Copyright 2012 by Sebastian Seung
All rights reserved
For information about permission to reproduce selections from this book, write to Permissions, Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company, 215 Park Avenue South, New York, New York 10003.
www.hmhbooks.com
Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data
Seung, Sebastian. Connectome : how the brains wiring makes us who we are / Sebastian Seung. p. cm. Includes bibliographical references and index. ISBN 978-0-547-50818-4 I. Title. II. Title: How the brains wiring makes us who we are. [DNLM: 1. Brainanatomy & histology. 2. Brainphysiology. 3. Brainpathology. 4. Cognitionphysiology. 5. Nervous System Physiological Phenomena. WL 300] 612.8'2dc23 2011028602
Book design by Brian Moore
Printed in the United States of America
DOC 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
Figure Credits appear on .
To my beloved mother and father, for creating my genome and molding my connectome
Introduction
No road, no trail can penetrate this forest. The long and delicate branches of its trees lie everywhere, choking space with their exuberant growth. No sunbeam can fly a path tortuous enough to navigate the narrow spaces between these entangled branches. All the trees of this dark forest grew from 100 billion seeds planted together. And, all in one day, every tree is destined to die.
This forest is majestic, but also comic and even tragic. It is all of these things. Indeed, sometimes I think it is everything. Every novel and every symphony, every cruel murder and every act of mercy, every love affair and every quarrel, every joke and every sorrowall these things come from the forest.
You may be surprised to hear that it fits in a container less than one foot in diameter. And that there are seven billion on this earth. You happen to be the caretaker of one, the forest that lives inside your skull. The trees of which I speak are those special cells called neurons. The mission of neuroscience is to explore their enchanted branchesto tame the jungle of the mind (see Figure 1).
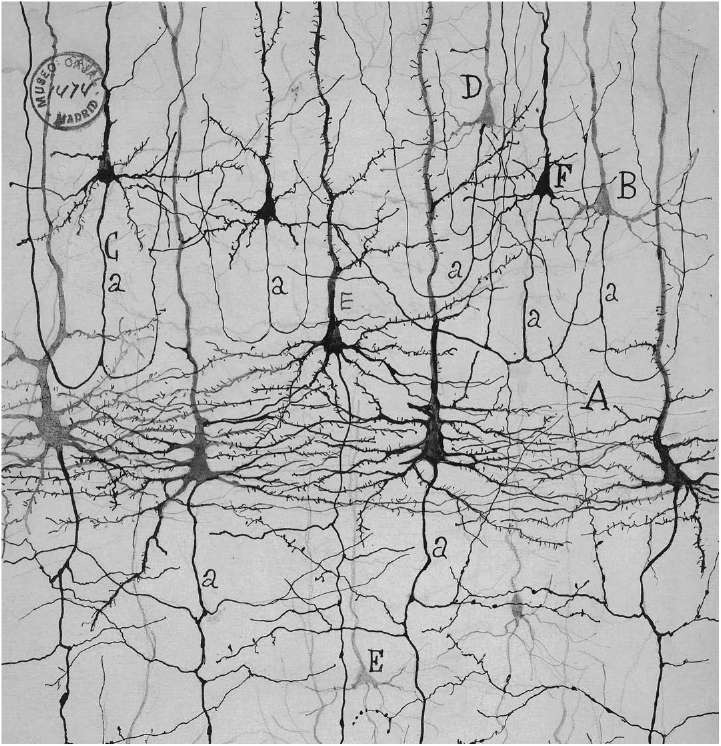
Figure 1. Jungle of the mind: neurons of the cerebral cortex, stained by the method of Camillo Golgi (18431926) and drawn by Santiago Ramn y Cajal (18521934)
Neuroscientists have eavesdropped on its sounds, the electrical signals inside the brain. They have revealed its fantastic shapes with meticulous drawings and photos of neurons. But from just a few scattered trees, can we hope to comprehend the totality of the forest?
In the seventeenth century, the French philosopher and mathematician Blaise Pascal wrote about the vastness of the universe:
Let man contemplate Nature entire in her full and lofty majesty; let him put far from his sight the lowly objects that surround him; let him regard that blazing light, placed like an eternal lamp to illuminate the world; let the earth appear to him but a point within the vast circuit which that star describes; and let him marvel that this immense circumference is itself but a speck from the viewpoint of the stars that move in the firmament.
Shocked and humbled by these thoughts, he confessed that he was terrified by the eternal silence of these infinite spaces. Pascal meditated upon outer space, but we need only turn our thoughts inward to feel his dread. Inside every one of our skulls lies an organ so vast in its complexity that it might as well be infinite.
