
2019 Smithsonian Institution. e name Smithsonian and the Smithsonian
logo are registered trademarks owned by the Smithsonian Institution.
Danica Kassebaum


Contributing Author
Allison Duarte, M.A.
Consultants
Tamieka Grizzle, Ed.D.
K5 STEM Lab Instructor
Harmony Leland Elementary School
Valerie Neal
Curator and Chairperson of the Space History Department
Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum
Publishing Credits
Rachelle Cracchiolo, M.S.Ed., Publisher
Conni Medina, M.A.Ed., Managing Editor
Diana Kenney, M.A.Ed., NBCT, Content Director
Vronique Bos, Creative Director
June Kikuchi, Content Director
Robin Erickson, Art Director
Seth Rogers, Editor
Mindy Duits, Senior Graphic Designer
Smithsonian Science Education Center
Image Credits: front cover, pp.23, pp.45, p.6 (insert), pp.67, p.7 (top), p.10, 11
(bottom), p.12, p.13, p.14, p.15, p.17 (top), p.19 (both), 32 (right) NASA; p.7 (bottom) Public
Domain; p.8 Vicspacewalker/Shutterstock, pp.1617, p.18 Stephen Frink Collection/
Alamy; p.22 UpperCut Images/Alamy; p.24 FDR Presidential Library & Museum, photo
by Margaret Suckley; p.27 (top) Aabejon/Getty Images; all other images iStock and/or
Shutterstock.
Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data
Names: Kassebaum, Danica, author.
Title: Underwater training / Danica Kassebaum.
Description: Huntington Beach, CA : Teacher Created Materials, [2018] |
Audience: K to grade 3. | Includes index.
Identiers: LCCN 2017060490 (print) | LCCN 2017061607 (ebook) | ISBN
9781493869220 (e-book) | ISBN 9781493866823 (pbk.)
Subjects: LCSH: Aquatic exercises--Juvenile literature. | Aquatic
exercises--Therapeutic use--Juvenile literature. | Physical education and
training--Juvenile literature.
Classication: LCC GV838.53.E94 (ebook) | LCC GV838.53.E94 K36 2018 (print)
| DDC 613.7/16--dc23
LC record available at https://lccn.loc.gov/2017060490
5301 Oceanus Drive
Huntington Beach, CA 92649-1030
www.tcmpub.com
ISBN 978-1-4938-6682-3
2019 Teacher Created Materials, Inc.
2019 Smithsonian Institution. The name Smithsonian
and the Smithsonian logo are registered trademarks
owned by the Smithsonian Institution.
Synched Read-Along Version by:
Triangle Interactive LLC
PO Box 573
Prior Lake, MN 55372
ISBN-13: 978-1-6845-2056-5 (ebook)
Table of Contents
Under the Surface ...........................................
Staying Neutral
...............................................
Under the Sea
................................................
More than Training
......................................
Benets of Water
...........................................
STEAM Challenge
........................................
Glossary
.........................................................
Index
..............................................................
Career Advice................................................

Under the Surface
Water is used for many things . You drink it . You use
it to wash things . You swim in it . But , did you know
water is used to train astronauts ?
There is very little gravity in space . That means that
astronauts float around in their spacecraft . This makes
them feel weightless . Training in water helps them get
ready for what it feels like to be in space .
Astronauts are not the only people who train in water .
Athletes train in water , too . Water can also be used
to help people get better after they have been injured.
And water can help people with
chronic conditions , such as
arthritis .
Astronaut Robert L. Curbeam Jr.
trains in a pool .
