Information and Computer Engineering
Volume
Data structures and algorithms analysis New perspectives
Edited by
Xingni Zhou
Volume
ISBN 9783110676051
e-ISBN (PDF) 9783110676075
e-ISBN (EPUB) 9783110676167
Bibliographic information published by the Deutsche Nationalbibliothek
The Deutsche Nationalbibliothek lists this publication in the Deutsche Nationalbibliografie; detailed bibliographic data are available on the Internet at http://dnb.dnb.de.
2020 Walter de Gruyter GmbH, Berlin/Boston
Nonlinear structure with layered logical relations between nodes tree
Main Contents
The definition of tree and basic terminologies
The concept of binary tree and its storage structure
The traversal of binary tree
Huffman tree and its applications
The concept, storage structure and basic operations of lists
Learning Aims
Comprehend the transition from linear structure to nonlinear structure of the logical structure of data
Comprehend linear structures that contain child structure
Understand the functionality of linked storage structure in expressing nonlinear data structures
Comprehend the concept, storage method and basic operations on trees
Understand the concept, structural characteristics and storage/representation methods of lists
1.1 Tree in actual problems
1.1.1 Introductory example to tree 1 tree-like structures in our daily life
If we enter a huge library, and want to find a reference book for data structures, how can we find it facing several floors, multiple rooms, rows of bookshelves and tens of thousands of books? The first thing before we search for it should be to understand the classification and layout rules of books in the library. After we know the representational methods of the classification of books, we can easily find the needed books in the library, and it will be very convenient for the librarian to uniformly manage the books. shows partial classifications about computer according to the library classification method of China.
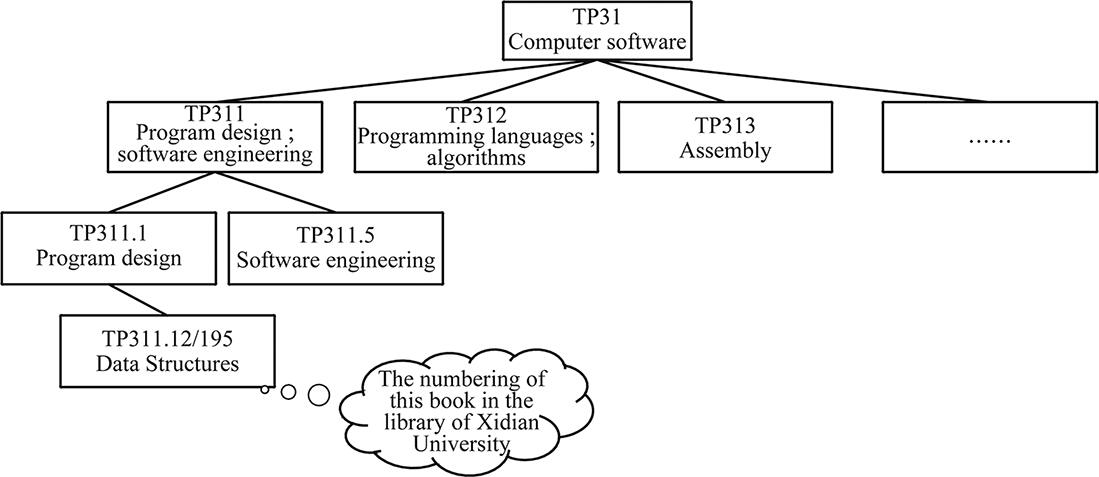
Fig. 1.1: Classification structure of books.
Observe the classification structure of . It looks very much like a reversed tree in nature, that is, the point at the top is the root, while the points at the bottom ends are leaves. Therefore, we call it as tree structure, and abbreviate it as tree.
Tree-like structures are very common in our daily life. Examples include genealogy records, organizational structures and match results of a tournament. They are all structures produced after a certain classification of information.
1.1.2 Introductory example of tree 2 the directory structure of computer
Everyone who has used computers is familiar with the directory structure of files. This is also a classification structure, as shown in . In this directory hierarchy, we can see that it is a leveled (layered) structure. For the computer to manage such directories, what are the potential problems involved?
