BONE AND MUSCLE
STRUCTURE, FORCE, AND MOTION
THE HUMAN BODY
BONE AND MUSCLE
STRUCTURE, FORCE, AND MOTION
EDITED BY KARA ROGERS, SENIOR EDITOR, BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES

Published in 2011 by Britannica Educational Publishing
(a trademark of Encyclopdia Britannica, Inc.)
in association with Rosen Educational Services, LLC
29 East 21st Street, New York, NY 10010.
Copyright 2011 Encyclopdia Britannica, Inc. Britannica, Encyclopdia Britannica,
and the Thistle logo are registered trademarks of Encyclopdia Britannica, Inc. All
rights reserved.
Rosen Educational Services materials copyright 2011 Rosen Educational Services, LLC.
All rights reserved.
Distributed exclusively by Rosen Educational Services.
For a listing of additional Britannica Educational Publishing titles, call toll free (800) 237-9932.
First Edition
Britannica Educational Publishing
Michael I. Levy: Executive Editor
J.E. Luebering: Senior Manager
Marilyn L. Barton: Senior Coordinator, Production Control
Steven Bosco: Director, Editorial Technologies
Lisa S. Braucher: Senior Producer and Data Editor
Yvette Charboneau: Senior Copy Editor
Kathy Nakamura: Manager, Media Acquisition
Kara Rogers: Senior Editor, Biomedical Sciences
Rosen Educational Services
Alexandra Hanson-Harding: Senior Editor
Nelson S: Art Director
Cindy Reiman: Photography Manager
Matthew Cauli: Designer, Cover Design
Introduction by David J. Crerand
Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data
Bone and muscle: structure, force, and motion / edited by Kara Rogers.1st ed.
p. cm.(The human body)
In association with Britannica Educational Publishing, Rosen Educational Services.
Includes index.
ISBN 978-1-61530-249-9 (eBook)
1. Musculoskeletal system. I. Rogers, Kara.
QP301.B56 2010
612.7dc22
2009043138
On the cover: This digital composite shows a close up of a man flexing his biceps. Together, bones, such as the humerus (upper arm bone), and muscles, such as biceps and triceps, allow humans to move in ways both powerful and precise. Adam Gault/Digital Vision/Getty Images
p.www.istockphoto.com.
CONTENTS




INTRODUCTION
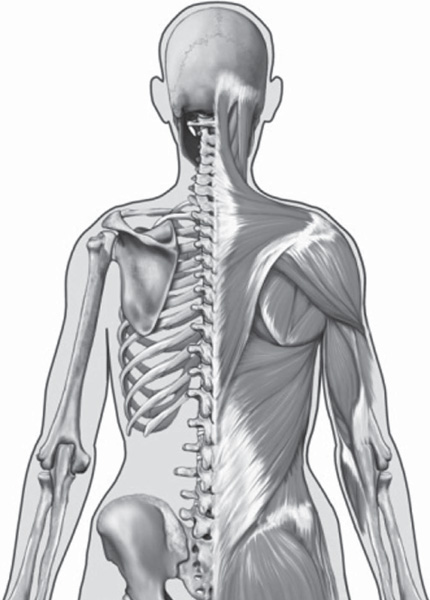
B one and muscle do more than just hold a body together. They underlie every move, every touch, every stepin essence, every action undertaken. Even the inhalation and exhalation of life-sustaining breath is made possible by muscles that support the lungs, which are protected by the bones that comprise the rib cage.
This volume presents a detailed examination of the human skeletal system and related muscle systems of the human body. Using an easily understandable format, this book creates for the reader an accessible map of the skeletal system and the contributing musculature that enable motion and organ function.
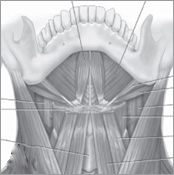
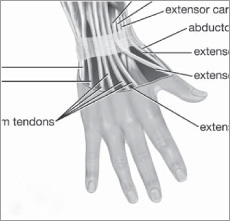
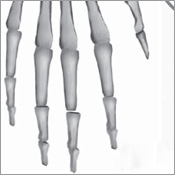
The human skeleton provides support and protection for the bodys organs and facilitates movement by providing the framework for the arms and legs to swing free. All the bones in the body are connected by joints, some of which contain fluid and hence are mobile and permit complex motions such as twisting. While such features are common to many other members of the Animal kingdom, the human skeleton has several distinct features that are found only in the Primate order, the group to which humans belong. The specialized bones in the human hand, for example, enable the action of opposable thumbs, a trait that has played a vital role in allowing humans to grasp objects and to use tools.
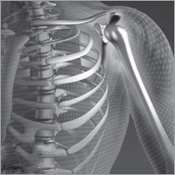
As humans evolved, their bone structure and musculature began to change. Standing upright and the ability to travel bipedally are credited with forming the first major directional course in human evolution. Major developmental impacts to the human skeletal system brought on by the evolution of bipedalism included changes in the foot bone arrangement and size, hip size and shape, knee size, leg bone length, and vertebral column shape and orientation. The human spine developed an S-curved shape that acts as a shock absorber when standing upright, and helps to hold up the heavy skull. Walking on two feet also demanded monumental changes to the musculature of the upper and lower limbs, the head and neck, and the muscles of the trunk or torso. Such changes were required to support and maintain this new, upright posture.
This posture has provided humans with some distinct evolutionary advantages. Unlike chimpanzees, humans do not spend much time hanging from trees or otherwise using their hands for locomotion. Instead, bipedal movement freed the hands, allowing humans to use their hands to grasp tools and weapons, to build shelters, and to skin animals for clothes. As civilizations evolved, humans began to use their hands to create great works of art and to play instruments. This allowed humans to create a hand-mind connection that made their brains grow larger as well.
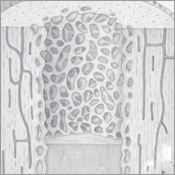
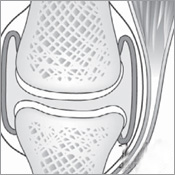
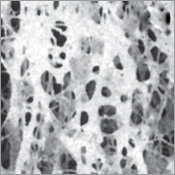
There are two primary types of bone material. Compact bone, which makes up 80 percent of all bone, is the dense, rigid outer layer of that provides strength and structural integrity. Cancellous bone, of which the remaining 20 percent is comprised, is honeycombed bone in structure and makes up much of the enlarged ends of the long bones and ribs. The structure of this type of bone enables it to absorb large amounts of stress.
Next page