As a neuroscientist myself, I have come to know firsthand Pascals feeling of dread. I have also experienced embarrassment. Sometimes I speak to the public about the state of our field. After one such talk, I was pummeled with questions. What causes depression and schizophrenia? What is special about the brain of an Einstein or a Beethoven? How can my child learn to read better? As I failed to give satisfying answers, I could see faces fall. In my shame I finally apologized to the audience. Im sorry, I said. You thought Im a professor because I know the answers. Actually Im a professor because I know how much I dont know.
Studying an object as complex as the brain may seem almost futile. The brains billions of neurons resemble trees of many species and come in many fantastic shapes. Only the most determined explorers can hope to capture a glimpse of this forests interior, and even they see little, and see it poorly. Its no wonder that the brain remains an enigma. My audience was curious about brains that malfunction or excel, but even the humdrum lacks explanation. Every day we recall the past, perceive the present, and imagine the future. How do our brains accomplish these feats? Its safe to say that nobody really knows.
Daunted by the brains complexity, many neuroscientists have chosen to study animals with drastically fewer neurons than humans. The worm shown in Figure 2 lacks what wed call a brain. Its neurons are scattered throughout its body rather than centralized in a single organ. Together they form a nervous system containing a mere 300 neurons. That sounds manageable. Ill wager that even Pascal, with his depressive tendencies, would not have dreaded the forest of C. elegans. (Thats the scientific name for the one-millimeter-long worm.)
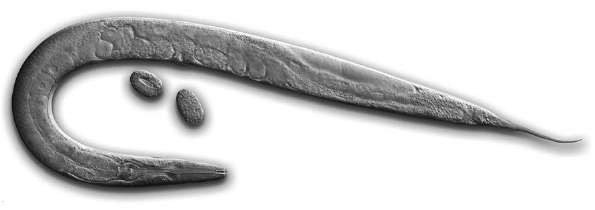
Figure 2. The roundworm C. elegans
Every neuron in this worm has been given a unique name and has a characteristic location and shape. Worms are like precision machines mass-produced in a factory: Each one has a nervous system built from the same set of parts, and the parts are always arranged in the same way.
Whats more, this standardized nervous system has been mapped completely. The resultsee Figure 3 is something like the flight maps we see in the back pages of airline magazines. The four-letter name of each neuron is like the three-letter code for each of the worlds airports. The lines represent connections between neurons, just as lines on a flight map represent routes between cities. We say that two neurons are connected if there is a small junction, called a synapse, at a point where the neurons touch. Through the synapse one neuron sends messages to the other.
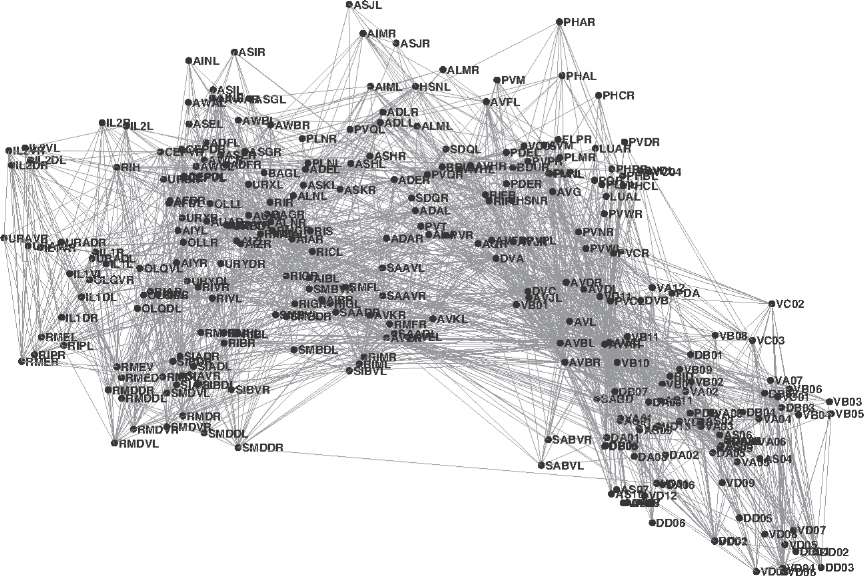
Figure 3. Map of the C. elegans nervous system, or connectome
Engineers know that a radio is constructed by wiring together electronic components like resistors, capacitors, and transistors. A nervous system is likewise an assembly of neurons, wired together by their slender branches. Thats why the map shown in Figure 3 was originally called a wiring diagram. More recently, a new term has been introducedconnectome. This word invokes not electrical engineering but the field of genomics. You have probably heard that DNA is a long molecule resembling a chain. The individual links of the chain are small molecules called nucleotides, which come in four types denoted by the letters A, C, G, and T. Your genome is the entire sequence of nucleotides in your DNA, or equivalently a long string of letters drawn from this four-letter alphabet. Figure 4 shows an excerpt from the three billion letters, which would be a million pages long if printed as a book.

Figure 4. A short excerpt from a human genome
Next page