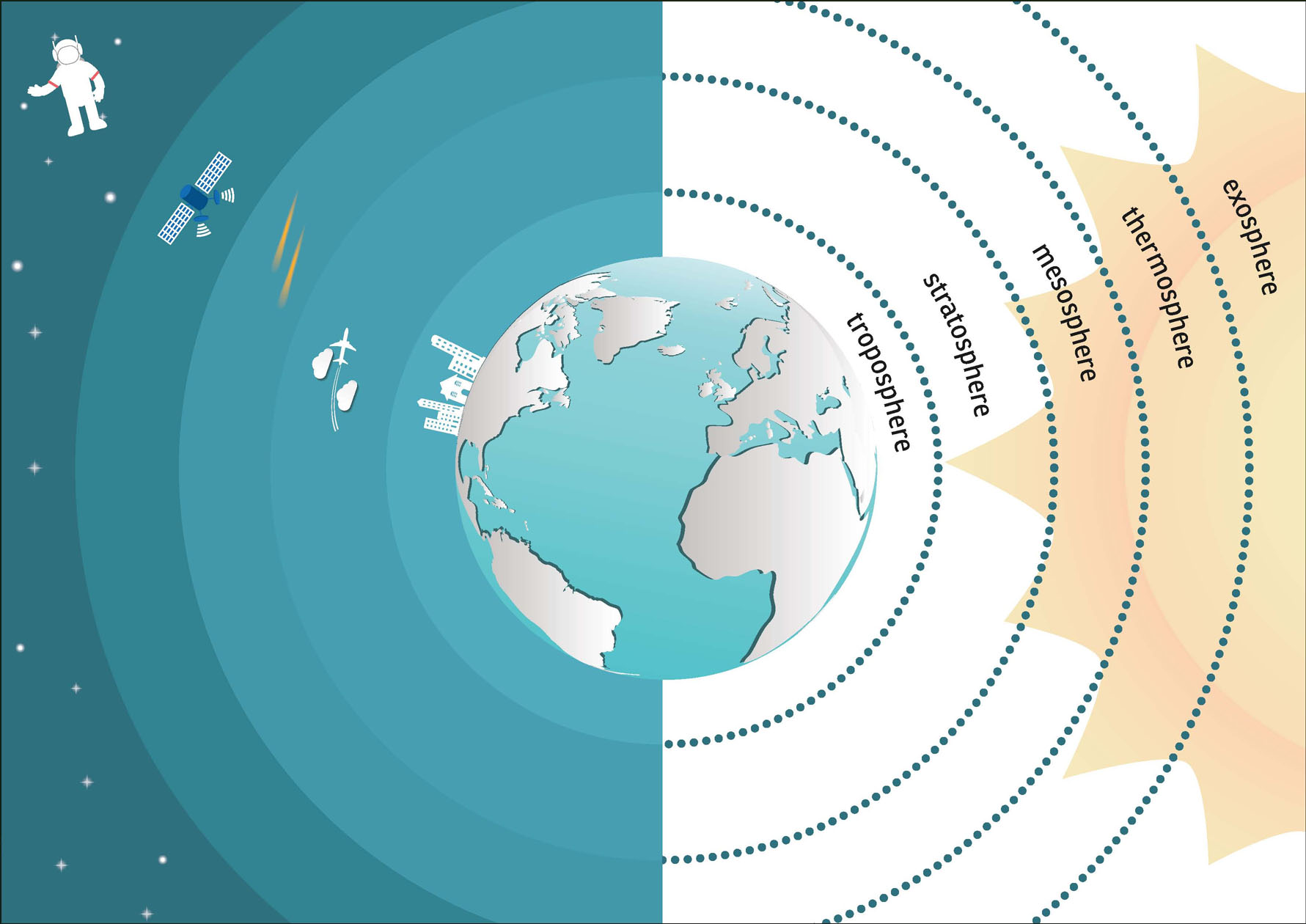
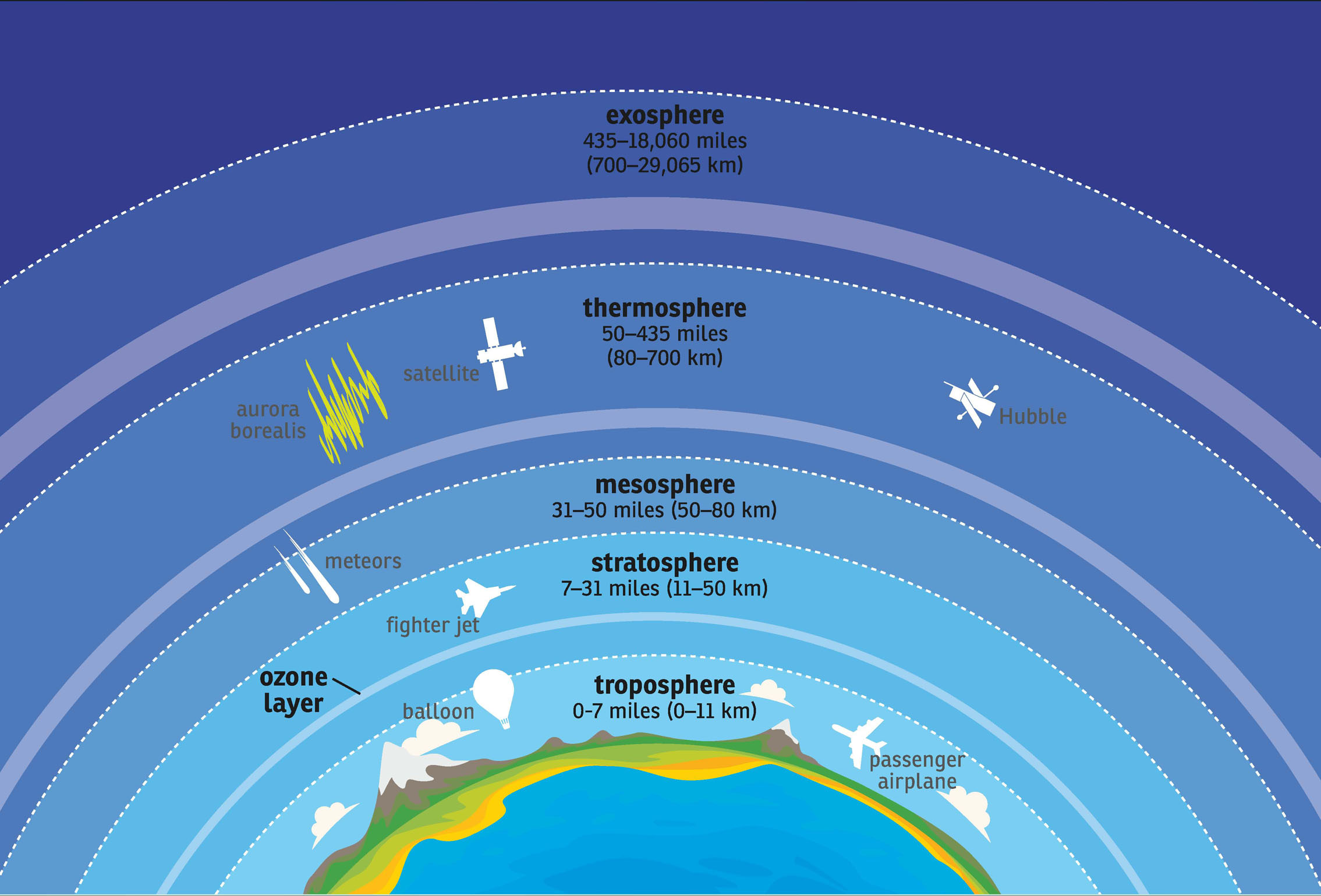
One problem of the stratosphere is that any particle that ends up in this layer can stay there for a long time for months or even years. Ozone-destroying chemicals like chlorofluorocarbons are one concern in the stratosphere. Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are chemicals that contain atoms of carbon, chlorine, and fluorine. They are used in the manufacturing of aerosol sprays and can destroy stratospheric ozone.
The mesosphere stretches from about 31 miles (50 km) above Earth to 50 miles (80 km) above Earth. Less is known about the mesosphere than any of the other layers. Its difficult for scientists to study this layer. Its too high for weather balloons and aircraft to fly, and its too low for satellites.
