Examining Erosion Joelle Riley

Copyright 2013 by Lerner Publishing Group, Inc.
All rights reserved. International copyright secured. No part of this book may be
reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means
electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwisewithout the prior written
permission of Lerner Publishing Group, Inc., except for the inclusion of brief quotations in
an acknowledged review.
Lerner Publications Company
A division of Lerner Publishing Group, Inc.
241 First Avenue North
Minneapolis, MN 55401 U.S.A.
Website address: www.lernerbooks.com
Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data
Riley, Joelle.
Examining erosion / by Joelle Riley.
pages cm. (Searchlight booksDo you dig Earth science?)
Includes index.
ISBN 9781467700214 (lib. bdg. : alk. paper)
1. ErosionJuvenile literature. 2. Sedimentation and depositionJuvenile
literature. I. Title.
QE581.R53 2013
551.352dc23 2012022474
Manufactured in the United States of America
1 CG 7/15/12
Contents
THE CHANGING
EARTH ... page
BREAKING UP THE
GROUND ... page
Chapter
THE CHANGING
EARTH
Earth is changing
all the time. Some
changes happen
quickly. In moments,
an earthquake can move
large amounts of rock
and soil. Other changes
happen slowly. It takes
many years for a mountain
to form.
An earthquake caused this
crack in the ground. Do all
changes to Earth happen as
quickly as an earthquake?
Erosion is the movement of rock, soil, and other bits
of earth. Erosion happens everywhere on the planet.
It usually happens very slowly. But over time, erosion
makes big changes in the land.
Erosion helps to change
the lands shape
everywhere on the planet.
Mountains
Erosion changes
the shapes of tall
mountains. The
mountains in the
eastern United
States are old.
Once they were tall
and had sharp tops.
But over thousands
of years, erosion
wore them down.
The mountains
are not as tall as
they once were.
Their peaks have
become rounded
and smooth. And
erosion is still at
work. It is making
the mountains
smaller and smaller.
The Appalachian Mountains
are in the eastern United
States. They are old and
have rounded tops.
The mountains of the western United States are
young. They have tall, pointed tops. But erosion is slowly
changing them. In many years, these mountains will be
worn down too.
The Rocky Mountains are in
the western United States.
They are young and have
pointed tops.
Chapter
BREAKING UP
THE GROUND
Big pieces of earth are
harder to move than
small pieces. Erosion
cant move a whole
mountain at once. But it
can move pieces that have
broken off a mountain.
Erosion can move rocks
and bits of soil. Making large
pieces of earth into smaller
pieces is called weathering.
Water, ice, and growing plants all
cause weathering.
Rock from this mountain has
broken into small pieces.
What can cause rock to break?
During a heavy rain, water pounds down. Big raindrops
hit the ground. The raindrops break off pieces of earth.
Some of the rainwater soaks into the soil. The rest of
the water runs across the ground. As the water flows,
it rubs against the ground. The flowing water breaks off
more small pieces of earth.
The rain pounds on the ground.
It breaks off little bits of earth.
Rivers, Streams, and Waves
The water in rivers and streams rubs against the ground
too. As a stream flows, pieces of soil and rock break
loose. Fast streams push harder than slow streams. So
fast streams break away more earth than slow streams.
This stream flows very
fast. It can break loose
a lot of rock and soil.
Soft earth
weathers quickly.
A stream flowing
over soft ground
spreads out. It
becomes shallow
and wide. The
stream meanders
across the ground.
It bends from side
to side in big loops.
This stream bends
back and forth. It
is meandering.
Hard rock
weathers very
slowly. Streams
flowing across hard
rock dont usually
spread out or
meander. Instead,
they follow a narrow,
straight path. As a
stream flows, it rubs
against the rock.
The stream digs
deeper and deeper
into the rock. After
a very long time, a
canyon forms. A
canyon is a deep,
narrow valley with
steep sides.
This is a canyon.
The stream flowing
at the bottom
created the canyon.
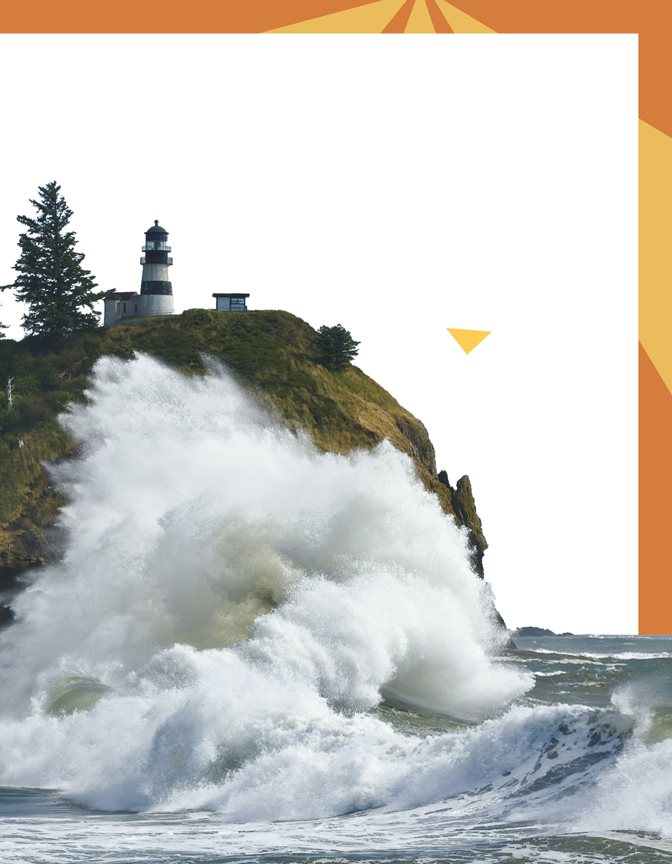
The water in lakes and oceans doesnt flow across the
land. But it moves back and forth in waves. The waves
pound against the shore. They break loose bits of rock,
sand, and soil.
POUNDING WAVES
CAUSE WEATHERING
OF ROCK AND SOIL.
Ice and Plants
Water also causes weathering when it freezes. Rainwater
soaks into tiny cracks in the ground and in rocks. If the
weather is cold enough, the water freezes. It becomes
ice. Ice takes up more space than water does. So as
water changes into ice, it gets bigger. It pushes against
the soil and rocks. It makes the tiny cracks bigger.
Pieces of soil and rock break loose.
These bottles started out with the same
amount of water. Then one bottle was frozen.
The water changed to ice. You can see that the