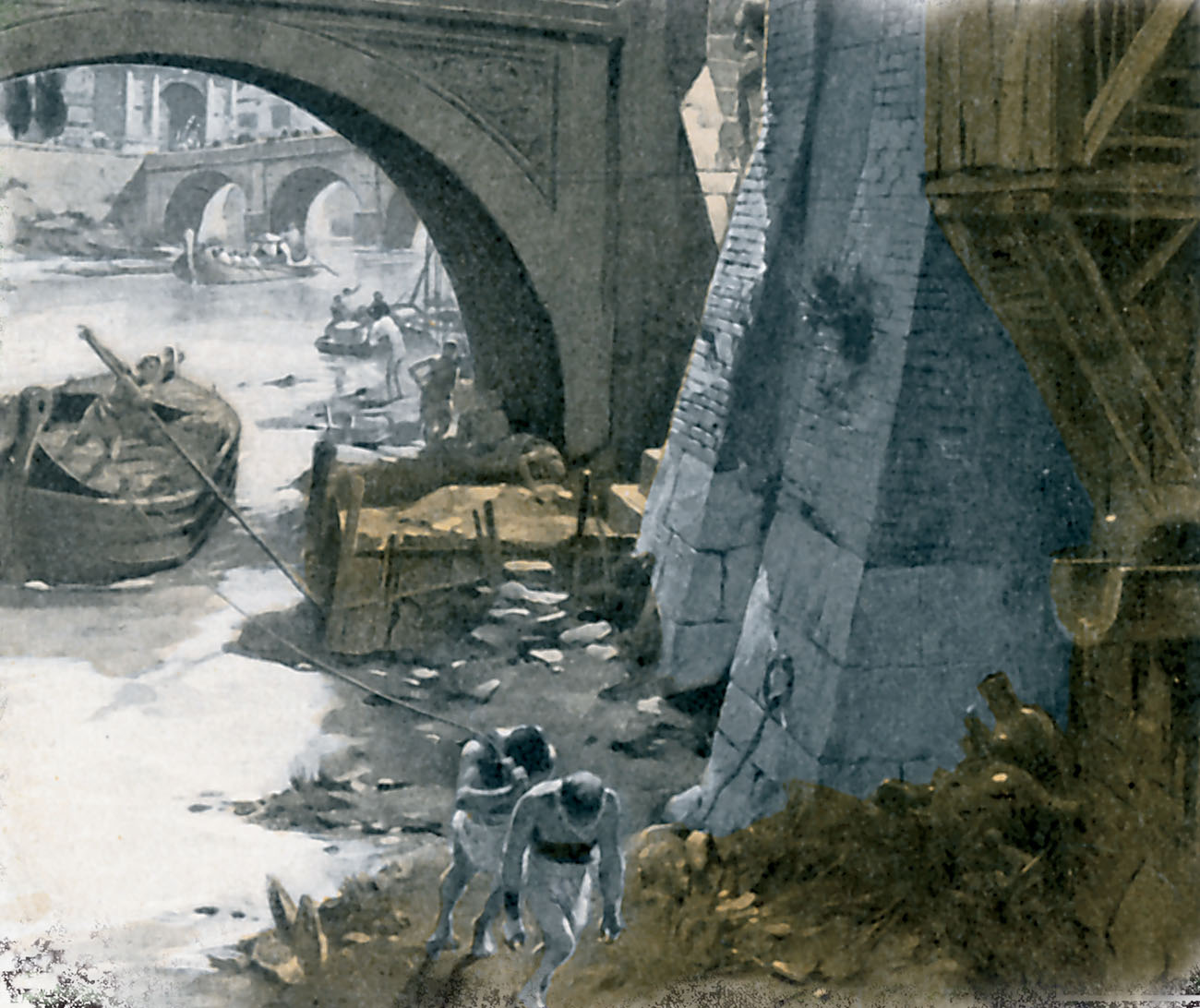
Romes sewers emptied into the nearby Tiber River. Rainwater was supposed to wash the waste from the sewers into the river. There were big openings on the street for people to dump waste into the sewers. The holes did nothing to hide the stench coming from them.
Few homes had toilets. Some people paid to use public toilets, which were set up over the sewers. Other people used chamber pots.
By law Romans were supposed to empty the chamber pots into a sewer drain. But some people lived in tall apartment buildings. They did not want to carry smelly pots down the many stairs to the drains. So they just emptied the pots out their windows. People passing by were sometimes showered in waste.
There were laws against throwing bodily fluids out the window. Because there were no streetlights, the laws were impossible to enforce at night.
The garbage and animal waste mixed together on the streets. Everyone walked in this slimy mess. Workers were hired by the city to keep the streets clean. But the sewage would always build up again.
The Tiber River was polluted with garbage and human waste.
FOUL FACT
Rome was a messy place. Citizens produced more than 110,000 pounds (50,000 kilograms) of solid waste every day.
Citizens and Slaves
In Rome there were free people and .
Although Roman women were citizens, they had fewer rights than men. Women could own property. But they could not vote or hold government offices. Women had male all their lives. The guardians were usually husbands or male relatives.
The wealthiest Roman citizens had power over the poor. Rich Romans bought and sold goods throughout the empire. They even bought and sold people.
