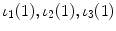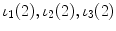1. Historical Reviews Around Evolving Ideas of the Invisible Hand
1.1 Modern Technology and the Rise of the Service Economy
To clarify the evolution of modern economics, I will first discuss modern technology. In the past, it was normal for industrial processes to improve a piece of technology to make it as efficient as possible, and then manage it for a longer period, since it took quite a long time to process a basic principle into a usable machine. Modern technology, however, is likely to have moved much more quickly from basic science to usable technology. So-called nanotechnology is a good example of this. In other words, it now takes much more time to generate a new basic principle than a new engineering process. In general, basic science provides us with a huge number of possibilities, which can lead to potentially many more combinations of technologies. Therefore, detecting a feasible technology will be a much more difficult task. This may require better techniques underlying statistical physics/mechanics. It may also apply to Information and Communication Technology (ICT).
ICT ensures that one of the core engines of society, particularly for services management, is also common to daily life for end-users as well as in production. Specifically, ICT can intermediate activities, and then provide services bilaterally. The ways in which ICT is connected to societal activities and service processes must be nonlinear, dynamic, and hierarchical over time, i.e., complex and/or synergetic. ICT is therefore naturally an attractive research subject for complex sciences. At the same time, future society is likely to be built on ICT intermediation.
It is therefore obvious that ICT will be decisive in our future as both hardware and software. In future, ICT may be a key factor, not only crucial to each process of production at the various different stages of an economic system, but also in generating new technologies. Looking at ICT, then, it is possible to generate a birds-eye view of the future profile of society. In this sense, designing ICT will serve as a policy measure to assess a social activity. In short, the new service-dominant economy will be realized if, and only if, ICT progresses as expected.
During the final quarter of the last century, the economy shifted towards services and away from manufacturing. This transition is part of the ongoing evolution of the modern economy since the industrial revolution, and in particular, changes in production and consumption. More detailed observations on this will be found in Chaps. the basic principles of production and consumption, either in classic political economy or neoclassical economics, depended on the view that the consumption of citizens should be achieved outside the economic process. In the neoclassical view, the household will by definition never participate in any productive process except by providing its labor, because the household cannot be a resource for production (productive factor). Even the reproduction of the labor force should be outside the bounds of production, because its negation implies slavery: the household as a labor production factory.
1.1.1 The Classical Production Scheme
For future reference, I will summarize here the traditional production scheme. We are used to a time profile of production starting from the initial period, when the primary factor enters the process, through the intermediate product, to the final one. There are two kinds of primary factor: land and labor. Consumption, the final column of the table, is outside the economic process. This means a complete separation of production from consumption. The traditional production scheme cannot help but be broken down if there is any intersection between production and consumption. The introduction of service-dominant processes suggests the emergence of such an intersection (Fig.).
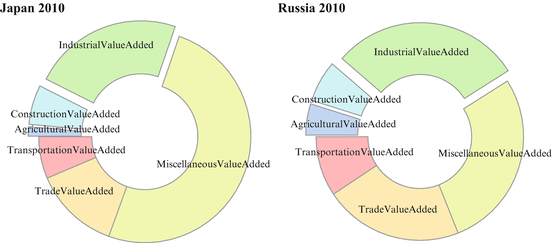
Fig. 1.1
Contribution of GDP industries
The actual time profile may become much more complicated with the existence of durable capital goods. The diagonal elements on the table show the vertically integrated process in this scheme of production, while the rows show the horizontally cross-operated process. The gray cells
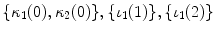
show the time structure of production. The bold framework shows the inputoutput relationship, with the time structure synchronized as a simultaneous system of production of general form with multiple final products, i.e., a joint-product system (Table ):
Table 1.1
The classical production scheme
Time | The primary factor | The intermediate product | The final product | Consumption |
|---|
The initial period | 1(0), 2(0) |
The first period | 1(1), 2(1) | 1(1) | 1(1) | Minus 1(1) |
The second period | 1(2), 2(2) | 1(2) | 1(2) | Minus 1(2) |
In Table
Table 1.2
The simultaneous system of production
Multiple processes | Multiple inputs | Multiple products |
|---|
Process (1) | | 1(1), 2(1) |
Process (2) | | 1(2), 2(2) |
Note: This is an extension of Table 10.1 in Aruka (, p. 165) from a single durable capital good to multiple durable capital goods
The replacement of land with capital as a primary factor has been promoted because of the prevalence of the Cobb-Douglas-type production function since the 1930s. However, its replacement was not recommended in a scientific sense, because capital is currently used as a reproducible good except in particular circumstances. Capital, after industrialization, must not be primarily perpetuated in a natural sense. Capital is merely an intermediate product even if it can be carried over for more than 1 year. Capital, in the production function, is a real product (and not financial) if its durability is a year, and a virtual intermediate product of a fictitious process if its durability is more than a year. Capital cannot be given the same status as labor in the production function.










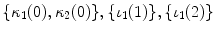 show the time structure of production. The bold framework shows the inputoutput relationship, with the time structure synchronized as a simultaneous system of production of general form with multiple final products, i.e., a joint-product system (Table ):
show the time structure of production. The bold framework shows the inputoutput relationship, with the time structure synchronized as a simultaneous system of production of general form with multiple final products, i.e., a joint-product system (Table ):