
ABOUT THE Author
Jason E. Konzelmann, BS, NR-P
Mr. Konzelmann has been a paramedic for 19 years in eastern Pennsylvania. He also is an EMT/paramedic adjunct instructor at Lehigh Carbon Community College in Allentown, Pennsylvania, and a PALS, ACLS, and CPR instructor with Lehigh Valley Health Network and St. Lukes University Health Network in Bethlehem, Pennsylvania.
Earlier in his career, Mr. Konzelman worked for 4 years as an administrative supervisor and simulation coordinator with the New York Simulation Center for the Health Sciences, a partnership between the New York University School of Medicine and the City University of New York. He then assumed the simulation coordinator role with the Network Simulation Center of St. Lukes University Health Network, serving the Temple-St. Lukes School of Medicine and St. Lukes School of Nursing, during which time he helped design and implement simulation education experiences for learners in all areas of medicine. He has a B.S. and secondary education certificate in chemistry from Muhlenberg College.
This product is neither sponsored nor endorsed by the National Registry Paramedic Exam.
This publication is designed to provide accurate and authoritative information in regard to the subject matter covered. It is sold with the understanding that the publisher is not engaged in rendering medical, legal, accounting, or other professional services. If legal advice or other expert assistance is required, the services of a competent professional should be sought.
2017 by Kaplan, Inc.
Published by Kaplan Publishing, a division of Kaplan, Inc.
750 Third Avenue
New York, NY 10017
All rights reserved under International and Pan-American Copyright Conventions. By payment of the required fees, you have been granted the non-exclusive, non-transferable right to access and read the text of this eBook on screen. No part of this text may be reproduced, transmitted, downloaded, decompiled, reverse engineered, or stored in or introduced into any information storage and retrieval system, in any form or by any means, whether electronic or mechanical, now known or hereinafter invented, without the express written permission of the publisher.
ISBN: 978-1-5062-1285-2
10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
Kaplan Publishing print books are available at special quantity discounts to use for sales promotions, employee premiums, or educational purposes. For more information or to purchase books, please call the Simon & Schuster special sales department at 866-506-1949.
Physiology, Pathophysiology, and Shock
Learning Objectives
- Explain cellular chemistry.
- Explain dynamic equilibrium and its role in the body.
- Describe the acid-base buffer system in the body.
- Differentiate between metabolic and respiratory acidosis and alkalosis.
- Differentiate, assess, and treat different causes for shock.
To fully understand the disease processes and syndromes you may encounter in the field, it is important to have a working knowledge of cellular processes, i.e., what is happening at the cellular level to cause disease, organ failure, and eventually organism death. However, before any meaningful discussion on that level can happen, understanding what comprises normal is paramount. Disease processes and syndromes can then be looked at as a collection of deviations from normal, rather than as discrete and separate from each other. This chapter will cover normal cellular function, including cellular chemistry and metabolism, life cycles, and homeostasis, or how a cell maintains its steady internal equilibrium with its harsh surroundings. From there, the chapter will discuss what a disruption of these processes can do to the cell and, by extension, to the whole body in the general term known as shock.
Cellular Chemistry
Although not often directly tested on any state or national paramedic examination, basic chemistry can subtly find its way into other questions. This section focuses on terminology, but references to cellular chemistry will occur in future chapters. A strong understanding of the basics can then be built into an improved understanding of physiology and anatomy.
Atomic Structure
All matter, anything that has mass or substance, at the most basic level is made up of at least 1 element but more likely a variety of elements. An element is a pure substance that is entirely comprised of the same atom, which is the smallest complete unit of an element that retains all the exclusive chemical properties of that element. Atoms are composed of discrete particles known as protons, neutrons, and electrons:
- Protons are located in the nucleus and carry a positive charge. The number of protons in the nucleus defines the atom in question. For example, all oxygen atoms have 8 protons in the nucleus, and all nitrogen atoms contain 7 protons. Finally, the atomic number of an element is indicated by the number of protons in the nucleus. Therefore, the atomic number of oxygen is 8, and for nitrogen it is 7.
- Neutrons, also found in the nucleus of the atom, are neutral in charge and serve to provide separation of the normally repellant positive charges of protons. Different isotopes of the same element (same number of protons) are caused by different numbers of neutrons in the nucleus. The sum total of the neutrons and protons in the nucleus approximates the atomic weight of the element. Helium, for example, has 2 protons and 2 neutrons in its nucleus and thus has an atomic weight of 4.
- Electrons are substantially smaller in weight than either neutrons or protons and do not contribute materially to the weight of an atom. They carry a negative charge and are in constant motion around the nucleus. A neutral atom has the same number of electrons and protons; that is, the positive charges in the nucleus perfectly balance the negative charges surrounding it. The model shows an atom and the relative location of the subatomic particles.
