Introduction
The Hindu tradition has an amazingly large corpus of religious texts, spanning Vedas, Vedanta (brahmanas,smritis, Puranas, dharmashastras and itihasa. For most of these texts, especially if one excludes classical Sanskrit literature, we dont quite know when they were composed and by whom, not that one is looking for single authors. Some of the minor Puranas (Upa Purana) are of later vintage. For instance, the Bhavishya Purana (which is often listed as a major Purana or Maha Purana) mentions Queen Victoria.
In the listing of the corpus above figures itihasa, translated into English as history. History doesnt entirely capture the nuance of itihasa, which is better translated as this is indeed what happened. Itihasa isnt myth or fiction. It is a chronicle of what happened; it is fact. Or so runs the belief. And itihasa consists of Indias two major epics, the Ramayana and the Mahabharata. The former is believed to have been composed as poetry and the latter as prose. This isnt quite correct. The Ramayana has segments in prose and the Mahabharata has segments in poetry. Itihasa doesnt quite belong to the category of religious texts in a way that the Vedas and Vedanta are religious. However, the dividing line between what is religious and what is not is fuzzy. After all, itihasa is also about attaining the objectives of dharma, and the Mahabharata includes Hinduisms most important spiritual textthe Bhagavad Gita.
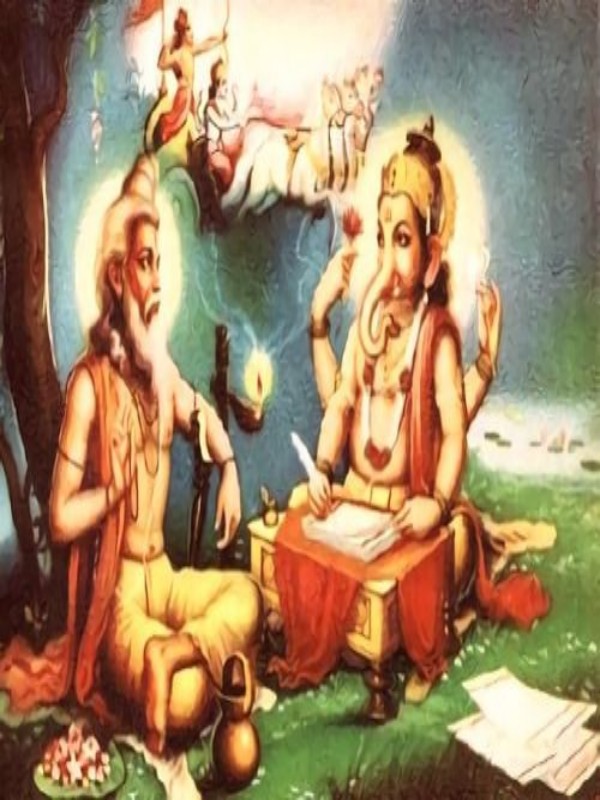
The epics are not part of the shruti tradition. That tradition is like revelation, without any composer. The epics are part of the smriti tradition. At the time they were composed, there was no question of texts being written down. They were recited, heard, memorized and passed down through the generations. But the smriti tradition had composers. The Ramayana was composed by Valmiki, regarded as the first poet or kavi. The word kavi has a secondary meaning as poet or rhymer. The primary meaning of kavi is someone who is wise. And in that sense, the composer of the Mahabharata was no less wise. This was Vedavyasa or Vyasadeva. He was so named because he classified (vyasa) the Vedas. Vedavyasa or Vyasadeva isnt a proper name. It is a title. Once in a while, in accordance with the needs of the era, the Vedas need to be classified. Each such person obtains the title and there have been twenty-eight Vyasadevas so far.
At one level, the question about who composed the Mahabharata is a pointless. According to popular belief and according to what the Mahabharata itself states, it was composed by Krishna Dvaipayana Vedavyasa (Vyasadeva). But the text was not composed and cast in stone at a single point in time. Multiple authors kept adding layers and embellishing it. Sections just kept getting added and it is no ones suggestion that Krishna Dvaipayana Vedavyasa composed the text of the Mahabharata as it stands today.
Consequently, the Mahabharata is far more unstructured than the Ramayana. The major sections of the Ramayana are known as kandas and one meaning of the word kanda is the stem or trunk of a tree, suggesting solidity. The major sections of the Mahabharata are known as parvas and while one meaning of the word parva is limb or member or joint, in its nuance there is greater fluidity in the word parva than in kanda.
