Solidity Smart Contracts
Build DApps In The Ethereum Blockchain
Introduction
I want to thank you and congratulate you for getting this book, Solidity Smart Contracts: Build Dapps in the Ethereum Blockchai n .
This book contains proven steps and strategies on how to become a master in solidity, smart contract creation and Ethereum blockchain development.
Hello and welcome to our course about smart contracts with Solidity.
In order to be able to start making your own smart contracts first, we need to take a step back and go through some of the most essential aspects of the Ethereum blockchain.
We will start with a little history about what exactly is the Ethereum blockchain and its part in this fast-growing global evolution in technology.
In order to understand the whole system and how to make our smart contract the best way possible with as fewer functionality costs, we need to go through the mechanics of the Ethereum blockchain.
I ll show you how to make your first wallet, how to manage it and from there w e ll move on to a little cryptography, block analysis and gas prices.
Things might look a bit overwhelming at first but once you get the hang of it yo u ll appreciate that knowledge when we get to the coding part.
Every developer that makes smart contracts needs to have access to the test net network on which we will deploy our contracts. In order to do that we have to make a test net account alongside our main net one and most importantly we have to get some test net ether to work with.
I will show you a couple of easy ways to get as much ether as you might need, in your le t s call it journey, into creating smart contracts with solidity.
W e ll take a look at some block transactions and graph explanations. Some free to use but extremely helpful websites to help you track the blockchain network and much, much more.
Thanks again for buying this book, I hope you enjoy it!
Copyright 2019 by Unibul Press Ltd. - All rights reserved.
This document is geared towards providing exact and reliable information in regards to the topic and issue covered. The publication is sold with the idea that the publisher is not required to render accounting, officially permitted, or otherwise, qualified services. If advice is necessary, legal or professional, a practiced individual in the profession should be ordered.
- From a Declaration of Principles which was accepted and approved equally by a Committee of the American Bar Association and a Committee of Publishers and Associations.
In no way is it legal to reproduce, duplicate, or transmit any part of this document in either electronic means or in printed format. Recording of this publication is strictly prohibited and any storage of this document is not allowed unless with written permission from the publisher. All rights reserved.
The information provided herein is stated to be truthful and consistent, in that any liability, in terms of inattention or otherwise, by any usage or abuse of any policies, processes, or directions contained within is the solitary and utter responsibility of the recipient reader. Under no circumstances will any legal responsibility or blame be held against the publisher for any reparation, damages, or monetary loss due to the information herein, either directly or indirectly.
Respective authors own all copyrights not held by the publisher.
The information herein is offered for informational purposes solely, and is universal as so. The presentation of the information is without contract or any type of guarantee assurance.
The trademarks that are used are without any consent, and the publication of the trademark is without permission or backing by the trademark owner. All trademarks and brands within this book are for clarifying purposes only and are the owned by the owners themselves, not affiliated with this document.
What Is The Ethereum Blockchain?
In this first chapter, w e re going to talk about the Ethereum blockchain and what it actually is.
During the past couple of years ther e s not many people that have n t heard at least a little about Bitcoins, Ethereum or the blockchain technology.
All the buzz generated by the media has led the industry to a giant leap and the best is yet to come.
I ll try to keep things as simple as possible and I wo n t go into non-essential stuff that might get you confused.
Ethereum by definition is an open-source public service that uses blockchain technology to aid smart contracts and cryptocurrency trading securely without a third party.
Ethereum offers two types of accounts: externally owned - those are the public accounts to which we own our private keys. Second ones are the contract accounts. Those are the accounts on which Ethereum developers deploy all kinds of smart contracts.
The Ethereum blockchain remains the biggest smart contract ecosystem being home to numerous alt coins and apps.
With its fast growing community and potential, a lot of big companies like JP Morgan, Intel and Microsoft are getting involved into the smart contract business and decentralized services.
Now w e ll talk a little about the currency behind the Ethereum blockchain or the so-called ether.
That is the currency that w e re going to use in our smart contract development with Solidity and it is the main currency that sponsors most of the ICOs.
By most predictions, it is expected that at some point in the not so far future it will even beat Bitcoin in market cap.
Being able to make your own smart contract not only gives you the ability to start a career in this fast growing industry, but it allows you to make your own DApp.
Some of the most famous ones are Crypto Kitties and IDEX.
The general idea, which the founder of Ethereum - Vitalik Buterin - had, was that the blockchain technology could do way beyond just payment transactions. So, at the age of 19 he released a white paper describing what would ultimately become Ethereum using a general scripting language.
The key difference from the mother coin - Bitcoin - was the platfor m s ability to trade more than just cryptocurrency.
Some of you migh t ve heard about projects like Crypto Kitties, decentralized chats and all sort of other apps.
The thing i s blockchain technology is still evolving but everyone that has any interaction with it sees it is potential. The security behind every transaction is impenetrable because of the blockchain consensus algorithm.
In the next video I m going to show you what blocks are, how are they generated and I ll show you the mechanics behind every operation that is being sent through the blockchain.
At last, w e ll take a look at the current state of the blockchain, the problems that it faces and possible solutions.
Get FREE Video Lessons on Solidity at
codingsrc.com/solidity
Going More In Debth
In this chapter, w e re going to talk about some technical but necessary things in the blockchain. Do n t be scare d I ll keep things as simple as possible.
I am going to open a webpage called etherscan.io
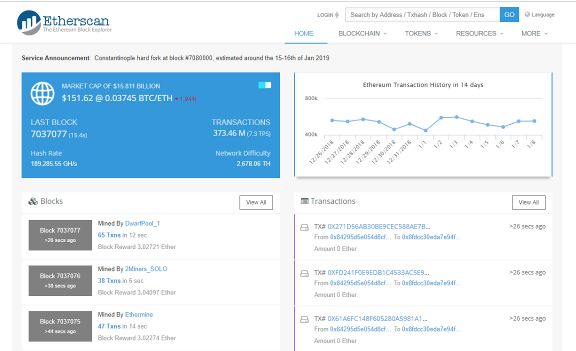
In this website, we can pretty much see every relevant statistic that we might need in order to track the blockchain movement.
First let us talk about how exactly information is being transmitted and stored on the blockchain.
If you have ever owned any kind of cryptocurrency, you would know that you have to pay some sort of transaction fee in order to send your money to someone else. That is not the same kind of fee that banks charge us when we make bank transfers but it is a fee to network itself.
Look at it this wa y . When you hit sen d , your transaction goes into a pool of other transactions that are waiting to be transmitted and validated by the network. And that validation, at least in the Ethereum blockchain, is being made by the so-called miners.
Next page






![Debajani Mohanty [Debajani Mohanty] - Ethereum for Architects and Developers: With Case Studies and Code Samples in Solidity](/uploads/posts/book/119695/thumbs/debajani-mohanty-debajani-mohanty-ethereum-for.jpg)
![Chris Dannen [Chris Dannen] - Introducing Ethereum and Solidity: Foundations of Cryptocurrency and Blockchain Programming for Beginners](/uploads/posts/book/119690/thumbs/chris-dannen-chris-dannen-introducing-ethereum.jpg)
![Fatima Castiglione Maldonado [Fatima Castiglione Maldonado] - Introduction to Blockchain and Ethereum](/uploads/posts/book/119687/thumbs/fatima-castiglione-maldonado-fatima-castiglione.jpg)
