
For my niece, Emi, and my father, Eugene
Published in 2022 by The Rosen Publishing Group, Inc.
29 East 21st Street, New York, NY 10010
Copyright 2022 by The Rosen Publishing Group, Inc.
First Edition
Designer: Rachel Rising
Editor: Greg Roza
Portions of this work were originally authored by Leslie Green and Pat Kelly and published as I Have Diabetes. Now What? All new material in this edition authored by Henrietta Toth.
All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced in any form
without permission in writing from the publisher, except by a reviewer.
Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data
Names: Toth, Henrietta.
Title: I have diabeteswhats next? / Henrietta Toth.
Description: New York: Rosen Publishing, 2022. | Series:
Getting real: strategies for teens in need
Identifiers: ISBN 9781499470710 (pbk.) | ISBN 9781499470727
(library bound) | ISBN 9781499470734 (ebook)
Subjects: LCSH: Diabetes--Juvenile literature. |
Diabetes in adolescence--Juvenile literature.
Classification: LCC RC660.4 T67 2022 | DDC 616.462--dc23
Some of the images in this book illustrate individuals who are
models. The depictions do not imply actual situations or events.
Manufactured in the United States of America
Find us on 
CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION
Diabetes is a chronic, but noncontagious disease that requires lifelong management. It occurs when the levels of glucose, or sugar, in your blood are too high. Glucose is the primary source of energy and the main fuel for the brain and is derived from food. Glucose is transported to our cells by insulin, a hormone thats produced by the pancreas. The pancreas is a small organ that sits behind the stomach. If the pancreas doesnt make enough or any insulin, then the glucose stays in the blood instead of reaching the cells to supply energy.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), more than 34 million people, or more than 10 percent of the American population, have diabetes. Nearly 27 million Americans have been diagnosed with diabetes, while more than 7 million dont know they even have the disease. The International Diabetes Federation (IDF) reports that worldwide, about 463 million adults have diabetes and this number could rise to 700 million by 2045. More than 1.1 million children and young adults across the globe have type 1 diabetes.
