Goodman - Guitar and Harmonica Method
Here you can read online Goodman - Guitar and Harmonica Method full text of the book (entire story) in english for free. Download pdf and epub, get meaning, cover and reviews about this ebook. genre: Children. Description of the work, (preface) as well as reviews are available. Best literature library LitArk.com created for fans of good reading and offers a wide selection of genres:
Romance novel
Science fiction
Adventure
Detective
Science
History
Home and family
Prose
Art
Politics
Computer
Non-fiction
Religion
Business
Children
Humor
Choose a favorite category and find really read worthwhile books. Enjoy immersion in the world of imagination, feel the emotions of the characters or learn something new for yourself, make an fascinating discovery.
Guitar and Harmonica Method: summary, description and annotation
We offer to read an annotation, description, summary or preface (depends on what the author of the book "Guitar and Harmonica Method" wrote himself). If you haven't found the necessary information about the book — write in the comments, we will try to find it.
Guitar and Harmonica Method — read online for free the complete book (whole text) full work
Below is the text of the book, divided by pages. System saving the place of the last page read, allows you to conveniently read the book "Guitar and Harmonica Method" online for free, without having to search again every time where you left off. Put a bookmark, and you can go to the page where you finished reading at any time.
Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
GUITAR AND HARMONICAMETHOD
By George Goodman
Copyright 2013 GeorgeGoodman
Smashwords Edition,License Notes
This ebook is licensedfor your personal enjoyment only. This ebook may not be re-sold orgiven away to other people. If you would like to share this bookwith another person, please purchase an additional copy for eachrecipient. If youre reading this book and did not purchase it, orit was not purchased for your use only, then please return toSmashwords.com and purchase your own copy. Thank you for respectingthe hard work of this author.
Visit us on the web at:http://www.georgegoodman.com
Email:contact@georgegoodman.com
Table of Contents
Hi, my name isGeorge Goodman and I love music - learning, playing, recording andteaching classic rock, folk and blues songs on guitar andharmonica.
There is a greatamount of materials available explaining and showing how to playguitar or how to play harmonica on their own but there is verylittle material that I have found that explains how to play the twotogether, how the harmonica relates to the guitar, what holes toplay when a particular chord is played on guitar, or how todetermine which harmonica to play when certain guitar chords areplayed.
In response tomany of my guitar and harmonica song lesson videos which you cansee on my website, georgegoodman.com , Ihave received many comments to the effect that it looks toodifficult to play both instruments at the same time.
So the reason Ihave assembled this eBook is threefold.
1) To provide thebasics to anyone who shares the same love for great songs and wantsto learn to play them on guitar and harmonica.
2) To fill in thevoid or absence of instruction relating the two instrumentstogether.
3) To dispel theillusion that playing guitar and harmonica at the same time is toodifficult.
This book isdivided into three sections. The first two sections deal withproviding basic instruction for both instruments as well as abreakdown of rhythm and counting the beat.
From a rhythmperspective, I believe that people have an innate ability to keeptime. When a persons favourite song is playing, the bodyinstinctively responds by tapping a foot to the beat of the music.The listener doesnt need to think about keeping in time with themusic. It just happens. Strumming a guitar to keep time or to playrhythm is very similar to tapping your foot in time. It is simplykeeping time with a different part of the body and can be practicedand learned so that rhythm guitar playing becomes instinctualallowing more focus to be available to be directed to the harmonicaplaying.
Basicunderstanding, having a basic setup guitar, harmonica, and holder- and a bit of practice on each instrument is all you need to getstarted and in the first two sections Ill take you through whatyou need to know.
The third sectionbrings the two instruments together. Basic music theory is exploredto help explain which key harmonica to use depending on the chordsof the song and what notes or holes to play depending on aparticular chord. Practice exercises bring these concepts home,bring the two instruments together, help refine the skills youdevelop from the first two sections and introduce ear training tohear chord tones, scale tones, degrees of the scale, intervals andto understand what youre hearing.
Lets do this.
Music theory isexplained in more depth in the chapter but reference to notes and othermusical elements is necessary when discussing any musical ideas andinstruments. So to get started, I wanted to briefly introduce acouple of music concepts, notes and intervals.