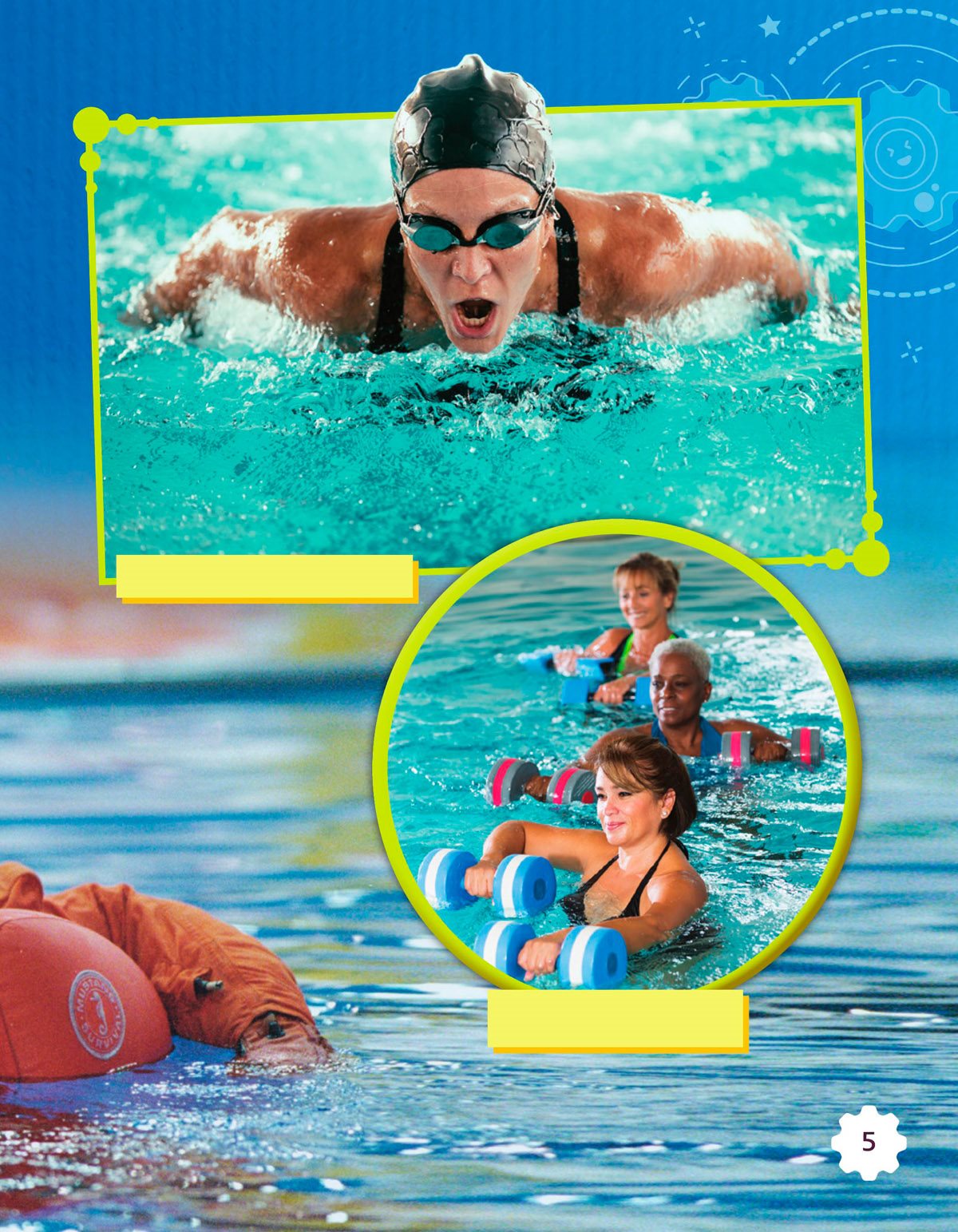

An athlete swims in a pool .
These women exercise
with weights in a pool .

Staying Neutral
You may have noticed that objects that are heavy on land
seem lighter when they are in the water . This is because
they are more buoyant in water than they are on land .
That makes some things that are hard to do on land much
easier in water . In the pool , you can lift your friends with
ease . You can even float !
The feeling you have when you are in water is almost
what it feels like to be in space . In fact , some astronauts
train for space in water . They train in labs that have large
pools . While in the pools , astronauts wear weights so that
they dont float to the top or sink to the bottom . This is
called neutral buoyancy (BOY-uhn-see).