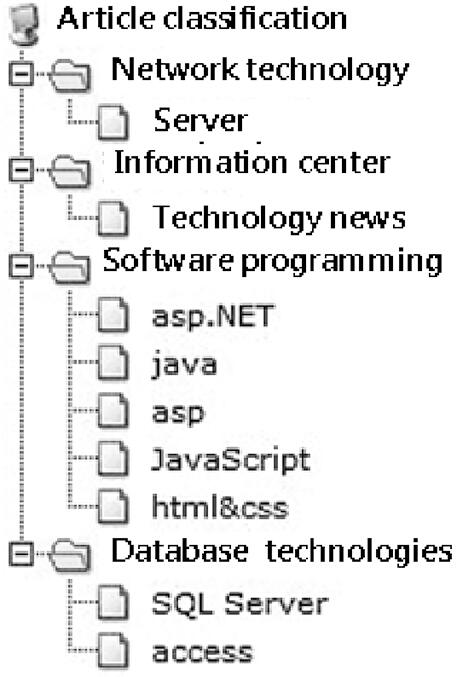
Fig. 1.2: Computer file directories.
According to our general concepts about directory management of computers, the operations include searching, adding files and deleting files. To realize such operations, the first thing to do is to store the folder information and the connections between layers into the machine, only then can it process them according to the .
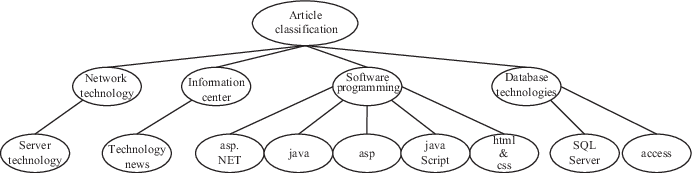
Fig. 1.3: The abstraction of directory structure.
Since the relation between nodes is not only one of predecessors and successors, tree structure is a nonlinear structure.
1.1.3 Introductory example of tree 3 tree-structured website
The connection between various pages within a website also forms a web-like structure. Such a web-like structure can take on multiple forms. The tree-like web structure with clearly defined layers is shown in . Website structure considered ideal from the perspective of search engine optimization is a tree structure, where each page is only directly linked to the page one layer above. In this manner, users can quickly navigate to channels and articles they are interested in. The search engine can also understand the structure and layers of the website better and thus better crawl the contents, which is conducive to increasing the ranking of the website and bringing in more visitors, eventually augmenting the sales or marketing effect of the website.
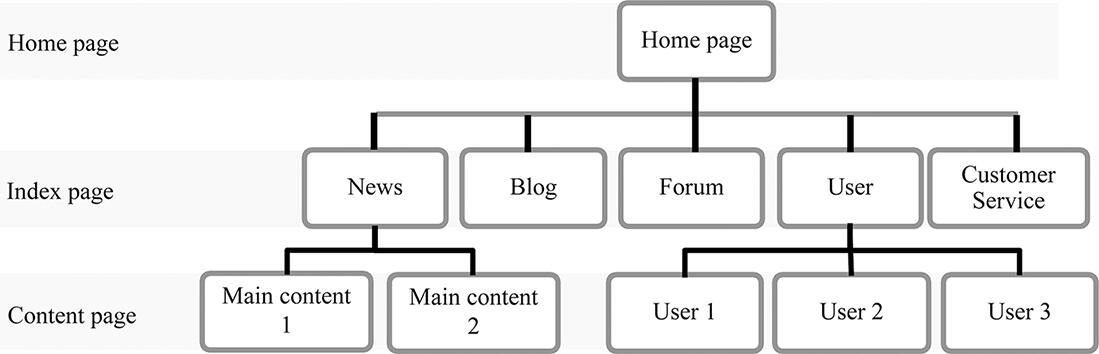
Fig. 1.4: Website with tree structure.
