








Decode History | 1
1. EVENTS FROM 18TH CENTURY
The Scientific Revolution (1550-1700)What & Why:
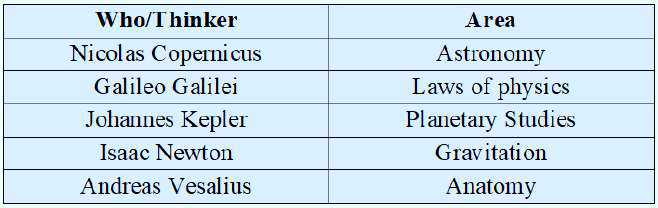
During Middle Ages (5th-15th Century) Church was a powerful force & dominated everyday life of majority of people.
This period was marked by unthinkable levels of cruelty, injustices and persecutions of those who went against
Church.
Church followed the Aristotelian system which had defined the laws of physics erroneously in many cases.
With the rise of the Renaissance, Churchs authority was questioned by many Europeans. This is especially true for field of science, that was used to explain miracles and questioned Churchs ideas.
Renaissance was marked by explorations, experiments, artists
& thinkers. It gave birth to Scientific Revolution which opened the doors to modern science.
Table 1 The Scientific Revolution
Impact:
Scientific Revolution improved popular understanding of physics, laws of motion, gravity and led to many inventions.
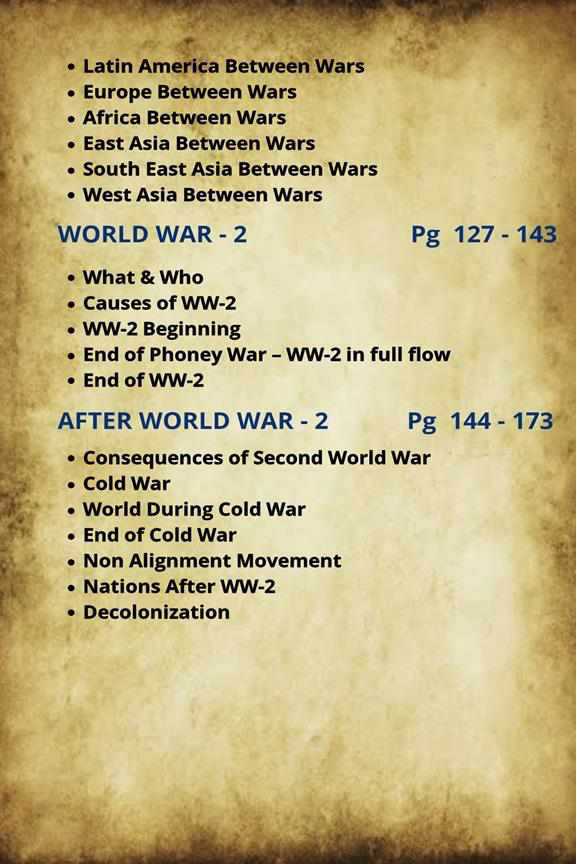
Field of Astronomy witnessed new developments; for example, Newtons explanations about the motions of heavenly bodies.

Decode History | 2
Experiments conducted during this period furthered the understanding of the human body and found cures for illnesses.
Led to spread of independent thoughts, discussions, knowledge
& intellect.
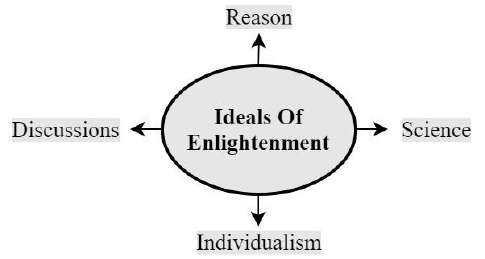
It led to individualism & rationalism-based age of Enlightenment, which applied scientific method to human behavior & society during 18th century & decreased reliance on traditional teachings of Church.
Current Relevance:
It transformed views of society & led to origin of modern sciences.
Hence, a lot of what exists today is because of scientific revolution.
Figure 1 Scientific Revolution
The Enlightenment (16501800)
What:
Enlightenment, also known as Age of Reason, was an intellectual, philosophical, cultural & social movement that spread through Europe during the 1700s.
It emphasized on reason and individualism and presented a challenge to traditional religious views. Its thinkers were the liberals of their day.
Decode History | 3
Why:
It overlapped with Scientific Revolution and marked a departure from the Middle Ages during which science was regarded as heresy, free-thinkers who tried to explain matters of faith were persecuted, serfdom was widespread and personal liberties or rights were curtailed.
Also, 30 Years War was criticized due to shear destruction it caused and this laid a road towards enlightenment.
There was growing support for individual freedoms, skepticism toward monarchy-religious authorities etc.
Table 2 The Enlightenment
How:
It led the struggle for independent thought, science, mathematics, physics etc.
Intellectual-philosophical discussions, reading books etc. were promoted.
But many uneducated and rural citizens could not participate in this movement until Industrial Revolution provided them with jobs.
Impact:
It transformed West into an intelligent & self-aware civilization.

Decode History | 4
It inspired ideas of America - French Revolutions.
However, it was questioned by Romanticism, a movement that was inspired by Rousseaus emphasis on emotion instead of reason.
Similarly, Skepticism also questioned the use of reason and eventually led to end of enlightenment.
Figure 2 The Enlightenment
Enlightenment was blamed for attacks on tradition and for inducing anarchy as productive changes took time to show.
People were persecuted for their new ideas.
But, soon it, led to strengthening of womens rights and scientific creations like steam engines and increased educational and job opportunities.
Current Relevance:
Enlightenment laid foundation of modern science. Its tenets of individualism and reasoning hold importance in 21st century as well.
It shaped concepts of freedom, especially freedom of expression to what it is today.
Decode History | 5
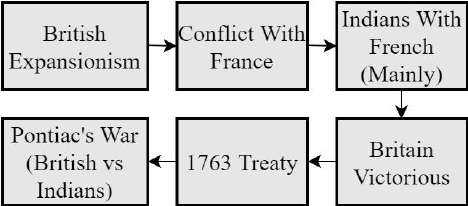
The French And Indian War (1754-1763)What:
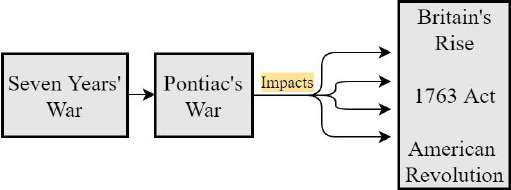
Conflict between French & Britain over colonial dominance in North America, led to the Seven Years War (1756 to 1763).
Indians, generally, sided with French & hence war is known as it is.
Why:
Tensions between British and French in America had been rising for some time, as each side wanted to increase its land holdings.
Who & How:
American colonists fought alongside British soldiers.
Undeclared war began in 1754 when George Washington demanded that French troops withdraw from the territory.
Washington's troops clashed with local French forces but tasted failure.
France and Britain formally declared war in May 1756.
Indians allied with the French and France dominated the war initially.
However, by 1758, Britain began to make peace with Indians
& gained major ground in war. By September 1760, British controlled entire North American frontier including major Canadian cities, Ohio etc.
Figure 3 Seven Years War
Next page
























