The Tyrant Series
Tyrant
Tyrant: Storm of Arrows
Tyrant: Funeral Games
Killer of Men Series
Killer of Men
Other Novels
Washington and Caesar
T YRANT
KING OF THE
BOSPORUS

CHRISTIAN CAMERON

Contents
For my daughter, Beatrice
Airyanm (Avestan) Noble, heroic.
Aspis (Classical Greek) A large round shield, deeply dished, commonly carried by Greek (but not Macedonian) hoplites.
Baqca (Siberian) Shaman, mage, dream-shaper.
Chiton (Classical Greek) A garment like a tunic, made from a single piece of fabric folded in half and pinned down the side, then pinned again at the neck and shoulders and belted above the hips. A mens chiton might be worn long or short. Worn very short, or made of a small piece of cloth, it was sometimes called a chitoniskos. Our guess is that most chitons were made from a piece of cloth roughly 60 x 90 inches, and then belted or roped to fit, long or short. Pins, pleating, and belting could be simple or elaborate. Most of these garments would, in Greece, have been made of wool. In the East, linen might have been preferred.
Chlamys (Classical Greek) A garment like a cloak, made from a single piece of fabric woven tightly and perhaps even boiled. The chlamys was usually pinned at the neck and worn as a cloak, but could also be thrown over the shoulder and pinned under the right or left arm and worn as a garment. Free men are sometimes shown naked with a chlamys, but rarely shown in a chiton without a chlamys the chlamys, not the chiton, was the essential garment, or so it appears. Men and women both wear the chlamys, although differently. Again, a 60 x 90 piece of cloth seems to drape correctly and have the right lines and length.
Daimon (Classical Greek) Spirit.
Ephebe (Classical Greek) A new hoplite; a young man just training to join the forces of his city.
Epilektoi (Classical Greek) The chosen men of the city or of the phalanx; elite soldiers.
Eudaimia (Classical Greek) Wellbeing. Literally, well-spirited. See daimon, above.
Gamelia (Classical Greek) A Greek holiday.
Gorytos (Classical Greek and possibly Scythian) The open-topped quiver carried by the Scythians, often highly decorated.
Himation (Classical Greek) A heavy garment consisting of a single piece of cloth at least 120 inches long by 60 inches wide, draped over the body and one shoulder, worn by both men and women.
Hipparch (Classical Greek) The commander of the cavalry.
Hippeis (Classical Greek) Militarily, the cavalry of a Greek army. Generally, the cavalry class, synonymous with knights. Usually the richest men in a city.
Hoplite (Classical Greek) A Greek soldier, the heavy infantry who carry an aspis (the big round shield) and fight in the phalanx. They represent the middle class of free men in most cities, and while sometimes they seem like medieval knights in their outlook, they are also like town militia, and made up of craftsmen and small farmers. In the early Classical period, a man with as little as twelve acres under cultivation could be expected to own the aspis and serve as a hoplite.
Hoplomachos (Classical Greek) A man who taught fighting in armour.
Hyperetes (Classical Greek) The Hipparchs trumpeter, servant, or supporter. Perhaps a sort of NCO.
Kithara (Classical Greek) A musical instrument like a lyre.
Kline (Classical Greek) A couch or bed on which Hellenic men and women took meals and perhaps slept, as well.
Kopis (Classical Greek) A bent bladed knife or sword, rather like a modern Ghurka kukri. They appear commonly in Greek art, and even some small eating knives were apparently made to this pattern.
Machaira (Classical Greek) The heavy Greek cavalry sword, longer and stronger than the short infantry sword. Meant to give a longer reach on horseback, and not useful in the phalanx. The word could also be used for any knife.
Parasang (Classical Greek from Persian) About thirty stades. See below.
Phalanx (Classical Greek) The infantry formation used by Greek hoplites in warfare, eight to ten deep and as wide as circumstance allowed. Greek commanders experimented with deeper and shallower formations, but the phalanx was solid and very difficult to break, presenting the enemy with a veritable wall of spear points and shields, whether the Macedonian style with pikes or the Greek style with spears. Also, phalanx can refer to the body of fighting men. A Macedonian phalanx was deeper, with longer spears called sarissas that we assume to be like the pikes used in more recent times. Members of a phalanx, especially a Macedonian phalanx, are sometimes called Phalangites.