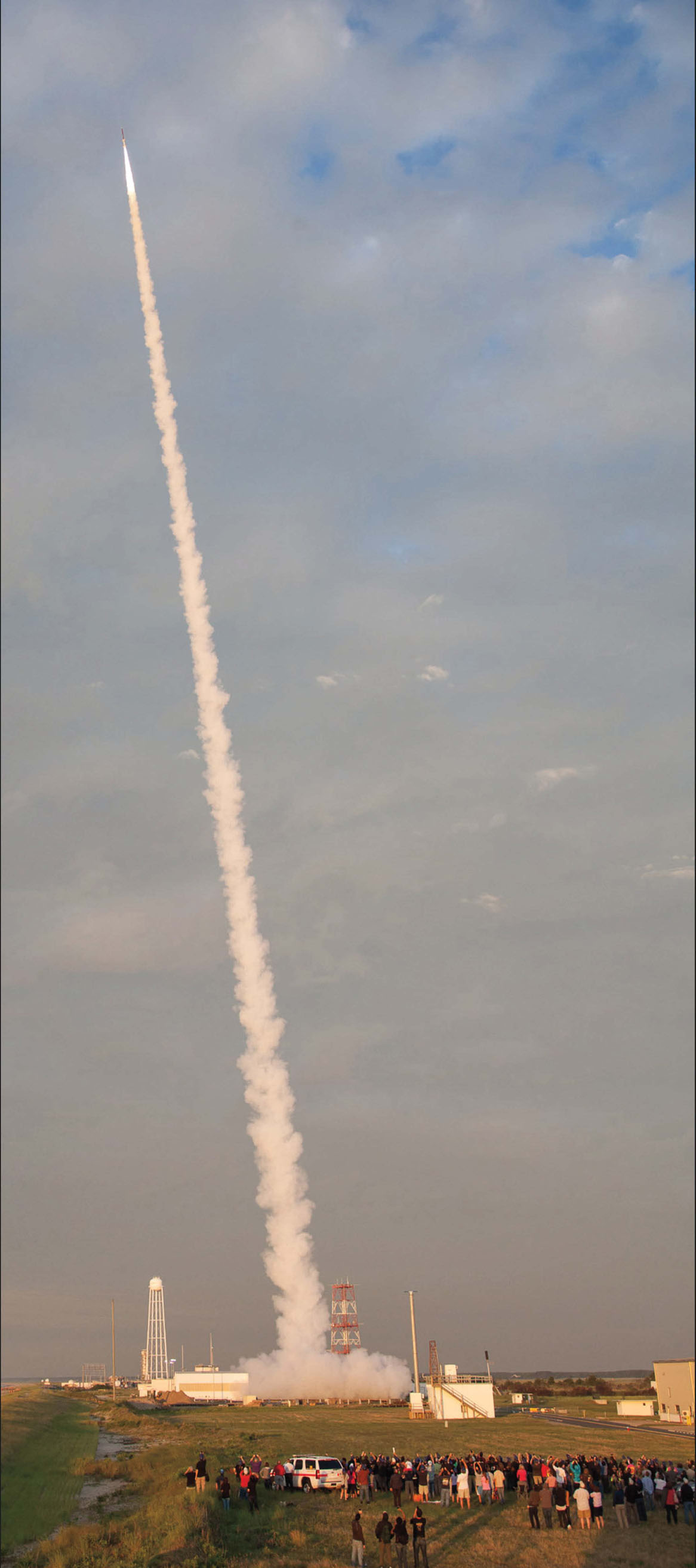
NASA launches a suborbital sounding rocket carrying student experiments on June 26, 2015.
FACT
To learn more about this layer, scientists from NASA send sounding rockets into the mesosphere. These rockets carry scientific instruments into space. These missions only last between 5 and 20 minutes. During that time scientists are able to obtain new data about this area of the atmosphere.
THERMOSPHERE
This layer of the atmosphere has very hot temperatures. The gases in this layer absorb high-energy radiation, causing extremely high temperatures in the thermosphere. The main parts of air in the upper thermosphere include oxygen atoms, nitrogen atoms, and helium.
EXOSPHERE
The highest part of the atmosphere is called the exosphere. There isnt a distinct line between Earths atmosphere and outer space. The atmosphere eventually gets so thin that it becomes an empty vacuum of space. Some scientists argue that outer space starts much lower in the thermosphere. Others think outer space begins at the edge of the exosphere. They say that atmosphere is still present until the lightest particles, such as hydrogen atoms, start escaping from Earths gravity and into space. The exosphere is composed almost entirely of hydrogen gas. There are only small amounts of other atmospheric gases like oxygen, helium, and carbon dioxide.
The word exosphere comes from the Greek word exo , which means outside, and sphaira , which means sphere.
