Improving Anti-Microbial Activity of Allicin and Carvacrol through Stabilized Analogs and Nanotechnology
Diana R. Cundell1 College of Life Sciences, Thomas Jefferson University, 4201 Henry Avenue, Philadelphia, PA 19128, USA
Abstract
Allicin and carvacrol have been appreciated as broad-spectrum antimicrobial agents since the early 20th century and used in both Ayurvedic and traditional Chinese medicines for at least five thousand years. Although research since the 1980s identified several important mechanisms of action for allicin and carvacrol, neither has become part of a classical pharmaceutical regimen. Allicin and carvacrol, like other natural phytochemicals, have been hard to purify and stabilize, which has been a major barrier in their entry into a drug discovery process. During the past two decades, two distinct strategies have changed this position. Bioengineering has allowed allicin and carvacrol to be bound to nanoparticles and immobilized onto coated surfaces or into gels; all these methods maximize the retention of activity coupled with a more targeted release. The fields of synthetic and computational chemistry have long been used to create semi-synthetic and synthetic variants of natural molecules or predict binding strengths of molecules that have improved activity and or bioavailability when compared with the parent compounds. Stabilization using one, or both, of these strategies, has been successful for both allicin (garlic) and carvacrol (oregano). This chapter will review the antimicrobial spectrum of these agents and document the methods that have currently been used to stabilize or generate semi-synthetic forms of each of them. Finally, potential and currently available delivery systems will be explored.
Keywords: Allicin, Carvacrol, Nanoparticles, Natural molecules, Semi-synthetic analogs, Nanotechnology.
.
GENERAL INTRODUCTION
Even before written records were kept, the man attempted to find interventions for pain and infectious diseases []. All
this is believed to have begun at least 60,000 years ago with evidence of herbal remedies buried with Neanderthal man [].
Ironically, although up to one-half of all current pharmaceuticals derive from medicinal plants and the majority relate to their original ethnopharmacological uses [].
With the rapid evolution of resistance to antibacterial and antifungal agents, scientists are now searching for new treatment strategies [] medications is also limited.
Creating semi-synthetic or synthetic forms of available medications with improved bioavailability that bypass resistance mechanisms has been relatively successful for antibiotics [].
Are we ready for a new approach to plant antimicrobials? Survey data suggest that between 30 and 80% of people are comfortable using them [).
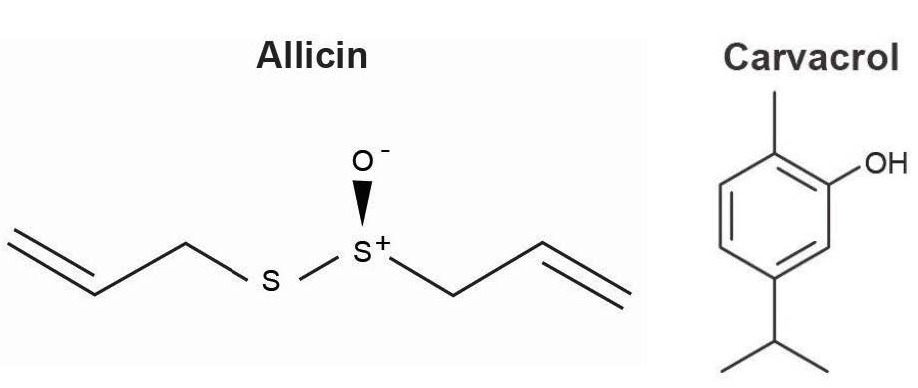
Fig. (1)) Chemical structures of allicin and carvacrol.
ALLICIN (FROM GARLIC Allium Sativum L.)
Introduction
Commercial garlic (Allium sativum L.) belongs to a large genus of plants that grow in a wide variety of climates []. Garlic cloves contain numerous phytochemicals and so to avoid confusion only studies employing allicin will be discussed in the following sections.
Proposed Antimicrobial Mechanisms of Action for Allicin
Allicins broad spectrum antimicrobial activities derive from its thiol structure allowing easy penetration of cell membranes and subsequent inactivation of a variety of intracellular [).
Most important among these are biofilm disruption [] functions.