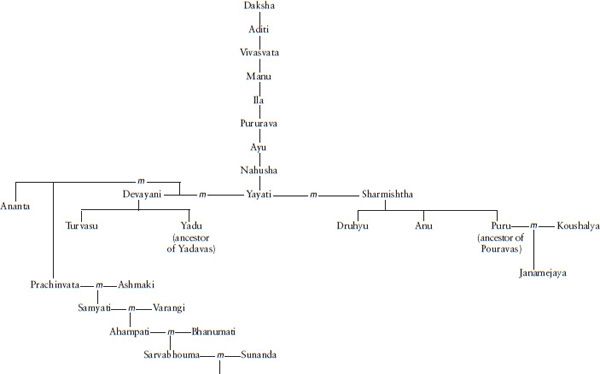
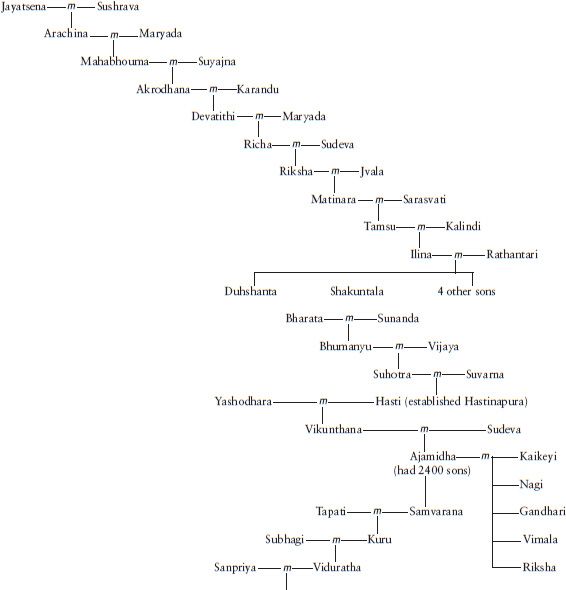
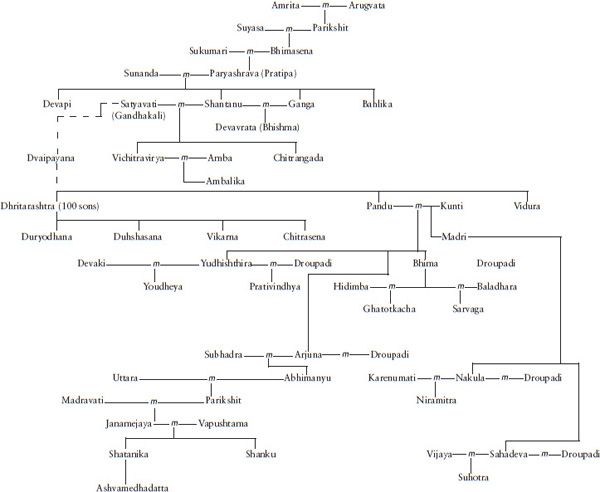
The Vyasadeva we are concerned with had a proper name of Krishna Dvaipayana. He was born on an island (dvipa). That explains the Dvaipayana part of the name. He was dark. That explains the Krishna part of the name. (It wasnt only the incarnation of Vishnu who had the name of Krishna.) Krishna Dvaipayana Vedavyasa was also related to the protagonists of the Mahabharata story. To go back to the origins, the Ramayana is about the solar dynasty, while the Mahabharata is about the lunar dynasty. As is to be expected, the lunar dynasty begins with Soma (the moon) and goes down through Pururava (who married the famous apsara Urvashi), Nahusha and Yayati. Yayati became old, but wasnt ready to give up the pleasures of life. He asked his sons to temporarily loan him their youth. All but one refused. The ones who refused were cursed that they would never be kings, and this includes the Yadavas (descended from Yadu). The one who agreed was Puru and the lunar dynasty continued through him. Purus son Duhshanta was made famous by Kalidasa in the DuhshantaShakuntala story and their son was Bharata, contributing to the name of Bharatavarsha. Bharatas grandson was Kuru. We often tend to think of the Kouravas as the evil protagonists in the Mahabharata story and the Pandavas as the good protagonists. Since Kuru was a common ancestor, the appellation Kourava applies equally to Yudhishthira and his brothers and Duryodhana and his brothers. Kurus grandson was Shantanu. Through Satyavati, Shantanu fathered Chitrangada and Vichitravirya. However, the sage Parashara had already fathered Krishna Dvaipayana through Satyavati. And Shantanu had already fathered Bhishma through Ganga. Dhritarasthra and Pandu were fathered on Vichitraviryas wives by Krishna Dvaipayana.