CHAPTER 2
THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION
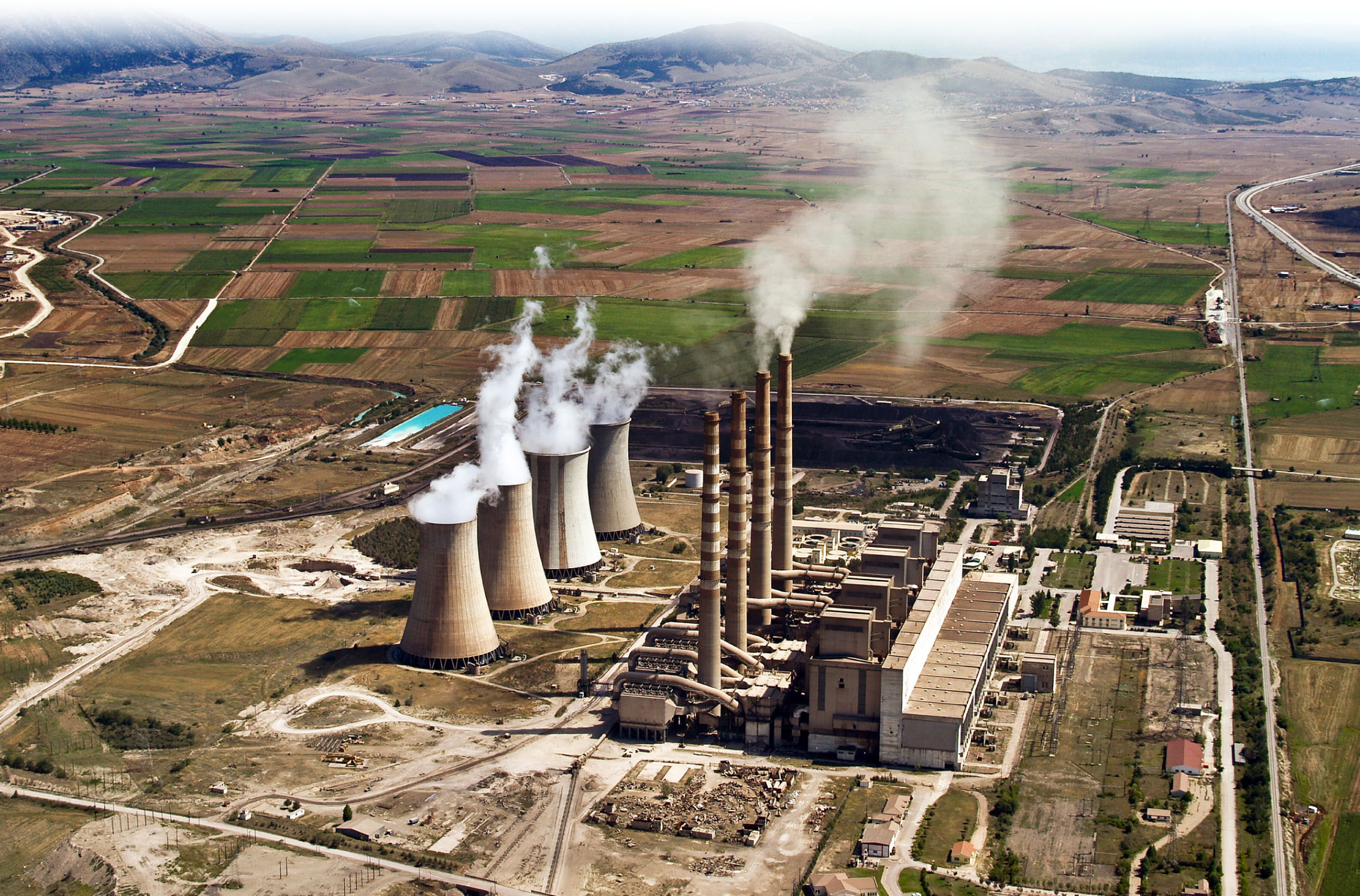
In the modern era, humans have made a big impact on the atmosphere. Humans began burning materials formed from plants and animals that died millions of years ago. Newly invented machines during this time needed energy to run. This energy came from the burning of the fossil fuel coal. Soon, coal smoke filled the sky. Some cities were so polluted it looked like nighttime in the middle of the day.
A fossil fuel power plant releases smoke into the air while operating.
