Pages
page i
Data Analytics for Accounting
THIRD EDITION
Vernon J. Richardson
University of Arkansas, Baruch College
Ryan A. Teeter
University of Pittsburgh
Katie L. Terrell
University of Arkansas

page ii

DATA ANALYTICS FOR ACCOUNTING
Published by McGrawHill LLC, 1325 Avenue of the Americas, New York, NY 10019. Copyright 2023 by McGrawHill LLC. All rights reserved. Printed in the United States of America. No part of this publication may be reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, or stored in a database or retrieval system, without the prior written consent of McGrawHill LLC, including, but not limited to, in any network or other electronic storage or transmission, or broadcast for distance learning.
Some ancillaries, including electronic and print components, may not be available to customers outside the United States.
This book is printed on acid-free paper.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 LWI 27 26 25 24 23 22
ISBN 978-1-265-09445-4
MHID 1-265-09445-4
Cover Image: sasirin pamai/Shutterstock
All credits appearing on page or at the end of the book are considered to be an extension of the copyright page.
The Internet addresses listed in the text were accurate at the time of publication. The inclusion of a website does not indicate an endorsement by the authors or McGraw Hill LLC, and McGraw Hill LLC does not guarantee the accuracy of the information presented at these sites.
mheducation.com/highered
page iii
Dedications
My wonderful daughter, Rachel, for your constant love, encouragement, and support. You always make me laugh and smile!
Vern Richardson
To my three wonderful little Teeter tots, who keep me on my toes.
Ryan Teeter
To the Mustache Running Club. Over many miles you all have learned more about accounting data analytics than you ever hoped for! Thanks for all of your supporton and off the trail.
Katie Terrell
page iv
Preface
Data Analytics is changing the business worlddata simply surround us! So many data are available to businesses about each of ushow we shop, what we read, what we buy, what music we listen to, where we travel, whom we trust, where we invest our time and money, and so on. Accountants create value by addressing fundamental business and accounting questions using Data Analytics.
All accountants must develop data analytic skills to address the needs of the profession in the futureit is increasingly required of new hires and old hands. Data Analytics for Accounting, 3e recognizes that accountants dont need to become data scientiststhey may never need to build a data repository or do the real hardcore Data Analytics or learn how to program a computer to do machine learning. However, there are seven skills that analytic-minded accountants must have to be prepared for a data-filled world, including:
Developed analytics mindsetknow when and how Data Analytics can address business questions.
Data scrubbing and data preparationcomprehend the process needed to clean and prepare the data before analysis.
Data qualityrecognize what is meant by data quality, be it completeness, reliability, or validity.
Descriptive data analysisperform basic analysis to understand the quality of the underlying data and their ability to address the business question.
Data analysis through data manipulationdemonstrate ability to sort, rearrange, merge, and reconfigure data in a manner that allows enhanced analysis. This may include diagnostic, predictive, or prescriptive analytics to appropriately analyze the data.
Statistical data analysis competencyidentify and implement an approach that will use statistical data analysis to draw conclusions and make recommendations on a timely basis.
Data visualization and data reportingreport results of analysis in an accessible way to each varied decision maker and his or her specific needs.
Consistent with these skills, its important to recognize that Data Analytics is an iterative process. The process begins by identifying business questions that can be addressed with data, extracting and testing the data, refining our testing, and finally, communicating those findings to management. Data Analytics for Accounting, 3e describes this process by relying on an established Data Analytics model called the IMPACT cycle:
Identify the questions.
Master the data.
Perform test plan.
Address and refine results.
Communicate insights.
Track outcomes.
page v
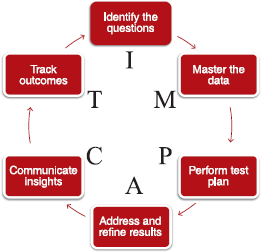
Adapted from Win with Advanced Business Analytics: Creating Business Value from Your Data, by Jean Paul Isson and Jesse S. Harriott.
The IMPACT cycle is described in the first four chapters, and then the process is illustrated in auditing, managerial accounting, financial accounting, and taxes in . In response to instructor feedback, Data Analytics for Accounting, 3e now also includes two new project chapters, giving students a chance to practice the full IMPACT model with multiple labs that build on one another.
Data Analytics for Accounting, 3e emphasizes hands-on practice with real-world data. Students are provided with hands-on instruction (e.g., click-by-click instructions, screenshots, etc.) on datasets within the chapter; within the end-of-chapter materials; and in the labs at the end of each chapter. Throughout the text, students identify questions, extract and download data, perform testing, and then communicate the results of that testing.
The use of real-world data is highlighted by using data from Avalara , LendingClub , College Scorecard , Dillards , the State of Oklahoma , as well as other data from our labs. In particular, we emphasize the rich data from Dillards sales transactions that we use in more than 15 of the labs throughout the text (including ).
Data Analytics for Accounting, 3e also emphasizes the various data analysis tools students will use throughout the rest of their career around two tracksthe Microsoft track (Excel, Power BI) and a Tableau track (Tableau Prep and Tableau Desktopavailable with free student license). Using multiple tools allows students to learn which tool is best suited for the necessary data analysis, data visualization, and communication of the insights gainedfor example, which tool is easiest for internal controls testing, which is best for analysis or querying (using SQL) big datasets, which is best for data visualizations, and so on.
Jean Paul Isson and Jesse S. Harriott, Win with Advanced Business Analytics: Creating Business Value from Your Data (Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2013).
page vi
About the Authors

Vernon J. Richardson
Vernon J. Richardson is a Distinguished Professor of Accounting and the G. William Glezen Chair in the Sam M. Walton College of Business at the University of Arkansas and a Visiting Professor at Baruch College. He received his BS, Master of Accountancy, and MBA from Brigham Young University and a PhD in accounting from the University of Illinois at UrbanaChampaign. He has taught students at the University of Arkansas, Baruch College, University of Illinois, Brigham Young University, Aarhus University, and University of Kansas, and internationally at the China Europe International Business School (Shanghai), Xian Jiaotong Liverpool University, Chinese University of Hong KongShenzhen, and the University of Technology Sydney.










![EMC Education Services [EMC Education Services] - Data Science and Big Data Analytics: Discovering, Analyzing, Visualizing and Presenting Data](/uploads/posts/book/119625/thumbs/emc-education-services-emc-education-services.jpg)