The standardWestern system of music is made up of 12 repeatable notes. Thesenotes are named by letters A, B, C, D, E, F and G, plus twomodifier symbols, sharp (#) and flat (b). Theinterval between two adjacent notes is called a semi-tone.Two semi-tones make up the interval known as a whole tone.To sharp a note is to raise the note by a semi-tone. To flat a noteis to lower a note by a semi-tone.
That should coverthe very basics so that I can introduce note names and intervalswithout having to delve right away into too much theory.
Lets get startedby learning the parts of a typical steel string acoustic guitar asshown below.
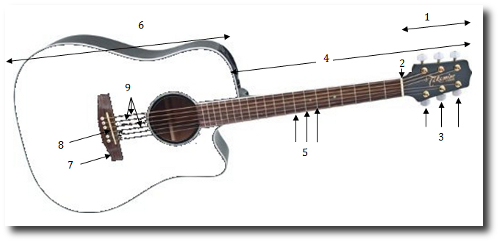
1) Head located at the end of the instrument and is outfitted with machineheads where the strings attach.
2) Nut strip of hard material where the neck meets the head. The nut hasgrooves in it to guide each of the strings laterally along thelength of the guitar.
3) MachineHeads or Tuning Keys located in the head of the guitar areused to tune the guitar by changing the tension in the strings.Increasing the tension raises the pitch while decreasing thetension lowers the pitch.
4) Neck consists of the guitars fretboard and frets, head and machineheads. In order for a guitar to stay in tune and produce constantpitches, the neck needs to withstand the tension of the stringswithout bending. This is one of the main features that separate agood guitar from a cheap guitar.
5) Fretboard orFingerboard lies along the flat of the neck and is dividedinto sections by small metal strips called frets. Pinching a stringagainst the fretboard effectively raises the pitch of a note byshortening the vibrating length of the string. The longer thevibrating length of a string, the lower the pitch. The shorter thelength, the higher the pitch.
6) Frets are raised metal strips that are inserted perpendicularly along thefretboard to divide the neck into segments. Each fret represents asemi-tone in the standard 12 tone western system.
7) Body The body of a guitar includes the main body cavity, thesound board, sound hole and internal bracing.In acoustic guitars, the body is a main determinant in overallsound quality. Sound vibrations are transferred to the body throughthe bridge and saddle via the sound board which isthe top of the guitar containing the sound whole and on which thebridge and saddle are mounted. The main factors that determinesound quality are the material used to create the sound board andthe shape and size of the resonant cavity of the body. The majorityof the guitars sound is heard through the vibration of the soundboard as the energy of the vibrating strings is transferred toit.
8) Bridge The bridge serves two main functions. It holds the strings in placeon the body by way of the saddle and bridge pins as well astransferring the vibration from the strings to the soundboard
9) Strings The standard acoustic guitar has 6 strings which are typicallymade from steel or alloy while classical guitars usually use bothnylon and metal. The 6 strings have varying thicknesses with thethickest string used for the lowest-pitched notes and the thinnestfor the highest pitched notes. Sets of guitar strings come indifferent gauges which determines the thicknesses of each of thestrings. String may come in extra-light through to heavy guage. Thelighter guage strings are easier to play and bend but will breakmore often while the heavier guage strings will be harder to playbut will provide a bigger sound.
Naming theFingers, Frets and Strings
In my videos, Ioften refer to a particular fret, string or finger by number. Withthat in mind, lets take a look at the numbering system forfingers, frets and strings.
Numbering
TheFingers The index finger is 1, middle finger is 2, ringfinger is 3 and the pinkie is 4.

Font size:
Interval:
Bookmark:
Similar books «Guitar and Harmonica Method»
Look at similar books to Guitar and Harmonica Method. We have selected literature similar in name and meaning in the hope of providing readers with more options to find new, interesting, not yet read works.
Discussion, reviews of the book Guitar and Harmonica Method and just readers' own opinions. Leave your comments, write what you think about the work, its meaning or the main characters. Specify what exactly you liked and what you didn't like, and why you think so.