Phylarch (Classical Greek) The commander of one file of hoplites. Could be as many as sixteen men.
Porne (Classical Greek) A prostitute.
Pous (Classical Greek) About one foot.
Prodromoi (Classical Greek) Scouts; those who run before or run first.
Psiloi (Classical Greek) Light infantry skirmishers, usually men with bows and slings, or perhaps javelins, or even thrown rocks. In Greek city-state warfare, the psiloi were supplied by the poorest free men, those who could not afford the financial burden of hoplite armour and daily training in the gymnasium.
Sastar (Avestan) Tyrannical. A tyrant.
Stade (Classical Greek) About 1/8 of a mile. The distance run in a stadium. 178 meters. Sometimes written as Stadia or Stades by me. Thirty Stadia make a Parasang.
Taxies (Classical Greek) The sections of a Macedonian phalanx. Can refer to any group, but often used as a company or a battalion. My taxeis has between 500 and 2,000 men, depending on losses and detachments. Roughly synonymous with phalanx above, although a phalanx may be composed of a dozen taxeis in a great battle.
Xiphos (Classical Greek) A straight-bladed infantry sword, usually carried by hoplites or psiloi. Classical Greek art, especially red-figure ware, shows many hoplites wearing them, but only a handful have been recovered and theres much debate about the shape and use. They seem very like a Roman gladius.
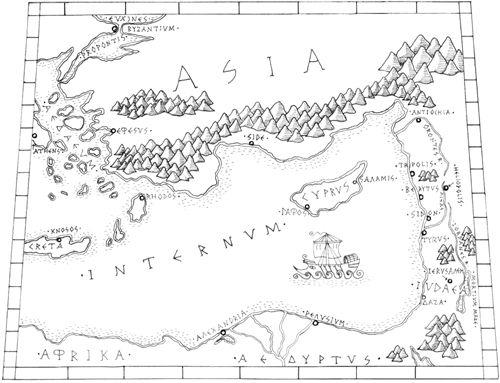
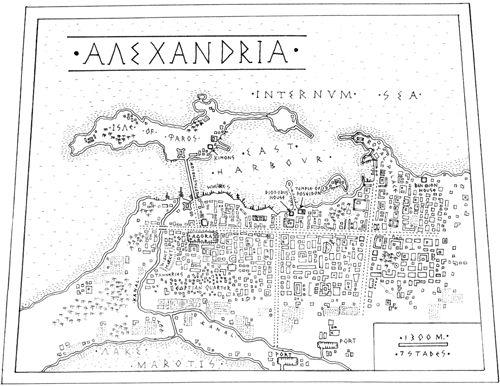
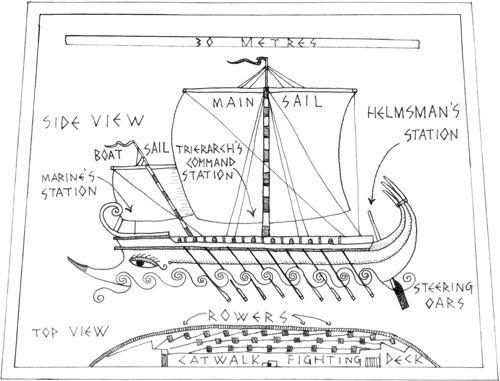
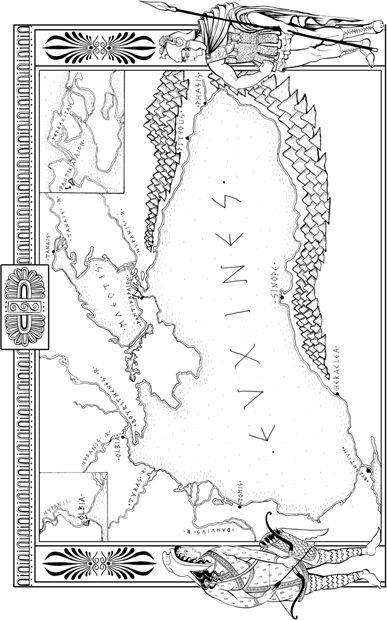
Next page


















