Table of Contents
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
I wish to thank Sam Hudson, London, for his unfailing advice on matters of substance and style. I also wish to thank the rector and staff at the Wissenschaftskolleg zu Berlin (Institute for Advanced Study) for the most generous hospitality during a sabbatical in the academic year 19992000, providing inspiration, good company, and an environment of intellectual challenge. At the Friedrich AlexanderUniversity of Erlangen, Institut fr Geschichte, Monika Frielinghaus and Markus Freidrich provided much welcome help, from library services to advice on how to make computers conform to authors wishes.
Modern Library Chronicles

MAPS
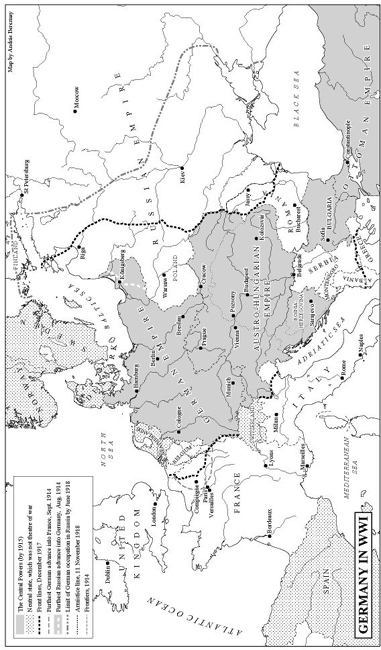
CHRONOLOGY
Please note that some dates are approximate or speculative.
184849 Social and political revolutions throughout most of continental Europe. The German parliament convenes in Frankfurts Paulskirche under pressure from the radical left as much as from the old guard. After the parliament adopts the Little-Germany concept (a nation-state excluding Austria), the Prussian king refuses the Imperial crown offered by the Frankfurt parliament. The liberal and democratic constitution drawn up there is never put into practice.
1852 Napoleon III becomes Emperor of France after a coup dtat.
185456 Crimean War. Great Britain, France and Piedmont-Sardinia go to war against Russia in the Crimean Peninsula to preserve the Ottoman Empire. Prussia is neutral, but pro-Russian. Peace of Paris. Russia surrenders her claim on the Ottoman Empire.
1859 Piedmont-Sardinia, supported by France under Napoleon III, goes to war against Austria. Prussia, Russia and Great Britain are neutral. The Prussian army is mobilized to put pressure on Austria.
186165 American Civil War. France sends troops to Mexico.
1862 William I makes Otto von Bismarck Prime Minister of Prussia.
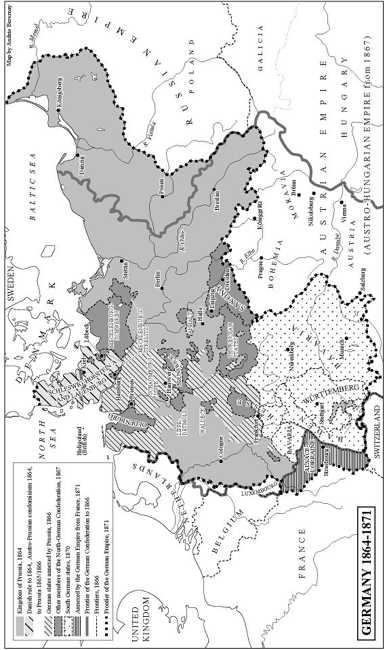
1864 FebruaryAugust: Prussia and Austria at war with the Kingdom of Denmark over national self-determination for the largely German-speaking provinces of Schleswig and Holstein. Condominium between Vienna and Berlin collapses. A promised referendum never takes place. After 1866 Schleswig-Holstein annexed by Prussia.
1866 April: Bismarck concludes a military alliance with Italy to prepare for war against Austria. JuneAugust: the German War between Prussia and Austria and the majority of the states of the German Confederation. Italy, on the side of Prussia, wins Lombardo-Venetia. After the battle of Kniggrtz an armistice and preliminary peace are made at Nikolsburg. After the Peace of Prague the electorate of Hesse, the Grand Duchy of Nassau, the Free City of Frankfurt and the Kingdom of Hanover are annexed by Prussia.
