Joyce Kay Avila - Snowflake: The Definitive Guide
Here you can read online Joyce Kay Avila - Snowflake: The Definitive Guide full text of the book (entire story) in english for free. Download pdf and epub, get meaning, cover and reviews about this ebook. year: 2022, publisher: OReilly Media, Inc., genre: Home and family. Description of the work, (preface) as well as reviews are available. Best literature library LitArk.com created for fans of good reading and offers a wide selection of genres:
Romance novel
Science fiction
Adventure
Detective
Science
History
Home and family
Prose
Art
Politics
Computer
Non-fiction
Religion
Business
Children
Humor
Choose a favorite category and find really read worthwhile books. Enjoy immersion in the world of imagination, feel the emotions of the characters or learn something new for yourself, make an fascinating discovery.
- Book:Snowflake: The Definitive Guide
- Author:
- Publisher:OReilly Media, Inc.
- Genre:
- Year:2022
- Rating:4 / 5
- Favourites:Add to favourites
- Your mark:
- 80
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Snowflake: The Definitive Guide: summary, description and annotation
We offer to read an annotation, description, summary or preface (depends on what the author of the book "Snowflake: The Definitive Guide" wrote himself). If you haven't found the necessary information about the book — write in the comments, we will try to find it.
Snowflake: The Definitive Guide — read online for free the complete book (whole text) full work
Below is the text of the book, divided by pages. System saving the place of the last page read, allows you to conveniently read the book "Snowflake: The Definitive Guide" online for free, without having to search again every time where you left off. Put a bookmark, and you can go to the page where you finished reading at any time.
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:

by Joyce Kay Avila
Copyright 2022 Joyce Kay Avila. All rights reserved.
Printed in the United States of America.
Published by OReilly Media, Inc. , 1005 Gravenstein Highway North, Sebastopol, CA 95472.
OReilly books may be purchased for educational, business, or sales promotional use. Online editions are also available for most titles (http://oreilly.com). For more information, contact our corporate/institutional sales department: 800-998-9938 or corporate@oreilly.com .
- Acquisitions Editor: Jessica Haberman
- Development Editor: Michele Cronin
- Production Editor:
- Copyeditor:
- Proofreader:
- Indexer:
- Interior Designer: David Futato
- Cover Designer: Karen Montgomery
- Illustrator:
- September 2022: First Edition
- 2021-08-04: First Release
See http://oreilly.com/catalog/errata.csp?isbn=9781098103828 for release details.
The OReilly logo is a registered trademark of OReilly Media, Inc. Snowflake: The Definitive Guide, the cover image, and related trade dress are trademarks of OReilly Media, Inc.
The views expressed in this work are those of the author, and do not represent the publishers views. While the publisher and the author have used good faith efforts to ensure that the information and instructions contained in this work are accurate, the publisher and the author disclaim all responsibility for errors or omissions, including without limitation responsibility for damages resulting from the use of or reliance on this work. Use of the information and instructions contained in this work is at your own risk. If any code samples or other technology this work contains or describes is subject to open source licenses or the intellectual property rights of others, it is your responsibility to ensure that your use thereof complies with such licenses and/or rights.
978-1-098-10382-8
[LSI]
With Early Release ebooks, you get books in their earliest formthe authors raw and unedited content as they writeso you can take advantage of these technologies long before the official release of these titles.
This will be the 2nd chapter of the final book.
If you have comments about how we might improve the content and/or examples in this book, or if you notice missing material within this chapter, please reach out to the editor at mcronin@oreilly.com.
In the last decade, computer data storage and computer performance had to evolve. Teams, both large and small, near or far apart, often need access to the same data at the same time. Having access to that data and the ability to generate actionable insights quickly is now an absolutely must. Just from the sheer amount and complexity of todays data, data warehouses had to evolve into incredibly data-intensive applications. Yet, as well discover in the next section, simply making modifications to existing data warehouse architectures did not solve the scalability problem. Then, Snowflake burst onto the scene with a unique architecture.
The Snowflake Data Cloud is an evolutionary modern data warehouse that solved the scalability problem. Compared to traditional cloud data warehouse architectures, Snowflake enables data storage and processing that is significantly faster and easier to use and is much more affordable. Snowflakes Data Cloud provides users with a unique experience by combining a new SQL query engine with an innovative architecture that was designed and built from the ground up and specifically for the cloud.
