absolute value: The distance from zero on the number line for a particular term (e.g., the absolute value of 7 is 7written |7|).
arc length: A section of a circle's circumference.
area: The space enclosed by a given closed shape on a plane; the formula depends on the specific shape (e.g., the area of a rectangle equals lengthwidth).
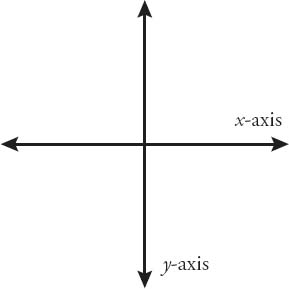
axis: One of the two number lines (x-axis or y-axis) used to indicate position on a coordinate plane. (See figure)
base: In the expression bn, the variable b represents the base. This is the number that you multiply by itself n times. Also can refer to the horizontal side of a triangle.
center (circle): The point from which any point on a circle's radius is equidistant.
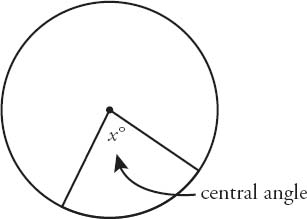
central angle: The angle created by any two radii. (See figure)
circle: A set of points in a plane that are equidistant from a fixed center point.
circumference: The measure of the perimeter of a circle. The circumference of a circle can be found with this formula: C = 2r, where C is the circumference and r is the radius.
coefficient: A number being multiplied by a variable. In the equation y = 2x + 5, the coefficient of the x term is 2.
common denominator: When adding or subtracting fractions, you first must find a common denominator, generally the smallest common multiple of both numbers.
Example:
Given (3/5) + (1/2), the two denominators are 5 and 2. The smallest multiple that works for both numbers is 10. The common denominator, therefore, is 10.
composite number: Any number that has more than two factors. Thus, composite numbers are not prime.
constant: A number that doesn't change, in an equation or expression. You may not know its value, but it's constant in contrast to a variable, which varies. In the equation y = 3x + 2, 3 and 2 are constants. In the equation of a line, y = mx + b, m and b are constants, even if you do not necessarily know their values.
coordinate plane: Consists of a horizontal axis (typically labeled x) and a vertical axis (typically labeled y), crossing at the number zero on both axes.
decimal: Numbers that fall in between integers. A decimal can express a part-to-whole relationship, just as a percent or fraction can.
Example:
The number 1.2 is a decimal. The integers 1 and 2 are not decimals. An integer written as 1.0, however, is considered a decimal. The decimal 0.2 is equivalent to 20% or to 2/10 (= 1/5).
denominator: The bottom of a fraction. In the fraction (7/2), 2 is the denominator.
diameter: A line segment that passes through the center of a circle and whose endpoints lie on the circle.
difference: When one number is subtracted from another, the difference is what is left over. The difference of 7 and 5 is 2, because 7 5 = 2.
digit: The ten numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9. Used in combination to represent other numbers (e.g., 12 or 0.38).
distributed form: Presenting an expression as a sum or difference. In distributed form, terms are added or subtracted. For example, x 2 1 is in distributed form, as is x 2 + 2x + 1. In contrast, (x + 1)(x 1) is not in distributed form; it is in factored form.
divisible: If an integer x divided by another number y yields an integer, then x is said to be divisible by y.
Example:
The number 12 divided by 3 yields the integer 4. Therefore, 12 is divisible by 3. However, 12 divided by 5 does not yield an integer. Therefore, 12 is not divisible by 5.
divisor: The part of a division operation that comes after the division sign. In the operation 22 4 (or 22/4), 4 is the divisor. Divisor is also a synonym for factor. (See factor)
equation: A combination of mathematical expressions and symbols that contains an equals sign. For example, 3 + 7 = 10 is an equation, as is x + y = 3. An equation makes a statement: left side equals right side.
equilateral triangle: A triangle in which all three angles are equal (and since the three angles in a triangle always add to 180, each angle is equal to 60). In addition, all three sides are of equal length.
even: An integer is even if it is divisible by 2. For example, 14 is even because 14/2 equals the integer 7.
exponent: In the expression bn, the variable n represents the exponent. The exponent indicates how many times to multiply the base, b, by itself. For example, 43 = 4 4 4, or 4 multiplied by itself three times.
expression: A combination of numbers and mathematical symbols that does not contain an equals sign. For example, xy is an expression, as is x + 3. An expression represents a quantity.
factor: Positive integers that divide evenly into an integer. Factors are equal to or smaller than the integer in question. For example, 12 is a factor of 12, as are 1, 2, 3, 4, and 6.
factored form: Presenting an expression as a product. In factored form, expressions are multiplied together. The expression (x + 1)(x 1) is in factored form: (x + 1) and (x 1) are the factors. In contrast, x 2 1 is not in factored form; it is in distributed form.
factor foundation rule: If a is a factor of b, and b is a factor of c, then a is also a factor of c. For example, 2 is a factor of 10 and 10 is a factor of 60. Therefore, 2 is also a factor of 60.
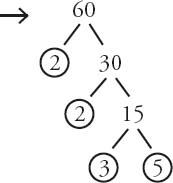
factor tree: Use the factor tree to break any number down into its prime factors. For example:
FOIL: First, Outside, Inside, Last; an acronym to remember the method for converting from factored to distributed form in a quadratic equation or expression. For example, (x + 2)(x 3) is a quadratic expression in factored form. Multiply the First, Outside, Inside, and Last terms to get the distributed form: xx = x 2, x 3 = 3x, x 2 = 2x, and 2 3 = 6. The full distributed form is x 2 3x + 2x 6. This can be simplified to x 2x 6.
fraction: A way to express numbers that fall in between integers (though integers can also be expressed in fractional form). A fraction expresses a part-to-whole relationship in terms of a numerator (the part) and a denominator (the whole); for example, 3/4 is a fraction.
hypotenuse: The longest side of a right triangle. The hypotenuse is always the side opposite the largest angle of a triangle, so in a right triangle, it is opposite the right angle.
improper fraction: Fractions that are greater than 1. An improper can also be written as a mixed number. For example, 7/2 is an improper fraction. This can also be written as a mixed number: 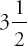 .
.
inequality: A comparison of quantities that have different values. There are four ways to express inequalities: less than (<), less than or equal to (), greater than (>), or greater than or equal to (). Can be manipulated in the same way as equations with one exception: when multiplying or dividing by a negative number, the inequality sign flips.
Next page





















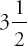 .
.