ICST Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering 2017
Leandros A. Maglaras , Helge Janicke and Kevin Jones (eds.) Industrial Networks and Intelligent Systems Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering 10.1007/978-3-319-52569-3_1
Spatial Keyword Query Processing in the Internet of Vehicles
Yanhong Li 1
(1)
College of Computer Science, South-Central University for Nationalities, Wuhan, China
(2)
Guangdong University of Petrochemical Technology, Maoming, China
(3)
School of Computer Science and Technology, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Rongbo Zhu (Corresponding author)
Email:
Abstract
This paper takes the first step to address the issue of processing Spatial Keyword Queries (SKQ) in the Internet of Vehicles (IoV) environment. As a key technique to obtain location-aware information, the Spatial Keyword Query (SKQ) is proposed. It can search qualified objects based on both keywords and location information. In the IoV, with the popularity of the GPS-enabled vehicle-mounted devices, location-based information is extensively available, and this also enables location-aware queries with special keywords to improve user experience. In this study, we focus on Boolean kNN Queries. And a Spatial Keyword query index for IoV environment (SKIV) is proposed as an important part of the algorithm design to be used to improve the performance of this type of SKQ. Extensive simulation is conducted to demonstrate the efficiency of the SKIV based query processing algorithm.
Keywords
Spatial keyword queries Internet of vehicles Wireless data broadcast
Introduction
The Internet of Vehicles (IoV) as a new emerging technology has caught widely attention, and has become a research hotspot [].
A spatial textual index is an important part in the SKQ processing [] augments an R-tree node with inverted lists. It has more powerful pruning ability since it combines R-tree and inverted lists to jointly prune the search space.
In this paper, we propose an algorithm for the spatial keyword query processing in the IoV environment, and we focus on Boolean kNN Queries.
The scientific contributions of this paper are summarized as follows:
The paper takes the first step to deal with SKQ in IoV. Specifically, we propose an index, SKIV, to deal with SKQ in IoV under wireless broadcast environments.
By using SKIV, an efficient algorithms is designed for Boolean kNN queries in the IoV environment.
Extensive simulations are conducted to evaluate the performance of the SKIV based query processing algorithm on a real road network in the IoV environment. The experimental results show that the proposed SKIV based method outperforms the Fixed Partition Based method (FPB) on tuning time and access latency.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section , we conclude this paper.
Related Work
Zhou et al. [] proposed an index structure called IR-tree which augments each node of the R-tree with an inverted file. Moreover, a variant of the IR-tree, the DIR-tree, was proposed to incorporate document similarity when computing Minimum Bounding Rectangles.
In [] discussed the issue of direction-aware spatial keyword query. Given a query with a location, a direction, and a set of keywords, it finds the k nearest neighbors of the query which are in the query direction and contain all the input keywords.
Jo
o et al. [] discussed reverse top-k Boolean spatial keyword query processing in road networks, and proposed filter-and-refinement frame work based algorithms for giving query result sets. To improve the query performance, several pruning heuristics and a data structure called count tree were proposed.
Wang et al. [] presented an air index called Network Partition Index (NPI) to support efficient spatial query processing in road networks on the air.
Definitions and Preliminaries
3.1 Definitions
In this study, we assume that each geo-textual object has a spatial location and a set of keywords, and we consider Boolean kNN queries in the IoV, under wireless broadcast environments. The frequently used symbols and their definitions are summarized in Table .
Table 1.
Symbols and definitions
Notation | Definition |
|---|
D | a set of points with keywords on a road network |
q | a spatial query point with a set of keywords |
| the network distance between two points p and 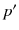 |
| the Euclidean distance between two points p and 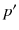 |
| the minimum network distance between regions 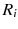 and 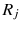 |
| the maximum network distance between regions 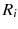 and 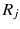 |
| the minimum Euclidean distance between regions 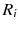 and 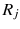 |
Dataset Setting. Let D be a set of geo-textual objects locating on the edges of a road network. Each geo-textual object
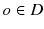
is defined as a tuple
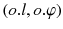
, where o . l is a spatial location and
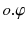












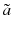 o et al. [] discussed reverse top-k Boolean spatial keyword query processing in road networks, and proposed filter-and-refinement frame work based algorithms for giving query result sets. To improve the query performance, several pruning heuristics and a data structure called count tree were proposed.
o et al. [] discussed reverse top-k Boolean spatial keyword query processing in road networks, and proposed filter-and-refinement frame work based algorithms for giving query result sets. To improve the query performance, several pruning heuristics and a data structure called count tree were proposed.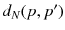
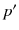
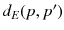
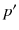
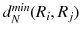
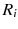 and
and 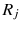
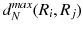
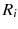 and
and 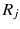
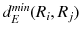
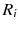 and
and 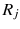
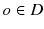 is defined as a tuple
is defined as a tuple 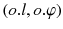 , where o . l is a spatial location and
, where o . l is a spatial location and