There are different types of diabetes. The two most common forms are called type 1 diabetes (T1D) and type 2 diabetes (T2D). In type 1 diabetes, the pancreas doesnt make any insulin so insulin must be administered each day by a needle injection or by a wearable pump. This insulin helps to convert the food you eat into energy to survive. Type 1 diabetes more often affects young people, but it can be diagnosed at any age. In type 2 diabetes, the body may still make some or not enough insulin, but it cant use it properly so medication is needed. This more common type of diabetes often affects older adults, but it also can be diagnosed in children and young adults. People who have a family history of diabetes, are overweight, or are not physically active may be more prone to developing type 2 diabetes. A condition called prediabetes can lead to type 2 diabetes. Eighty-eight million Americans have prediabetes.
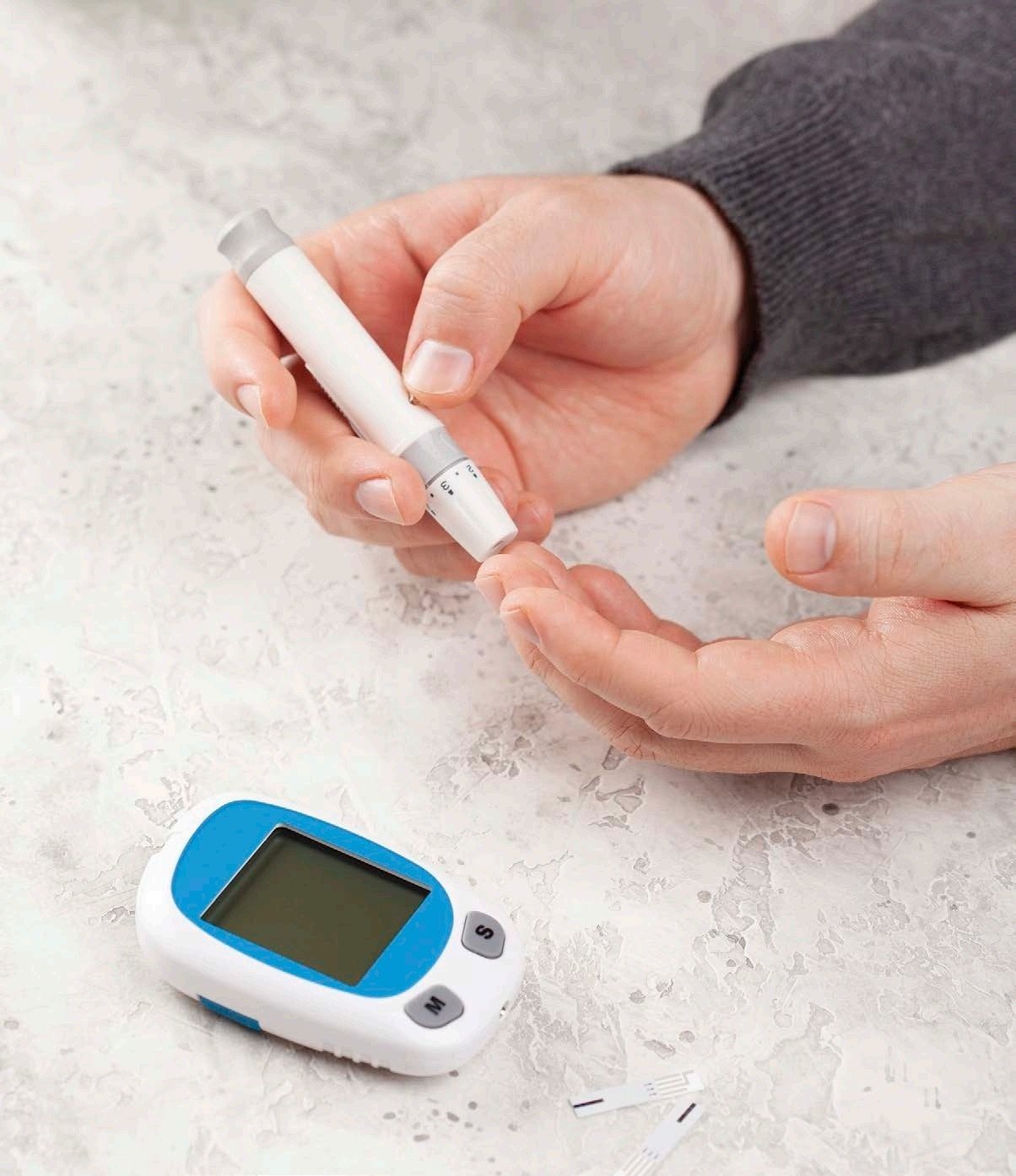

This glucose monitor uses test strips to measure the level of glucose, or sugar, in a drop of blood.
Having diabetes requires some adjustment and changes in lifestyle. You must test your blood glucose level several times a day, especially before eating and exercising. You also must monitor your food intake so you know how much insulin you need. Youll learn about the equipment and supplies required to measure your blood glucose levels and how to give yourself insulin. These can include a glucose monitor with test strips or a newer technology called a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) that gives you readings of your blood glucose levels. Insulin can be delivered by an injection or from a wearable insulin pump.
Currently, theres no cure for diabetes. Therefore, its important to keep blood glucose numbers in range and use insulin and other medications as prescribed in order to stay healthy with diabetes. Uncontrolled high levels of glucose or blood sugar can eventually lead to health problems, such as diseases of the eyes, heart, and kidneys, nerve damage, and even death. Diabetics can live successfully with the disease and reach their life goals through daily management of their diabetes at school, at work, on sick days, when playing sports or being physically active, and when traveling. Advances in the management of diabetes have made it easier to live with the disease, and research in better ways to manage it continues.