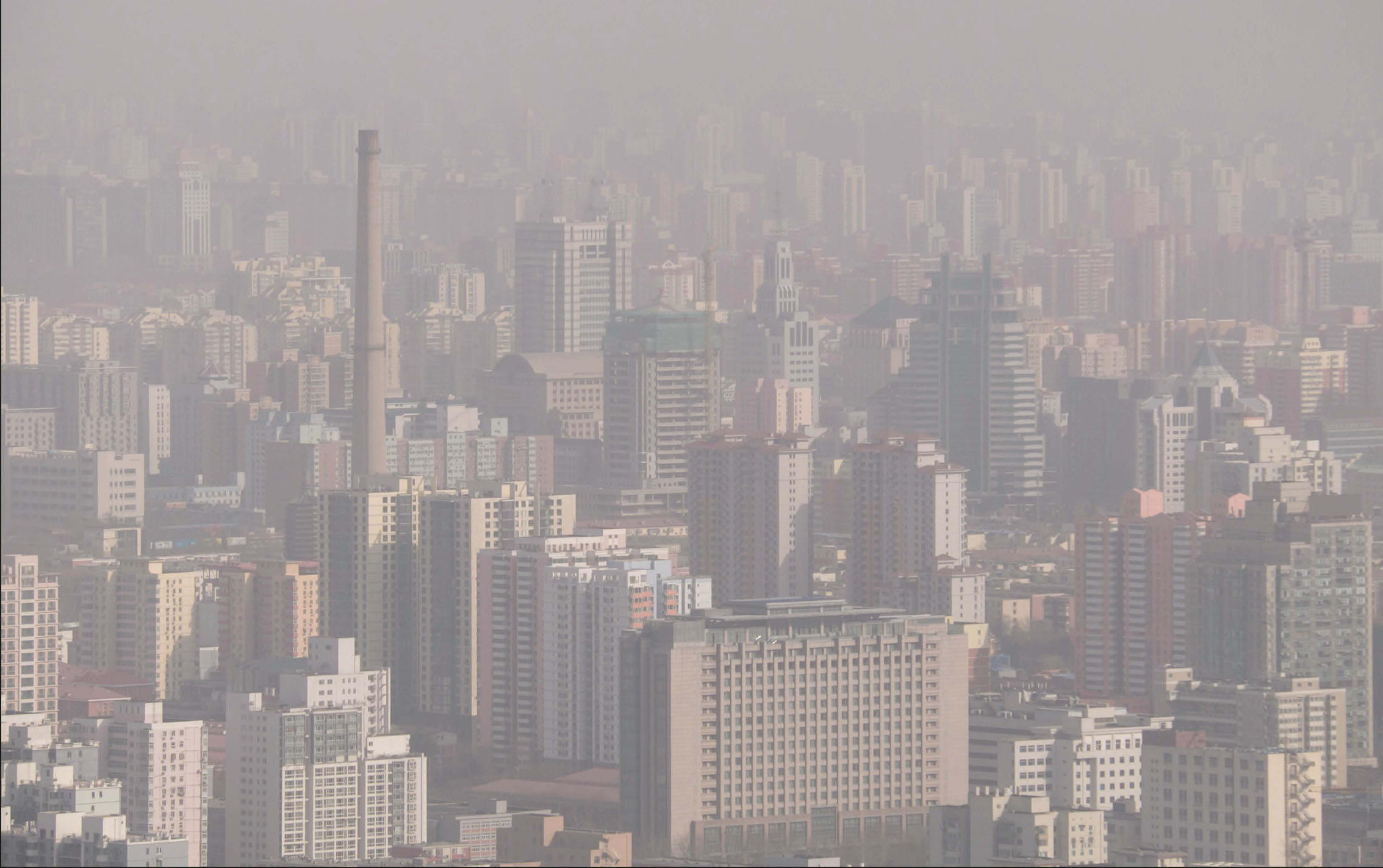
These types of conditions remained in some cities into the mid-1900s. They are still present in places that lack air pollution regulations. The city of Beijing, China, for example, is highly polluted. The majority of homes and power plants still burn coal. When conditions are really severe in Beijing, people have to wear masks. They also have to limit outdoor activities as much as possible.
Air pollution fills the air in Beijing, China, in 2015.
In the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, some factory owners thought it didnt matter how much smoke they put into the air. Over time, though, humans have learned how dangerous it is to treat the atmosphere this way.