. Corresponding mathematical expressions can be obtained by different search strategies. In database systems, tree structure is also an important form of information organization. Besides, there are decision trees used for the classification and prediction in data mining.
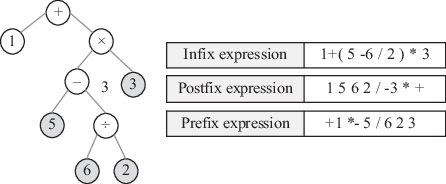
Fig. 1.5: Expression tree.
Generally, tree is very widely applied in various fields of computer science. All problems with layered relation can be described using trees.
1.2 Logical structure of tree
From the previous introductory examples, we can see that when the relation between data elements is not one-to-one correspondence, but one-to-many correspondence. After the correspondence relation gets more complicated, linear structure does not suffice to conveniently describe such complex scenarios. We need other methods that fit the features of tree structure to describe such nonlinear structures with layered relations.
1.2.1 The definition and basic terminologies of tree
1.2.1.1 The definition of tree
Tree is a finite collection with n nodes, among which:
One specific node is called root node or root. It only has immediate successors, but has no immediate predecessors.
Data elements other than the root node are divided into m (m 0) nonintersecting collections T1, T2,, Tm, among which each collection Ti(1 im) itself is also a tree, called a subtree of the root.
When the collection of trees is empty, n = 0. In this case, it is called empty tree. An empty tree has no nodes.
Tree is a recursive structure in the definition of tree we use the definition of tree again: a nonempty tree constitutes several subtrees, and child trees can constitute several even smaller subtrees.
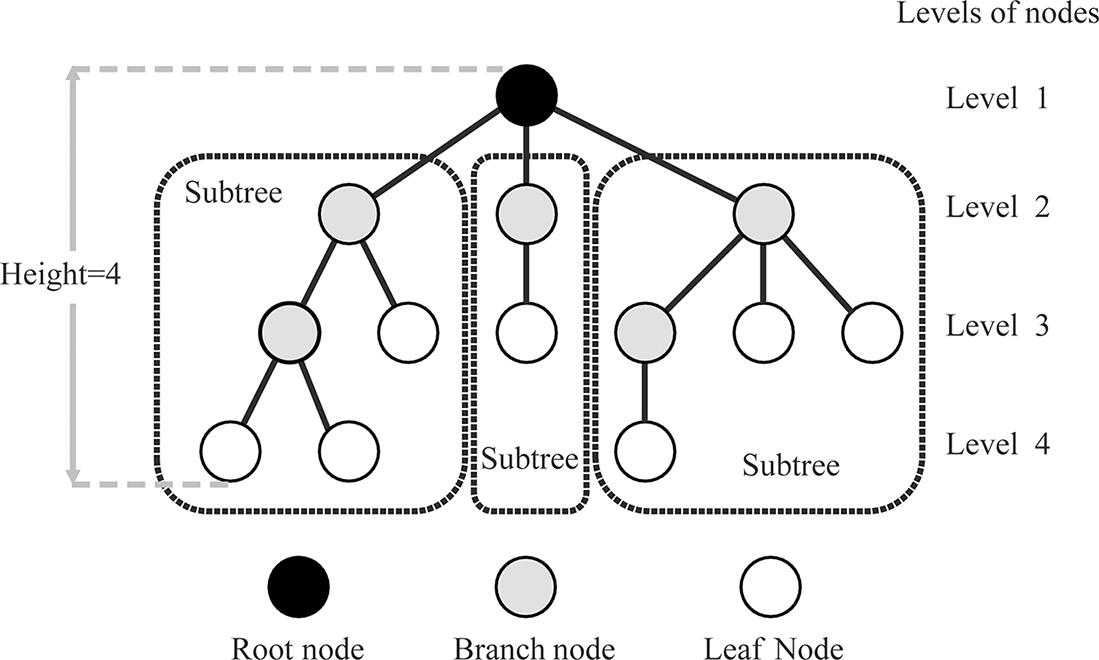
Tree has the following characteristics, as shown in .