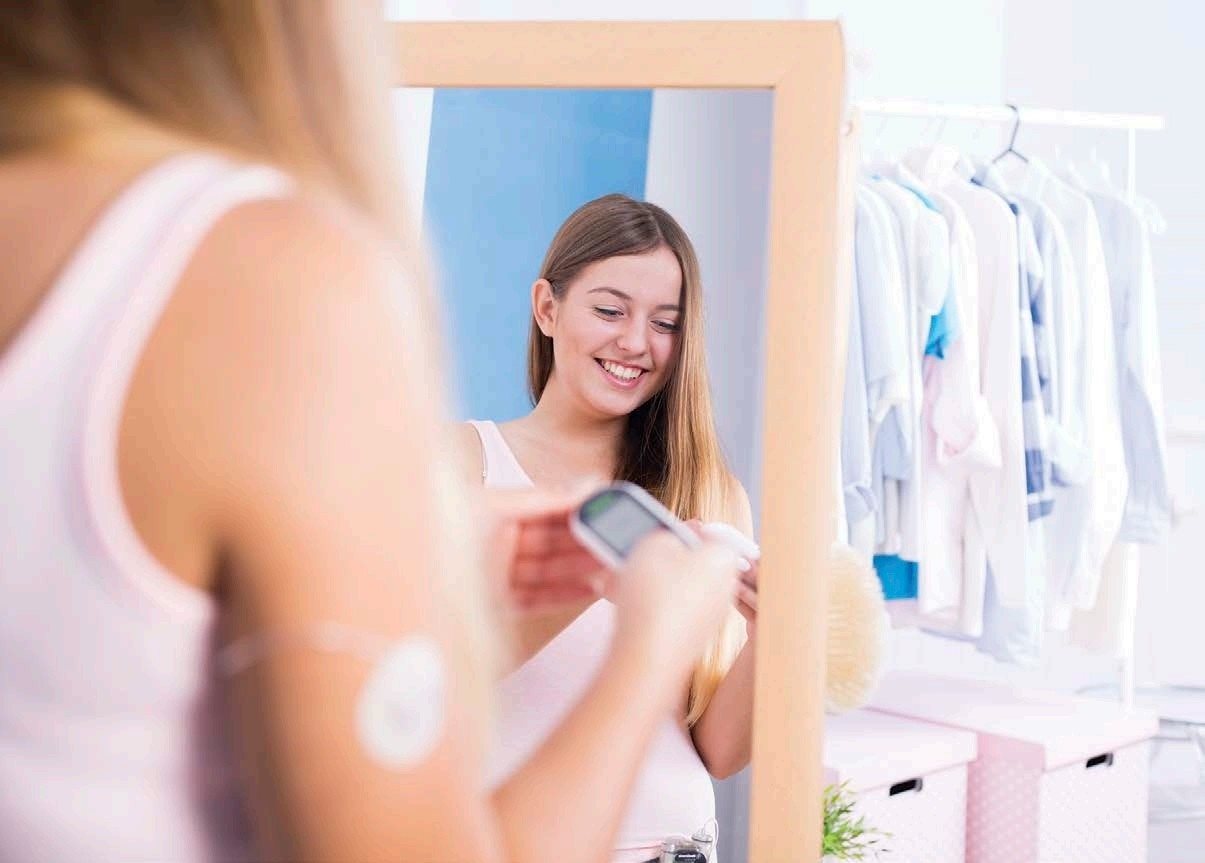

Managing diabetes may seem like a lot of work, but newer technology has made it easier than ever to monitor and regularly test your blood glucose levels.
CHAPTER 1
DEFINING DIABETES
According to the American Diabetes Association, there are about 1.5 million new cases of diabetes diagnosed each year. These new cases include about 24,000 young people diagnosed with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Having diabetes raises many questions: What is diabetes and how did I get it? What kinds of diabetes are there? Understanding what diabetes is can help patients to better manage their disease.

Diabetes affects many different parts of the body, including the heart.
THE CAUSES OF DIABETES
The bodys immune system plays an important role in the development of diabetes. When functioning properly, the immune system protects the body from foreign substances, such as viruses and bacteria, which may enter it. However, the immune system of a person with diabetes seeks out the cells that produce insulin in the pancreas and destroys them. This causes the body to stop producing insulin either partially or completely. Without the presence of insulin in the body, diabetes develops.
Heredity also plays a role in determining who will develop diabetes, especially type 2 diabetes. A person is at a higher risk for developing diabetes if someone in his or her family has or had the disease.
THE PANCREAS
The pancreas is a long, thin organ located behind the stomach, next to the upper intestine. The pancreas is made up of two different kinds of tissue: exocrine and endocrine. The exocrine tissues make up the main part of the pancreas and produce enzymes used in digestion. The endocrine cells are scattered in clumps throughout the pancreas. These are called the islets of Langerhans. These islets are made of three different types of cells and each produce a different hormone used in the body. The alpha cells secrete glucagon, the beta cells produce the protein insulin, and the delta cells produce the hormone somatostatin.