CHAPTER 3
FOSSIL FUELS
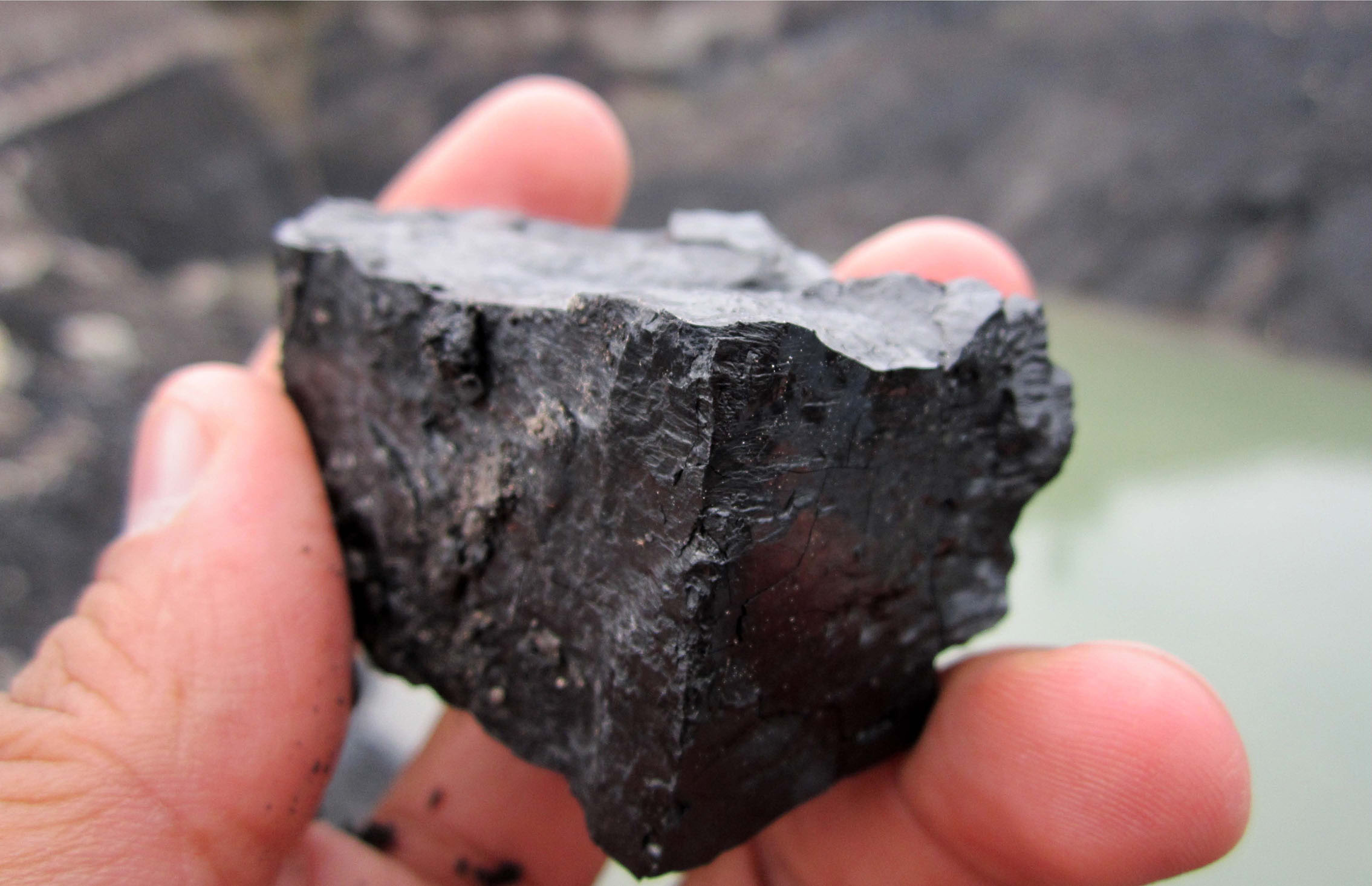
Fossil fuels formed from dead plants and animals. Their bodies were buried in the earth. Other layers piled on top. Great pressure caused the organic materials to turn to rock. Some of this organic material became coal. Living things are made up of carbon, so fossil fuels also have carbon. When fossil fuels are burned, carbon turns into carbon dioxide. Then it is released into the atmosphere.