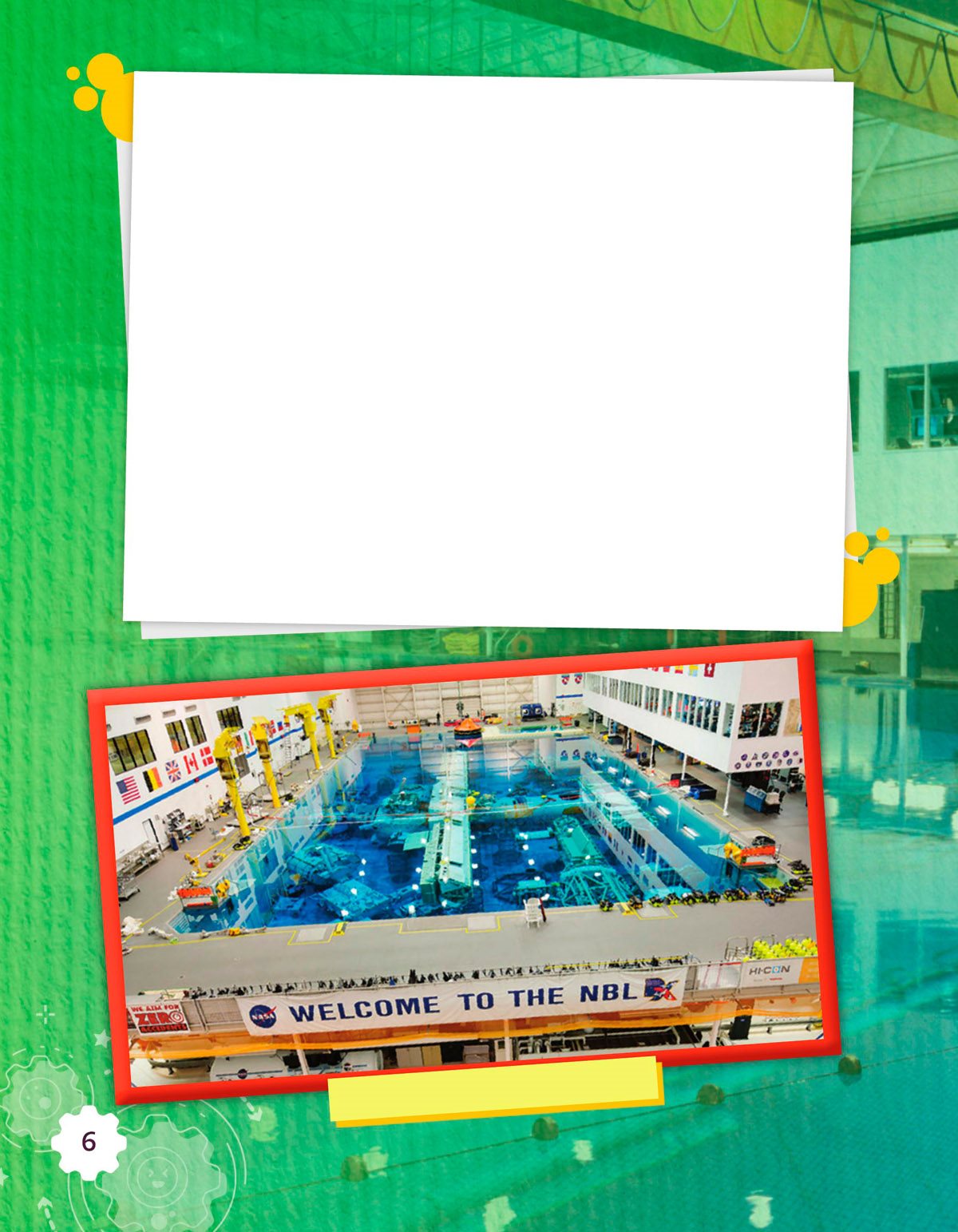
NASAs Neutral Buoyancy Lab
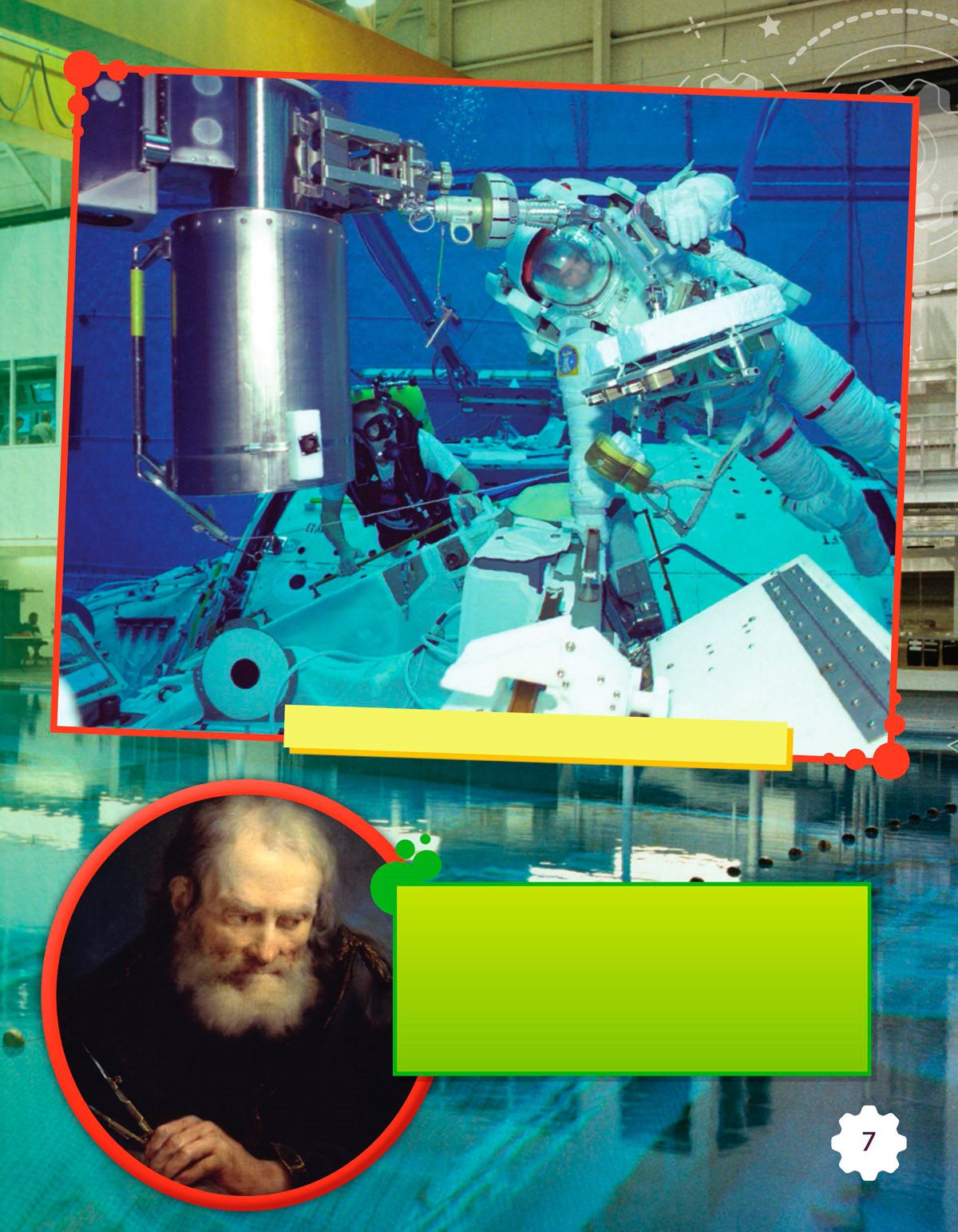

An astronaut trains in a neutral buoyancy pool .
When Archimedes (ahr-kuh-MEE-deez)
discovered buoyancy , he is said to have
cried , Eureka ! It means I have found
it . It is now a well -known phrase
when someone gures something out .

Train Around the World
There are neutral buoyancy pools all over the world . There
is one in Russia . There is also one in Germany . Chinese
astronauts practice in a pool in Beijing.
In the United States , there is a pool in Houston , Texas . It was
built in 1995 . It is part of the Neutral Buoyancy Lab . Many
things are placed in the pool to help astronauts train . Even
space stations have been put in the pool ! When an entire
station does not fit in the pool , it is split into pieces . A big
crane is used to put pieces in the pool.
Astronaut Michael Barratt
trains for a space walk in a
























