Speed Learning
for Anatomy
SYSTEMS AND FUNCTIONS OF THE HUMAN BODY QUICK AND EASY
Justina C. Bachsteiner PhD
Copyright 2017 Justina C. Bachsteiner PhD
All rights reserved.
ISBN: 1507571801
ISBN 13: 9781507571804
Library of Congress Control Number: 2016907783
CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform
North Charleston, South Carolina
Dedicated to my darling daughters
Stephanie, Jessica, and Lauren
Preview
Chapters
Learn More
Introduction
Anatomy is a science of classification.
It is a study of the bodys structures and the relationships of all the bodys parts to one another.
Speed Learning for Anatomy is a system of learning.
It is designed to help students reach their learning goals faster and with less effort.
Want to learn faster than ever?
Then this book was written for you.
We utilize a grouping method for terms that are related. For example, when you are looking for the definitions of similar terms, such as vein and artery, you will see that these terms are grouped together in the same category, which is blood vessels. The grouping method enables you to quickly learn each terms definition and compare the differences at a glance. In this category, for example, you will also find the terms: aorta, coronary arteries, carotid artery, arterioles, capillaries, pulmonary arteries, venous system, vena cava, venules, pulmonary veins, vascular, avascular, and lymph.
This book contains more than twelve hundred of the most common anatomy terms. Our special grouping method, along with our concise writing style, speeds up your learning by eliminating the usual confusion that is associated with cross-referencing and understanding technical terms.
What also makes this book so very special is that it is designed for busy students like you who need to learn very quickly. It will be the learning tool that will help you significantly reduce your time studying. The bottom line is when you learn faster, you have more time to learn and more time to devote to other important tasks.
Great for students, teachers, athletes, fitness trainers, coaches, and all health-conscious people.
We go the extra mile!
If you study it, why not learn how to apply it?
Weve expanded this scope to include:
Aerobic calculations
Aerobic training guidelines
Stretch response
Health conditions
-Cancer
-Diabetes
-Heart Conditions
Body-building charts and guidelines
Eye Anatomy
Vitamin and mineral descriptions
Medical terms, and much more
In Speed Learning for Anatomy you will not only learn basic anatomy, but also how to apply your acquired knowledge to enhance your own life.
You will learn about the many functions of muscle tissue and then learn how best to develop your own muscle composition. Weve even included workout charts explaining what machines to use for each muscle group.
Weve included simplified formulas for heart rate and aerobic calculations, such as
-Karvonen Formula
-VO2 Max
-Maximum/Maximal Aerobic Capacity
-Maximum/Maximal Oxygen Consumption
-Maximum Heart Rate (MHR)
Weve chosen to discuss some of the most common health conditions simply because they are part of the human condition and are always related to our anatomy. Awareness and understanding of health conditions have unlimited benefits.
Speed Learning for Anatomy gives you a tremendous learning advantage. The following nine chapters define a vast array of information relating to anatomy. The definitions are crisp, to the point, and designed for you to understand concepts quickly and easily. Simplifying anatomy terms and saving you valuable learning time is what makes this book so special.
No other anatomy book defines anatomy terms so clearly, or so simply.
Table of Contents
CHAPTER 1
The Muscular System
1.1
Anatomy of the Muscular System
1.1.1
Introduction to the Muscular System
T here are more than six hundred muscles within the human body and more than 430 are voluntary muscles. Muscles are responsible for a great variety of functions, including body motion, strength, posture, heat production, and much more. Muscle is composed of approximately 75 percent water, 20 percent protein, and 5 percent salts and other chemicals.
1.1.2
Types of Muscle Tissue
1.Skeletal Muscle (Voluntary Muscle Tissues)
2.Smooth Muscle (Involuntary Muscle Tissues)
3.Cardiac Muscle (Involuntary Muscle Tissues)
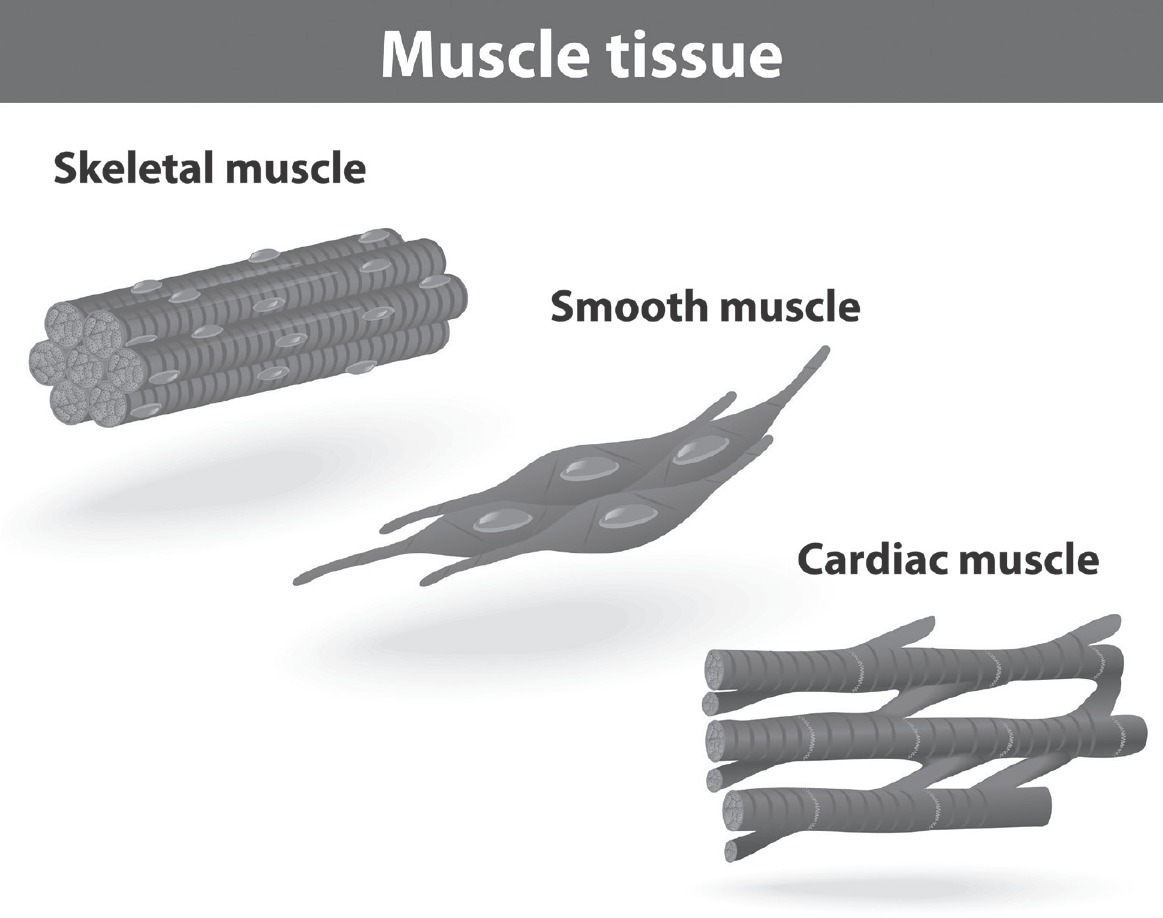
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscles form the muscles of the arms, legs, chest, back, neck, and head. They are primarily responsible for body movements.
The skeletal muscles also have other important functions, including the ability to increase basal metabolic rates (BMR), store energy, add body strength, and improve body appearance.
Smooth Muscle
Smooth muscle, also called visceral muscles, help to form the walls of certain internal organs, such as the esophagus, the stomach, the intestines, and blood vessels.
Next page