1867 The North German Confederation is founded under Prussian hegemony. The constitution provides for democratic elections and a liberal parliament, but control of the administration and the army remain firmly in the hands of the presidium, i.e., the King of Prussia. Bismarck becomes Prime Minister, foreign minister and chancellor.
186768 The Customs Union, comprising both northern and southern states, acquires a parliament and passes the liberal Gewerbeordnung (trading regulation), setting free market forces. The four German states south of the river Main are linked to Prussia through military integration. There is popular resentment in the south against Prussian domination.
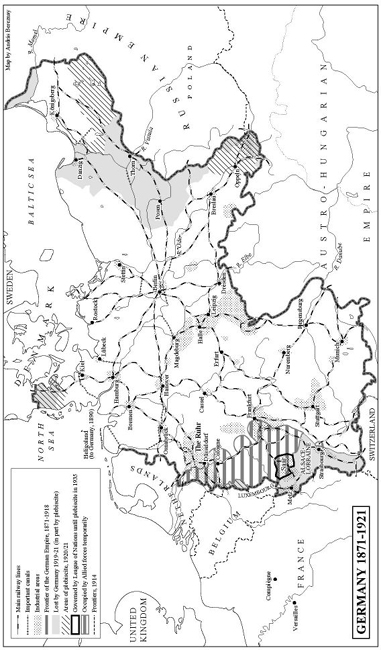
187071 The Spanish Parliament offers the crown to a Prince from the Catholic, South German line of the Hohenzollern. King William of Prussia declines the offer, but Bismarck uses this to create a storm of French public opinion against Prussia and Napoleon III finds himself forced into war with Prussia and, by implication, the whole of Germany. After the surrender of the Imperial army, war is fought and lost by the Third French Republic. Uprising of the Commune of Paris. January 1871: King William I of Prussia proclaimed German Emperor at Versailles.
May 1871: the Frankfurt Peace Treaty takes Alsace and Lorraine from France and demands five billion francs in reparations.
187172 Deutsche Bank and Dresdner Bank founded. German population at 41 million (as compared to 68 million in 1913).
1873 Three Emperors Alliance is initiated by Bismarck to prevent war between Russia and Austria. Kulturkampf beginsa campaign of the State against the Church.
1874 Richard Wagner moves into Haus Wahnfried in Bayreuth.
1876 Nikolaus Otto invents the internal-combustion engine.
187677 Balkan wars: Serbia and Russias battle against Ottoman Empire ends in Russian victory. The Tsar dictates the peace treaty of San Stefano.
1878 Bismarck calls the Congress of Berlin to settle the conflict between Great Britain and Russia over controls of the Eastern Mediterranean. Resentment in Russia against German interference on behalf of Austria-Hungary.
In Germany an anti-socialist law bans the Socialist party but allows them parliamentary representation. Socialists dissociate themselves from anarchism and terrorism.
First football club is founded in Hanover.
1879 Germany makes a dual alliance with Austria-Hungary to deter Russian attack and to stabilize the Balkans. Anglo-Russian confrontation over Afghanistan: conflict over territory in Asia at its height.
German agriculture comes under competitive pressure from the U.S. and Russia and Germany turns from her traditional free-trade policy to protectionism.
Siemens Company builds first electrical locomotive.
1881 Bismarck achieves a new secret Three Emperors Alliance to last for three years.
A telephone network is launched in Berlin.
1882 Robert Koch develops antidote to tuberculosis. New colonial expansion of the European powers is led by Great Britain and France. In the following years Germany acquires colonies in east Africa and south-west Africa.
188485 Congo Conference in Berlin is called. To prevent major colonial confrontations boundaries are drawn to delineate spheres of influence between the great powers in Europe.
1886 Gottlieb Daimler and Carl Benz have their four-wheel cars patented.
1887 Emil Berliner develops the gramophone record-player. Heinrich Hertz discovers electrical waves.
188790 Germany makes a secret Reinsurance Treaty with Russia specifying both their neutrality should war break out with Russia or France.
Next page