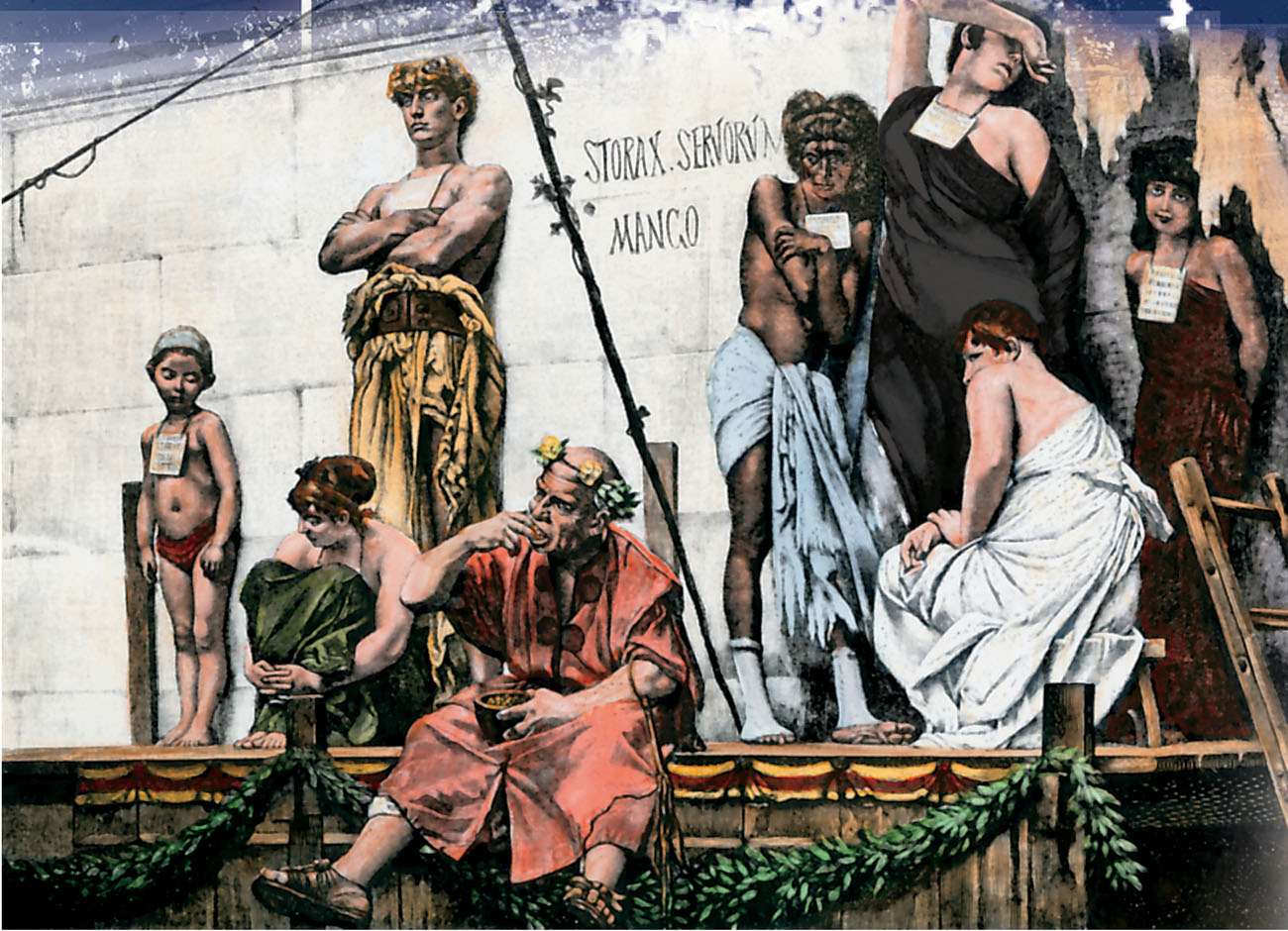
Thousands of slaves worked in and around Rome. Slaves were bought and sold at auctions. There they were stripped naked and kept in pens. This way, potential buyers could see for themselves that the slaves were healthy.
Some slaves were treated well. A few were paid, and some gained their freedom. But for most, life as a slave was horrible. Some slaves killed their babies at birth rather than allow them to become slaves.
White signs around the slaves neck told potential buyers everything they needed to know about the slave before buying.
Some owners branded or tattooed their slaves faces. Other slaves were bound with heavy neck chains or collars so they could not escape. Some slaves had to wear tags that showed their masters names.
There was nothing fair in the treatment of slaves. An owner could beat, torture, or kill a slave for any reason. One Roman broke the legs of a slave who annoyed him. A slave who killed his owner was put to death. But so were all the other slaves in the householdmen, women, and children.
Deadly Homes
After a long day at work, imagine coming home to find three people sleeping in your bed! It might seem crowded, but ancient Romans were used to it.
At one time, the city of Rome was home to more than 1 million people. Most Romans lived in apartment buildings above shops. The poorest people shared rooms on the highest stories. Some buildings were eight or nine stories high. These buildings were not safe. The first floor or two might be made of sturdy stone. But the higher stories were often made only of mud and wood. Many buildings fell under their own weight. Those unlucky enough to be in a collapsing building often died.