CAN YOU SEE THE BOARD IN THE CLASSROOM?
We all face health problems once in a while. Maybe you have come down with the flu or you got a cavity. Perhaps you have ADHD or diabetes. Some people need glasses to see better or are allergic to bee stings. These handy guides teach you about your health and how all the parts of your body work together to keep you healthy most of the time.
About the Author
Dr. Alvin Silverstein is a retired professor of biology at the College of Staten Island, City University of New York. Virginia Silverstein translates scientific Russian and is a professional author. Together they have written more than 200 books for young people. Laura Silverstein Nunn has coauthored more than 100 books with her parents.

Image Credit: Shutterstock.com
Can you see the whiteboard in your classroom? If not, tell an adult. You may need to see an eye doctor.
Do you have trouble seeing the chalkboard clearly in school? Do things look blurry when you look at a computer screen or a video game? Do you rub your eyes and squint a lot? These are all signs that your eyes arent working quite right.
Your eyes are remarkable. You use them to see a rainbow of colors and a variety of shapes. You can see in bright sunshine or almost total darkness.
Your eyes let you see where you are going. They help you look out for cars before crossing the street. They keep you from bumping into furniture or tripping over things on the floor. Most importantly, your eyes also help you learn about and understand the world.
If you can see objects clearly from both far away and close up, you have good vision. But if some things look blurry to you, you probably have poor vision. Dont worry, thoughan opthalmologist, or eye doctor, can test your eyes to find out whats wrong. You may need eyeglasses to help you see better. But if you dont want to wear glasses, you may be able to wear contact lenses instead.
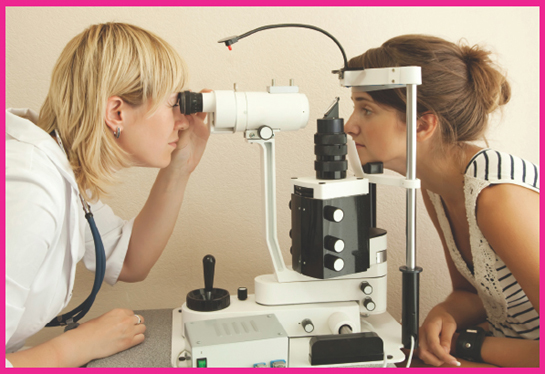
Image Credit: Iakov Filimonov/Photos.com
An eye doctor does a series of tests to check your vision and the health of your eyes. One of these exams is done with a slit lamp, a microscope with a light attached. It lets the doctor closely examine your cornea, iris, and lens.
Whether you have perfect vision or wear glasses, there are some things you can do to keep your eyes healthy and strong. Read on to learn more about how your eyes work and what you can do if something goes wrong.

Your eyes are your most important sense organ. About 80 percent of the information you gather about the world comes through your eyes.

Image Credit: Shutterstock.com
When you look at yourself in the mirror, you can see only a small part of your eyes. But theres more to your eyes than what you can see. What youre looking at is just the front part of your eyeball. An eyeball looks a bit like a big round marble. But a marble is hard, whereas an eyeball is soft. An eyeball is filled with a jellylike liquid.
Your eyelids protect your eyes. You can move them up and down like window shades. You can close them if the light is too bright. If an insect or a bit of dust zooms in toward your eyes, your eyelids quickly snap shutyou blink. Blinking is automatic. You dont even have to think about it.

Image Credit: Jupiterimages/Photos.com
The eyeball is round like a marble, but you see only the front part of it.
Blinking allows your eyelid to work like a pump. The closing action squeezes out a bit of liquid from your tear gland and then spreads it evenly over your corneathe clear covering on the surface of the eye. You make tears all the time. This keeps the eyes moist so the corneas wont dry out and get sore.
If you look at someones eyes, you could look right through the cornea and see the iristhe colored part of the eye. The color of a persons iris depends on the amount of pigment in it. Brown eyes have a lot of pigment; blue eyes have less.
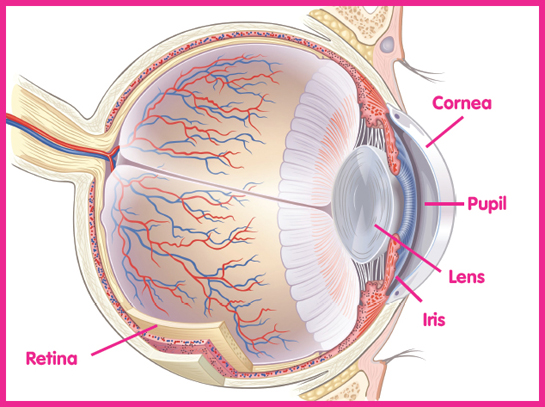
Image Credit: Shutterstock.com
This drawing of the eye shows some parts you cant see in the mirror.
The black dot in the middle of your iris is an opening called the pupil. Light rays enter your eye through the pupil. Muscles inside the iris can change the size of your pupil. When you are in a dark place, your pupils get larger so more light can enter your eyes. When you are in a bright place, your pupil gets smaller to let in less light.
Behind the pupil is a clear structure called the lens. Light rays pass through the lens and travel through the fluid in the eyeball. Then they strike the retina, a layer of light-sensitive cells that lines the back of the eyeball. Here, they form a picture, called an image.
Two kinds of cells in the retina respond to light. These cells are named for their shapes: rods and cones. Rod cells are shaped like short, straight sticks. Cone cells look similar to upside down ice cream cones. We need both rods and cones for good vision.
The rod cells in your retina can pick up tiny bits of light. They help you see shapes and movement in dim light, but the vision they provide is blurry and unclear. Cone cells are sensitive only to bright light. There are three different kinds of cone cells. Each cone cell reacts to just one kind of lightred, green, or blue. When you look at a green shirt, your green cone cells react, but the red and blue cells do not.
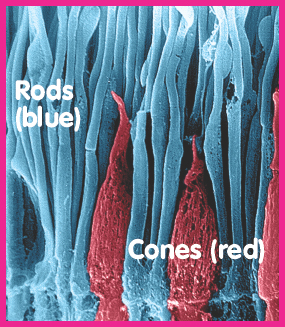
Image Credit: Ralph C. Eagle, Jr./Photo Researchers, Inc./Colorization by: Robin Treadwell
This magnified view of the retina shows rods and cones, which are artificially colored.

Image Credit: Shutterstock.com
The three primary colorsred, green, and bluecan be combined to make many different colors.
If there are just three kinds of cones, you might wonder how you see other colors. Your cone cells can work together. For example, when both your red and blue cones react, you see purple. Red, green, and blue are called primary colors because every other color can be made by combining them. Your cone cells thus allow you to see all the colors of the rainbow.
When you go outside on a moonlit evening, there is not enough light for your cone cells to work. Only the rod cells can react. Thats why you cant see colors at night. You can still make out shapes, but things are all in shades of gray.























