Machine component analysis with MATLAB
First edition
Dan B. Marghitu
Mihai Dupac

Table of Contents
List of tables
- Tables in Chapter Four
List of figures
- Figures in Chapter One
- Figures in Chapter Two
- Figures in Chapter Three
- Figures in Chapter Four
- Figures in Chapter Five
- Figures in Chapter Six
Landmarks
Copyright
Butterworth-Heinemann is an imprint of Elsevier
The Boulevard, Langford Lane, Kidlington, Oxford OX5 1GB, United Kingdom
50 Hampshire Street, 5th Floor, Cambridge, MA 02139, United States
Copyright 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, or any information storage and retrieval system, without permission in writing from the publisher. Details on how to seek permission, further information about the Publisher's permissions policies and our arrangements with organizations such as the Copyright Clearance Center and the Copyright Licensing Agency, can be found at our website: www.elsevier.com/permissions.
This book and the individual contributions contained in it are protected under copyright by the Publisher (other than as may be noted herein).
Notices
Knowledge and best practice in this field are constantly changing. As new research and experience broaden our understanding, changes in research methods, professional practices, or medical treatment may become necessary.
Practitioners and researchers must always rely on their own experience and knowledge in evaluating and using any information, methods, compounds, or experiments described herein. In using such information or methods they should be mindful of their own safety and the safety of others, including parties for whom they have a professional responsibility.
To the fullest extent of the law, neither the Publisher nor the authors, contributors, or editors, assume any liability for any injury and/or damage to persons or property as a matter of products liability, negligence or otherwise, or from any use or operation of any methods, products, instructions, or ideas contained in the material herein.
Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data
A catalog record for this book is available from the Library of Congress
British Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data
A catalogue record for this book is available from the British Library
ISBN: 978-0-12-804229-8
For information on all Butterworth-Heinemann publications visit our website at https://www.elsevier.com/books-and-journals

Publisher: Matthew Deans
Acquisition Editor: Brian Guerin
Editorial Project Manager: Isabella C. Silva
Production Project Manager: Nirmala Arumugam
Designer: Mark Rogers
Typeset by VTeX
Preface
Dan B. Marghitu; Mihai Dupac
This book is intended as a supplement for courses in machine component design and as a reference for mechanical engineers. The book uses MATLAB as a tool to analyze and solve machine component problems.
The solutions of the problems are obtained analytically and numerically using MATLAB. Many figures are generated with MATLAB programs. Specific functions dealing with machine components are created. The book will assist the undergraduate and advanced undergraduate students interested in machine element analysis. The project can be used for classroom instruction and it can be used for a self-study and can also be offered as distance learning.
The chapters of the book are: stress and deflection, fatigue failure, screws, rolling bearings, lubrication and sliding bearings, and spur gears.
Chapter One
Stress and deflection
Abstract
This chapter presents some of the key elements related to the theory of stress and strain, stress analysis and deformation of mechanical parts due to the action of forces (axial, bending, or combined loads) and moments exerted on them. The presented concepts cover the definition of normal and shear stress and strain, normal and shear components, principal stress components, Mohr's circle construction for two and three-dimensional state of stress and its graphical interpretation, Hook's law and Poisson's ratio, deflection and stress energy. Several problems presenting applications of the theory are solved analytically and numerically using MATLAB.
Keywords
Stress; Strain; Stress components; Deflection; Mohr's circle; Principal stresses; Stress energy
1.1 Stress components
In the design process, the uniform distribution of stresses is usually considered, that is, the results of forces and moments applied to an element represent pure shear or pure tension. If a force F (tension) acts at the ends of a straight bar its line of action incorporates the centroid of the section. If one piece is cut and removed from the bar (made of a homogeneous material), one can replace its effect through a force F=A 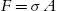 uniformly distributed at the cut. The normal stress can then be expressed as
uniformly distributed at the cut. The normal stress can then be expressed as
= F A ,
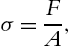 (1.1)
(1.1)
where A is the bar cross-sectional area. For an element in shear the uniform shear stress distribution is
= F A .
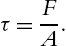 (1.2)
(1.2)
Stress elements represent a convenient way to show stresses acting at some point of a body. A three-dimensional Cartesian stress element with the normal stresses x 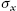 , y
, y 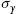 , and z
, and z 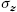 , and the shear stresses xz
, and the shear stresses xz 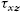 , zx
, zx 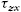 , xy
, xy 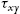 , yx
, yx 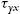 , yz
, yz 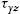 , and zy
, and zy 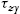 , is shown in A. For the shear stresses, using the static equilibrium, results in
, is shown in A. For the shear stresses, using the static equilibrium, results in
x z = z x , y x = x y , z y = y z .













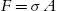 uniformly distributed at the cut. The normal stress can then be expressed as
uniformly distributed at the cut. The normal stress can then be expressed as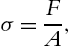 (1.1)
(1.1)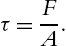 (1.2)
(1.2)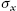 , y
, y 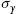 , and z
, and z 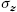 , and the shear stresses xz
, and the shear stresses xz 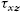 , zx
, zx 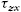 , xy
, xy 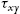 , yx
, yx 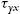 , yz
, yz 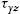 , and zy
, and zy 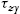 , is shown in A. For the shear stresses, using the static equilibrium, results in
, is shown in A. For the shear stresses, using the static equilibrium, results in