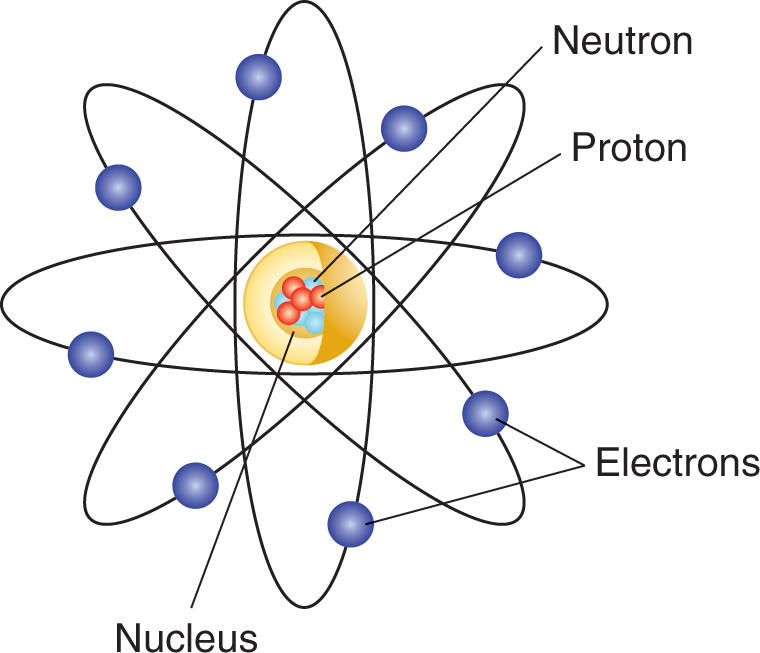
Figure 1.1 Atom Diagram
Simplified model of an atom showing relative locations of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Ions are formed when an atom loses an electron or gains an extra 1 from another source. If electrons outnumber protons in an atom, the atom has an overall negative charge and is referred to as a negative ion or anion, whereas protons outnumbering electrons form a positive ion or cation. Because neutral is always more stableless reactivethan charged ions, positively charged atoms often combine with negatively charged atoms to form molecules.
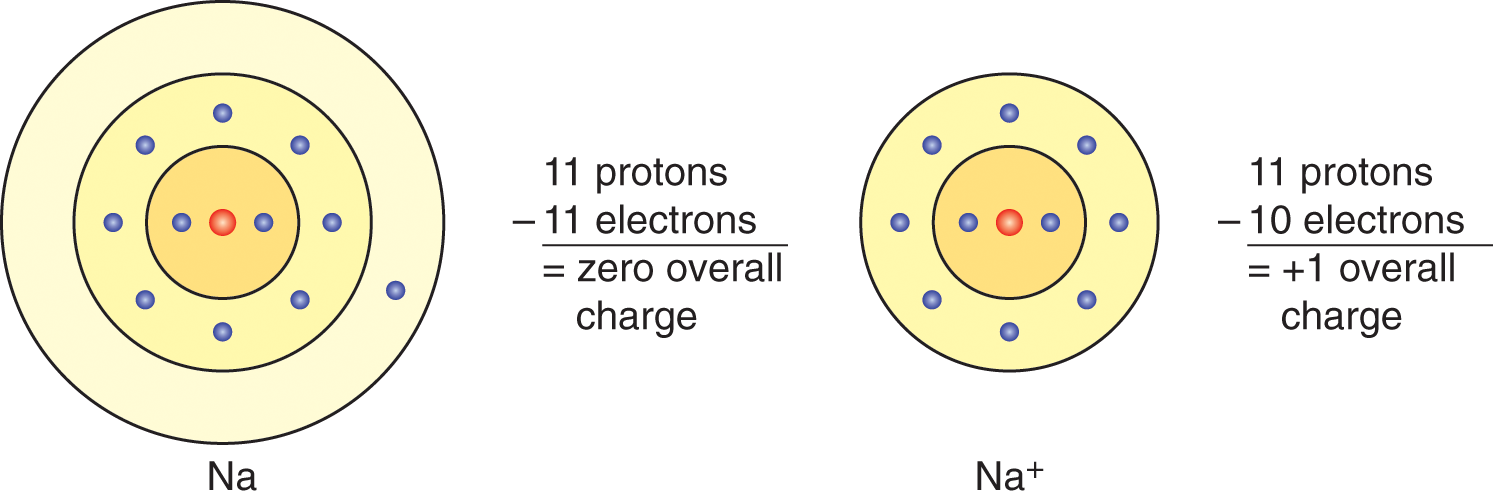
Figure 1.2 Positive Ion Formation
The electron is removed from its path around the nucleus, causing the number of protons to outnumber surrounding electrons.
Molecules and Bonding
A molecule is any structure comprised of 2 or more atoms bonded together. These atoms can be the same as in a molecule of nitrogen or iodine, or they can be different, as when a sodium ion combines with a potassium ion to form potassium chloride.
Within a bond, at least 1 electron is shared by each of the 2 atoms. The degree of sharing of this electron classifies the bond as either covalent or ionic. In covalent bonds, each atom participating in the formation of a bond provides an electron, and the resulting pair of electrons is nearly equally shared between the 2 atoms. This occurs in the same or similar atoms, more specifically when 2 atoms identified as nonmetals bond.
Next page



 Figure 1.1 Atom Diagram
Figure 1.1 Atom Diagram Figure 1.2 Positive Ion Formation
Figure 1.2 Positive Ion Formation