This chapter explains the definition and benefits of cloud computing . It also covers cloud computing deployment models and service models. Finally, it covers the metering and chargeback concepts. Tons of resources are available on cloud computing, hence the objective here is to give you a high-level overview.
Overview
The origin of cloud computing is not known, and it has nothing to do with real cloud. So why is it called cloud computing ? The word cloud is a metaphor to indicate the abstraction between the end user and the resources. Cloud computing is more of a pay-as-you-go model, compared to a do-it-yourself (DIY) model. This can easily be understood from an electricity example. You consume electricity and pay on the basis of the number of units consumed. While using it, you are not concerned about how the electricity is produced, distributed, or managed. Similarly, in cloud computing, you just pay for computing resources for the duration of your use. You are not concerned with how these computing resources are hosted or managed.
In database terms, you will get your database up and running very quickly. You dont need to worry about procurement of server, configuration, and installation of various software, or with, maintaining the datacenter, infrastructure, hardware, or operating system.
In this book, you will first learn about the cloud computing concepts, followed by database as a service details, and then you will learn about the major aspects of database administration, including provisioning, HA and DR setup, monitoring, day-to-day administration activities, and backup and recovery, all from the cloud perspective.
What Is Cloud Computing
Defining cloud computing is complex and many definitions exist. The official definition is given by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
Its essentially a web-based service for computing resources, including server, network, storage, and applications. This service is ubiquitous and provided as on-demand basis.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Companies have traditionally believed in owning the assets and managing them on their own, but this model meant large capital expenditure (CAPEX) and operating expenditure (OPEX) costs. Another challenge with this traditional approach is related to meeting the higher computing requirements due to a single business event. Buying extra hardware and resources for handling spikes means waste of resources during the non-peak times.
The biggest benefit of cloud computing is saving on CAPEX related to infrastructure costs. The various benefits are listed in Table .
Table 1-1.
Cloud Computing Benefits
Category | Benefits |
|---|
Provisioning | Faster provisioning makes cloud computing an ideal platform for test and dev environments |
Scalability | Scale up and scale out on-demand |
Resource release | Faster resource release/scale down |
CAPEX | No investment required for setting up the infrastructure |
OPEX | Lower OPEX due to pay-as-you-go model |
Availability | Highly available |
Skill requirements | Lower skill required due to built-in automation |
Accessibility | Accessible using web-based portal, hence it is ubiquitous |
Challenges of Cloud Computing
There are many challenges related to cloud computing, some of the key ones are listed here:
Cost of service: While cloud computing is good for ad hoc usage, it becomes more costly if you try to adopt it as the only solution for all your hosting requirements.
Laws of the land: Local laws in various countries dont allow you to keep data on servers that arent in direct control of the data owner. In a few cases, keeping data outside of a given country is also not allowed.
Cloud interoperability: Moving things between different cloud service providers is a very difficult task.
Geographical presence: Cloud vendors do not have a presence in all geographies, which means cloud computing becomes infeasible for some customers.
Application certification: Not all applications are certified to run in a cloud; this is one of the key challenges in cloud computing adoption.
Lack of an integrated solution provider: Currently no single vendor provides all the cloud services that any given organization needs. For example, converged infrastructure as a service is provided by Oracle, whereas physical hardware as IaaS is provided by IBM SoftLayer.
Security: Security used to be the biggest challenge for cloud computing, but this is less the case nowadays. Cloud service providers get all security certifications and have a proven track record. For example, AWS hosts the American Security agencys cloud computing infrastructure. Many organizations still perceive cloud security as a major challenge.
Cloud Computing Service Models
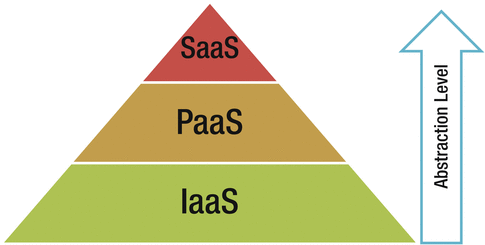
There are three commonly used service models (see Figure ):
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Figure 1-1.
Cloud computing service models
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS providers supply physical/virtual machines, storage, firewall, load balances, VLANs, etc. These are provided from a vast pool of resources. In IaaS, the consumer is responsible for patching and maintaining the operating system and the application software. In Oracle database context, IaaS means that the cloud service provider gives you the server, network, storage, OS, and other software that is required to run Oracle. Sometimes, Oracle software is preinstalled or the server comes with Oracle binaries. You are allowed to bring your own software image.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS providers give the dev environment like Dev toolkit (for example, Microsoft Azure and Google App engine). In PaaS, the consumer is not responsible for managing the underlying infrastructure and doesnt administer the underlying cloud components such as the operating system, database, etc. In Oracle database context, PaaS means Oracle database as a service. Here, you dont need to worry about installing Oracle or managing the database server.