In this section, well briefly review some traditional data warehouse architectures and approaches that were designed to improve scalability. Scalability is the ability of a system to handle an increasing amount of work. Well also discuss the limitations of these data warehouse architectures. Then, we will discover what makes the Snowflake Data Cloud architecture so unique. Afterward, we will learn about each of the three different Snowflake architecture layers in detail: Cloud Services Layer, Query Processing (Virtual Warehouse) Compute Layer, and the Centralized (Hybrid-Columnar) Database Storage Layer.
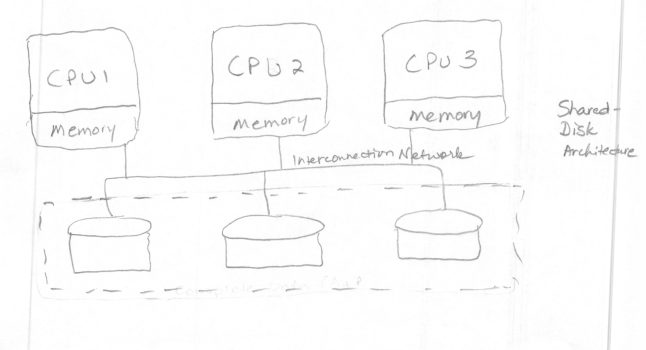
The shared-disk architecture was an early scaling approach designed to keep data stored in a central storage location, accessible from multiple database cluster nodes (). The data accessed by each of the cluster nodes is consistently available because all data modifications are written to the shared disk. This architecture is a traditional database design and is known for the simplicity of its data management. While the approach is simple in theory, it requires complex on-disk locking mechanisms to ensure data consistency. Additionally, concurrency is a major problem and adding more compute nodes only compounds the problem. Therefore, the true scalability of this architecture is limited.
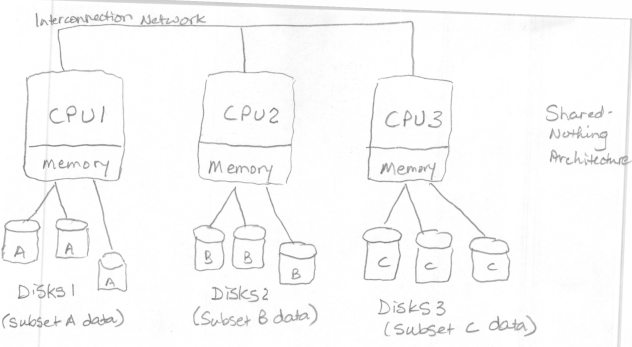
The shared-nothing architecture, in which processing and compute is scaled together (Figure 2-2), was designed in response to the bottleneck created by the shared-disk architecture. This evolution in architecture was made possible because storage had become relatively inexpensive. However, distributed cluster nodes along with the associated disk storage, CPU, and memory, requires data to be shuffled between nodes, which adds overhead. Depending on how the data is distributed across the nodes will determine the extent of the additional overhead. Striking the right balance between storage and compute is especially difficult. Even when it is possible to resize a cluster, it takes time to do so. Thus, organizations often overprovision shared-nothing resources, which results in unused, unneeded resources.
Most NOSQL solutions rely on shared-nothing architecture; thus, they have many of the same limitations. However, the benefit of NoSQL solutions is that they can store non-relational data without first requiring transformation of the data. Additionally, most NoSQL systems dont require schemas. NoSQL, a term that implies Not Only SQL rather than NO to SQL, is a good choice for storing e-mail, web links, social media posts and tweets, road maps, and spatial data.
There are four types of NoSQL databases. Document-based NoSQL databases such as MongoDB store data in JSON objects where each document has key-value pair like structures. Key-value databases such as DynamoDB are especially useful for capturing customer behavior in a specific session. Cassandra is an example of a column-based database where large numbers of dynamic columns are logically grouped into column families. Graph-based databases, such as Neo4j and Amazon Neptune, work well for recommendation engines and social networks where they are able to help find patterns or relationships among data points.
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
Similar books «Snowflake: The Definitive Guide»
Look at similar books to Snowflake: The Definitive Guide. We have selected literature similar in name and meaning in the hope of providing readers with more options to find new, interesting, not yet read works.
Discussion, reviews of the book Snowflake: The Definitive Guide and just readers' own opinions. Leave your comments, write what you think about the work, its meaning or the main characters. Specify what exactly you liked and what you didn't like, and why you think so.