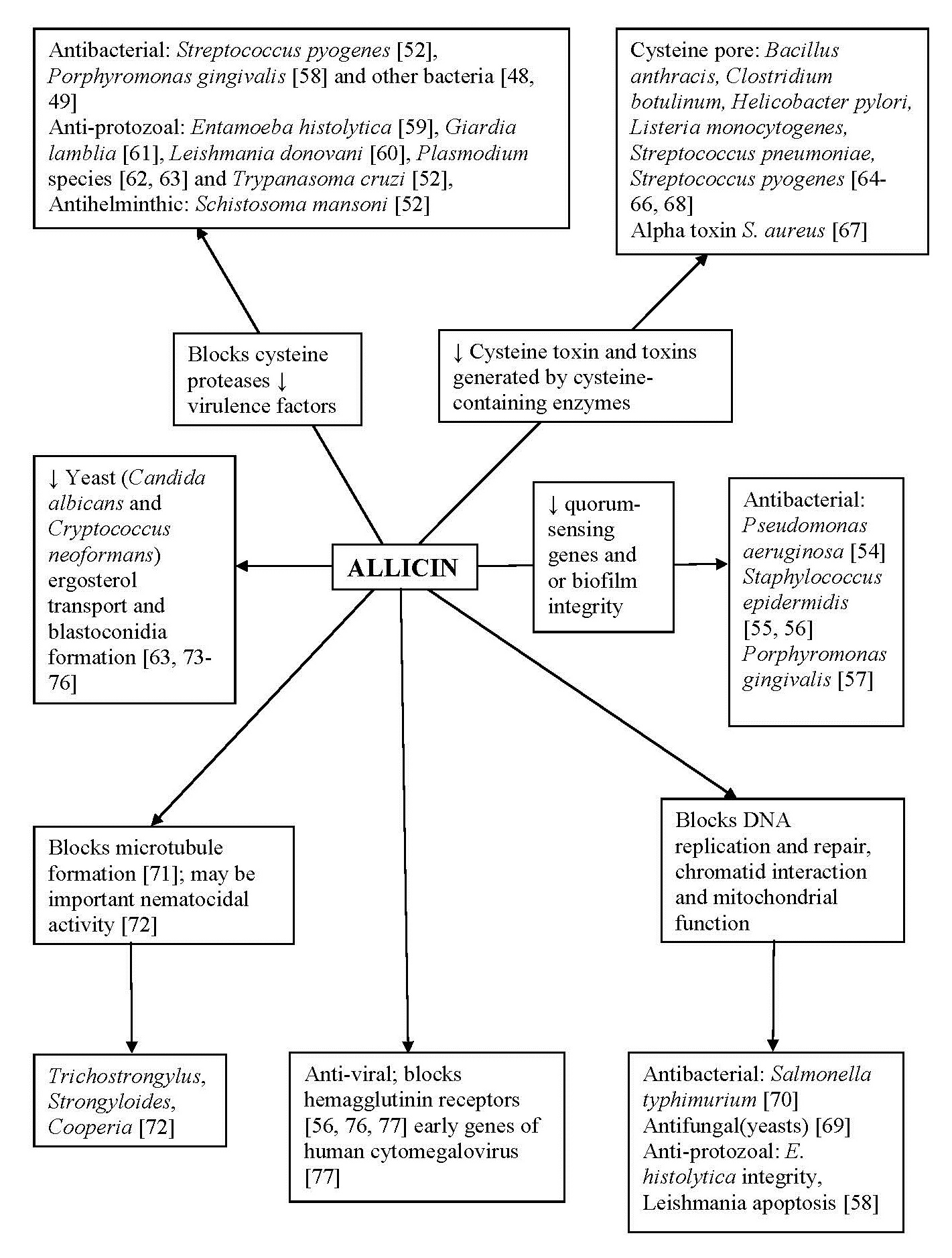
Fig. (2)) Possible antimicrobial mechanisms of allicin. Seven potential cellular targets in bacteria, fungi, protozoa, helminths and viruses have been identified for allicin that produce antimicrobial effects (references shown in parentheses).
Biofilm Disrupting Effects of Allicin
At least two mechanisms may be involved [].
Cysteine-Proteases as Major Targets for Allicin
Microbial cysteine proteases [] so allicin could be a useful against many species.
Allicin Targets Bacterial Cysteine-Containing Toxins and Alpha Toxins
Allicin is able to inhibit the highly conserved, cysteine-containing, pore-forming bacterial exotoxins of a further seven bacterial species including the important pathogens Bacillus anthracis, Clostridium botulinum, Helicobacter pylori, Listeria monocytogenes, Streptococcus pneumoniae and S. pyogenes [].
Allicin Affects Microtubule Polymerization
Studies of fibroblasts [] and this may explain its nematocidal activities.
Allicin Inhibits Ergosterol Transport in Yeasts
Anti-yeast activities may involve the ability of allicin to prevent the cellular protective response of ergosterol (fungal cholesterol) transport to the internal vacuoles that are central to their survival [].
Allicin Binds to Docking Receptors Preventing Viral Entry and Gene Synthesis
Highly conserved, viral hemagluttinin receptors on mammalian cells also contain thiol sulfur groups [].
Spectrum of Allicins Antimicrobial Activity
Antibacterial
Recently reviewed by Wagner-Graham [].
Only nine bacteria show limited responses to the effects of allicin [], hypothesized these had allowed the P. fluorescens to colonize garlic.
Allicin-resistant P. aeruginosa [].
Antifungal
The antifungal activities of allicin were recently reviewed by French-Arthur [].
Allicin has been investigated in two studies as a plant antifungal and shown efficacy against four fungal species [] found that allicin was able to kill Fusarium oxysporum but with a higher MIC (160 g/ml) than the standard treatment of fluconazole (100 g/ml).
Anti-protozoal and Anti-helminthic
Allicin has been shown to possess in vitro [].
Finally, allicin is anti-helminthic [].
Anti-viral
Both in vitro [].
Human DBRPCT of allicin as an upper respiratory infection antiviral did not identify the viruses involved but did report a produce a significant decrease in symptoms (p<0.001) [].
Semi-synthetic Allicin Analogs
Five literature studies have reported the creation of analogs of allicin and tested them against bacteria [], the remaining synthetic allicin analogs have all been designed in the past five years and none tested in animal models for antimicrobial activity. These studies do, however, give us an insight into how allicin might be modified for future mainstream use.
Table 1
In vitro antimicrobial activity of semi-synthetic analogs of allicin.| Analogs Created | Results | References |
|---|
| Alkyl analogs created using peracids tested using 20 bacteria | Branched alkyl chains activity (10-1, 200 M). n-pentyl-thiosulfinate stable and bactericidal (0.7 to 130 M). | [] |
| Twenty-four aminobenzene sulfur acid analogs tested positive and 6 gram-negative bacteria and 8 fungi | Broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity for cycloalkyl and aryl esters of 4-acylaminobenzenethiofulfoacids. Acyl residues substituted with fluorine were strongly fungicidal. Thiosulfinates were most effective against gram-positive bacteria, less so against gram-negative. |