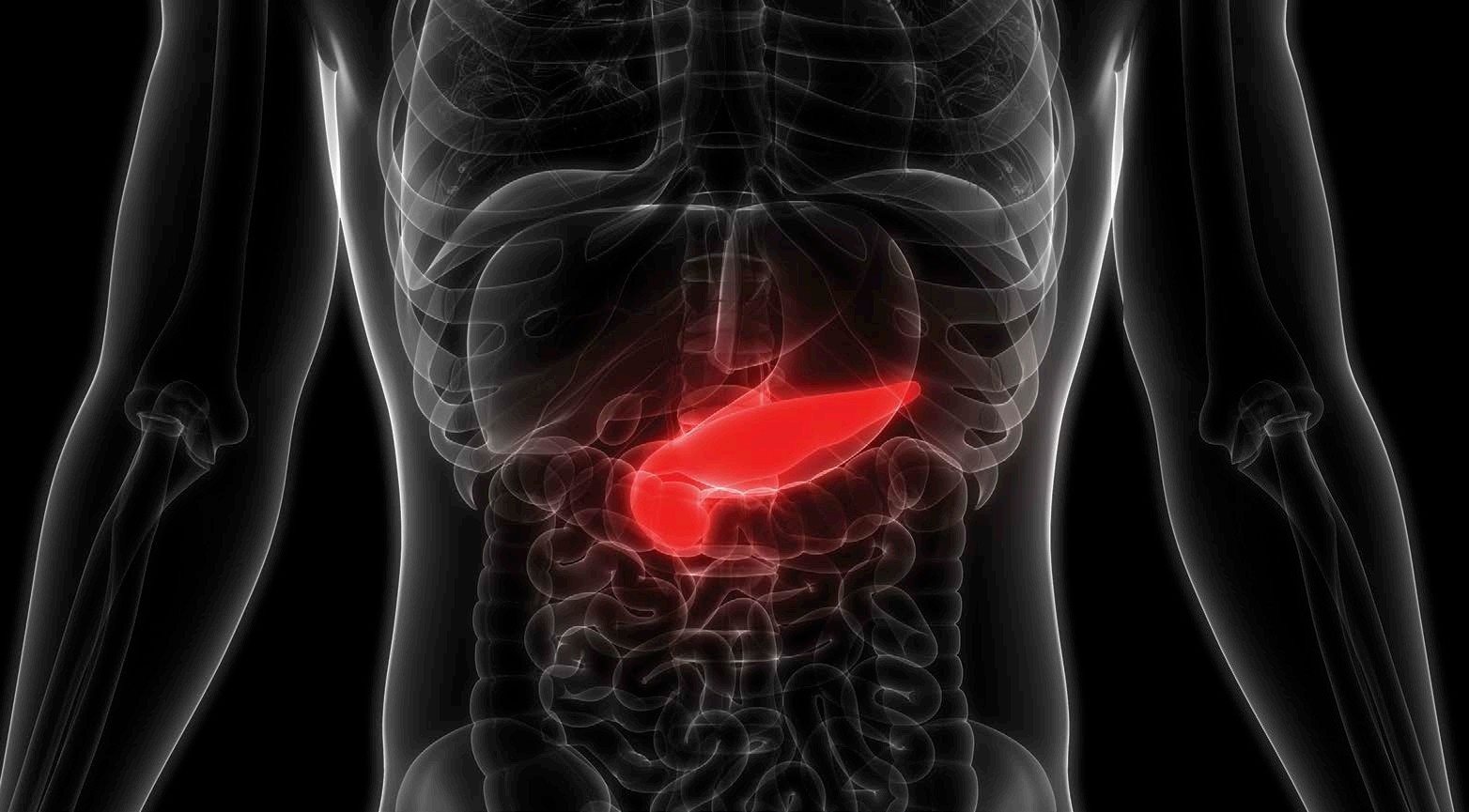
The pancreas, shown here in red, is located behind the stomach. It is about the same size as your hand.
Next page



















