
Table of Contents
List of Tables
- List of Abbreviations
- Chapter 5
- Chapter 7
- Chapter 8
List of Illustrations
- Chapter 1
- Chapter 2
- Chapter 3
- Chapter 4
- Chapter 5
- Chapter 6
- Chapter 7
- Chapter 8
- Chapter 9
Guide
Pages
IEEE Press
445 Hoes Lane
Piscataway, NJ 08854
IEEE Press Editorial Board
Ekram Hossain, Editor in Chief
| Jn Atli Benediktsson | David Alan Grier | Elya B. Joffe |
| Xiaoou Li | Peter Lian | Andreas Molisch |
| Saeid Nahavandi | Jeffrey Reed | Diomidis Spinellis |
| Sarah Spurgeon | Ahmet Murat Tekalp |
Whole-Angle MEMS Gyroscopes
Challenges and Opportunities
Doruk Senkal
Andrei M. Shkel
Copyright 2020 by The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc. All rights reserved.
Published by John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, New Jersey.
Published simultaneously in Canada.
No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, scanning, or otherwise, except as permitted under Section 107 or 108 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act, without either the prior written permission of the Publisher, or authorization through payment of the appropriate per-copy fee to the Copyright Clearance Center, Inc., 222 Rosewood Drive, Danvers, MA 01923, (978) 750-8400, fax (978) 750-4470, or on the web at www.copyright.com. Requests to the Publisher for permission should be addressed to the Permissions Department, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 111 River Street, Hoboken, NJ 07030, (201) 748-6011, fax (201) 748-6008, or online at http://www.wiley.com/go/permission.
Limit of Liability/Disclaimer ofWarranty: While the publisher and author have used their best efforts in preparing this book, they make no representations or warranties with respect to the accuracy or completeness of the contents of this book and specifically disclaim any implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. No warranty may be created or extended by sales representatives or written sales materials. The advice and strategies contained herein may not be suitable for your situation. You should consult with a professional where appropriate. Neither the publisher nor author shall be liable for any loss of profit or any other commercial damages, including but not limited to special, incidental, consequential, or other damages.
For general information on our other products and services or for technical support, please contact our Customer Care Department within the United States at (800) 762-2974, outside the United States at (317) 572-3993 or fax (317) 572-4002.
Wiley also publishes its books in a variety of electronic formats. Some content that appears in print may not be available in electronic formats. For more information aboutWiley products, visit our web site at www.wiley.com.
Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data is applied for
ISBN 9781119441885
Cover Design: Wiley
Cover Image: Courtesy of Doruk Senkal
List of Abbreviations
Table 1 Control system abbreviations.
| Symbol | Description |
| Quadrature | Unwanted component of oscillation that interferes with estimation of the pattern angle, manifests as a result of structural imperfections |
| AGC | Amplitude Gain Control, closedloop control of drive amplitude |
| PLL | Phase Locked Loop, closedloop control system that generates an AC signal with a predetermined phase offset from the resonator |
| FTR | Forcetorebalance, closedloop control system that actively drives the pattern angle to a setpoint |
| Quadrature null | Closedloop control system that actively suppresses the effects of structural imperfections within the gyroscope |
Table 2 Mechanical parameters of the resonator.
| Symbol | Description |
| f | Mean frequency of the two primary modes of the resonator |
| Mean energy decay time constant of the resonator |
| Qfactor | Ratio of stored energy to energy loss per vibration cycle (Q = f) |
| f | Frequency split between primary modes in Hz (f = fxfy) |
| Frequency split between primary modes in rad/s ( = xy) |
| 1 | Measure of anisodamping within the gyroscope (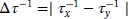 ) ) |
| Angle defining the orientation of actual versus intended axes of elasticity |
| Angle defining the orientation of actual versus intended axes of damping |
| (x, y, z) | Coordinate frame oriented along intended axes of symmetry x and y |
| n = 2 mode | A 4node degenerate mode pair of a wineglass or ring/disk system |
| n = 3 mode | A 6node degenerate mode pair of a wineglass or ring/disk system |
| Precession pattern | Vibration pattern formed by superposition of x and y vibratory modes, which is capable of changing its orientation (precesses) when subjected to Coriolis forces or an external forcing function |
| Pattern angle () | Orientation of the precession pattern in degrees, which is a measure of angular rotation in a Rate Integrating Gyroscope |
Preface
Coriolis Vibratory Gyroscopes (CVGs) can be divided into two broad categories based on the gyroscope's mechanical element: degenerate mode gyroscopes (type 1), which have xy symmetry, and nondegenerate mode gyroscopes (type 2), which are designed intentionally to be asymmetric in x and y modes.
Currently, nondegenerate mode gyroscopes fulfill the needs of a variety of commercial applications, such as tilt detection, activity tracking, and gaming. However, when it comes to inertial navigation, where sensitivity and stability of the sensors are very important, commercially available MEMS sensors fall short by three orders of magnitude. Degenerate mode gyroscopes, on the other hand, offer a number of unique advantages compared to nondegenerate vibratory rate gyroscopes, including higher rate sensitivity, ability to implement wholeangle mechanization with mechanically unlimited dynamic range, exceptional scale factor stability, and a potential for selfcalibration. For this reason, as the MEMS gyroscope development is reaching maturity, the Research and Development focus is shifting from highvolume production of lowcost nondegenerate mode gyroscopes to high performance degenerate mode gyroscopes. This paradigm shift in MEMS gyroscope research and development creates a need for a reference book to serve both as a guide and an entry point to the field of degenerate mode gyroscopes.
Next page












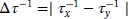 )
)