ROURKES SCHOOL to HOME C ONNECTIONS BEFORE AND DURING READING A CTI VITIES Before Reading: Building Back ground Knowledge and V oc abulary Building back ground knowledge can help childr en proce ss new information and build upon what they already know . Before r eading a book, it is important to tap into what childr en alre ady know about the topic. This will help them deve lop their vocabulary and incre ase their reading compr ehension. Questions and Activities to Build Back ground Knowledge: L ook at the front cov er of the book and re ad the title. What do you think this book will be about? 2. W hat do you already kno w about this topic? 3.
T ak e a book walk and skim the pag es. Look at the table of contents, photographs, captions, and bold words. Did these text f eatures gi ve you any inf ormation or pre dictions about what you will re ad in this book? During Reading: Reading f or Meaning and Understanding T o achieve dee p comprehension of a book, childr en are e ncouraged to use close re ading strategies. During reading, it is important to have children stop and mak e connections. These connections r esult in deeper analysis and understanding of a book. Close Reading a T ext During r eading, have childre n stop and talk about the following: Any confusing parts A ny unknown words T ex t to text, text to self, text to world connections The main idea in each chapter or heading Encourage childre n to use context clues to determine the meaning of any unknown wor ds.
These strategies will help childre n learn to analyze the text more thor oughly as they r ead. When you are nished r eading this book, turn to the last page fo r an After Reading Activity . V ocabulary Wo rds: Voc abulary: Voc abulary Is Ke y to Reading Comprehension Use the f ollowing directions to pr ompt a conve rsation about each wor d. R ead the vocabulary wor ds. W hat comes to mind when you see each word ? W hat do you think each word means? d ata d iagram e ngineers p rocesses s culpture seasons
Wha t s a Model? A model c an be a drawing or a diagram . It c an als o be 3-D .
A 3-D model has length, width, and height .
Models r epresent ideas and processes .
The y help us understand how things wo rk.

Who and Why? S cientists use models to solv e pr oblems and e xplain data . Math equations are a type of model.
Models help engineers learn how something will w ork .
Engineers often design computer models.
Artist s use models too . T hey may draw their ideas bef or e making a sculpture .
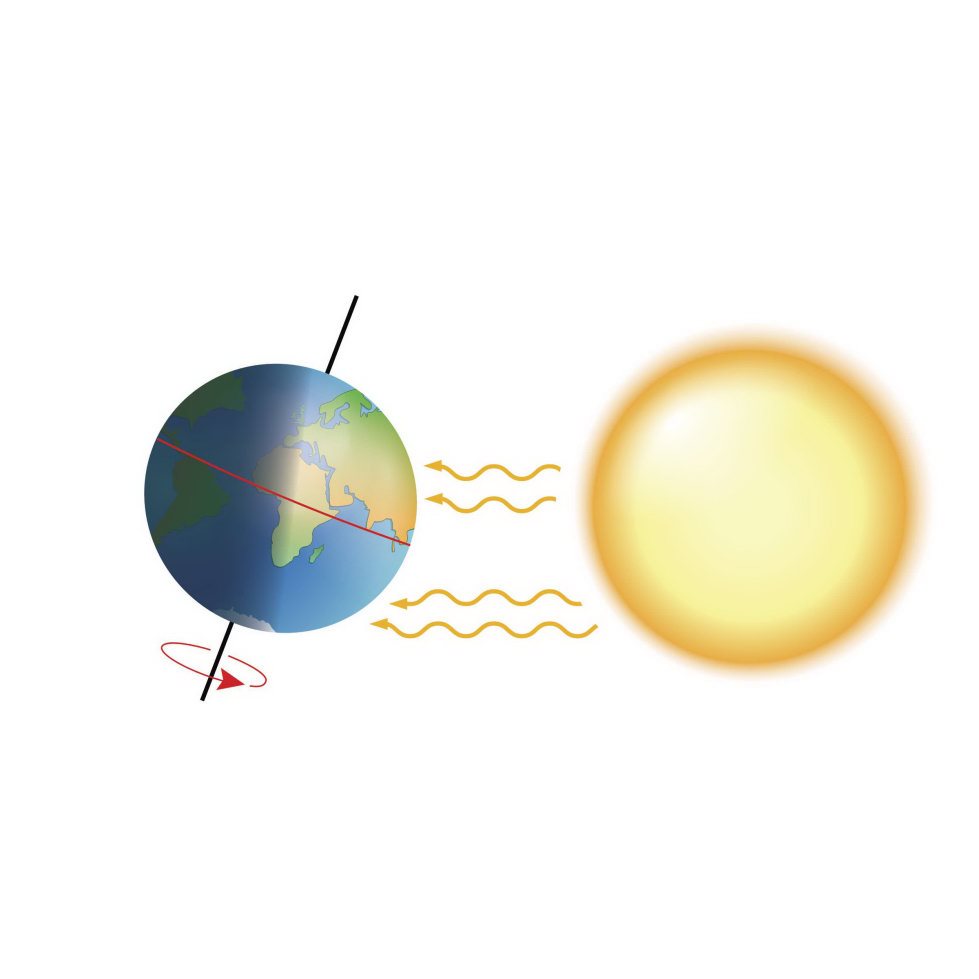
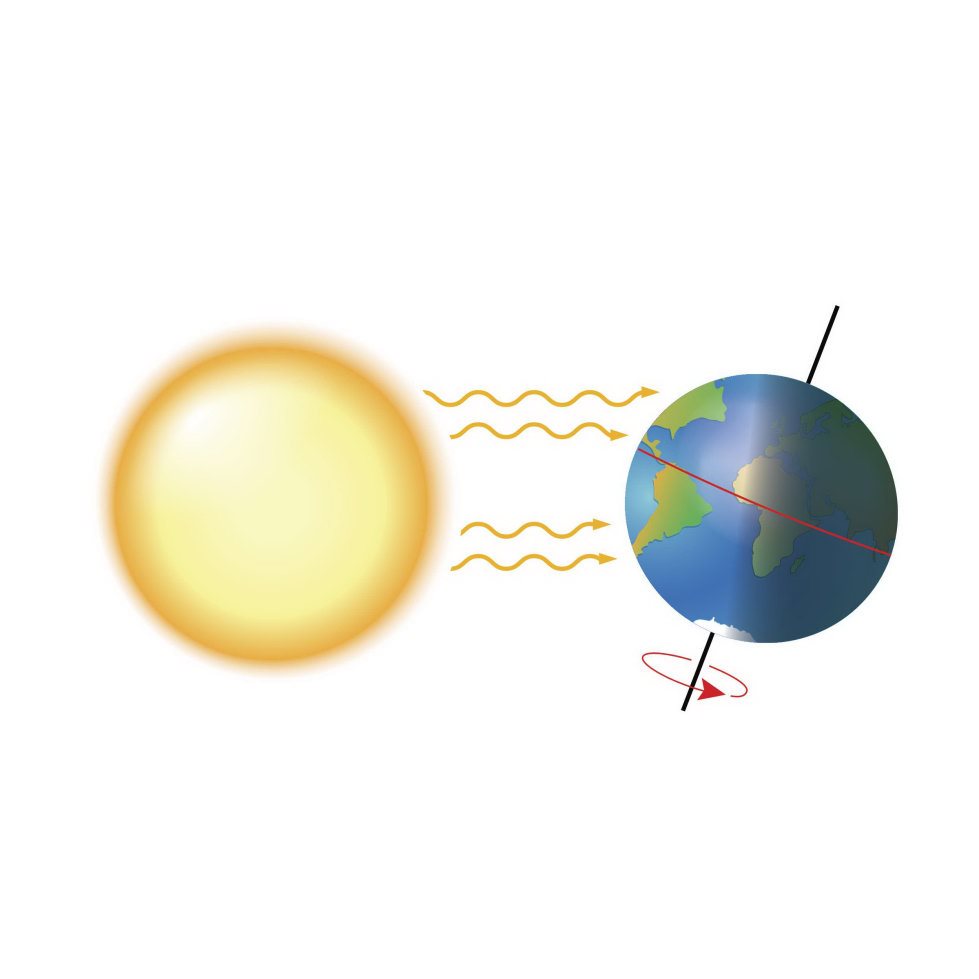
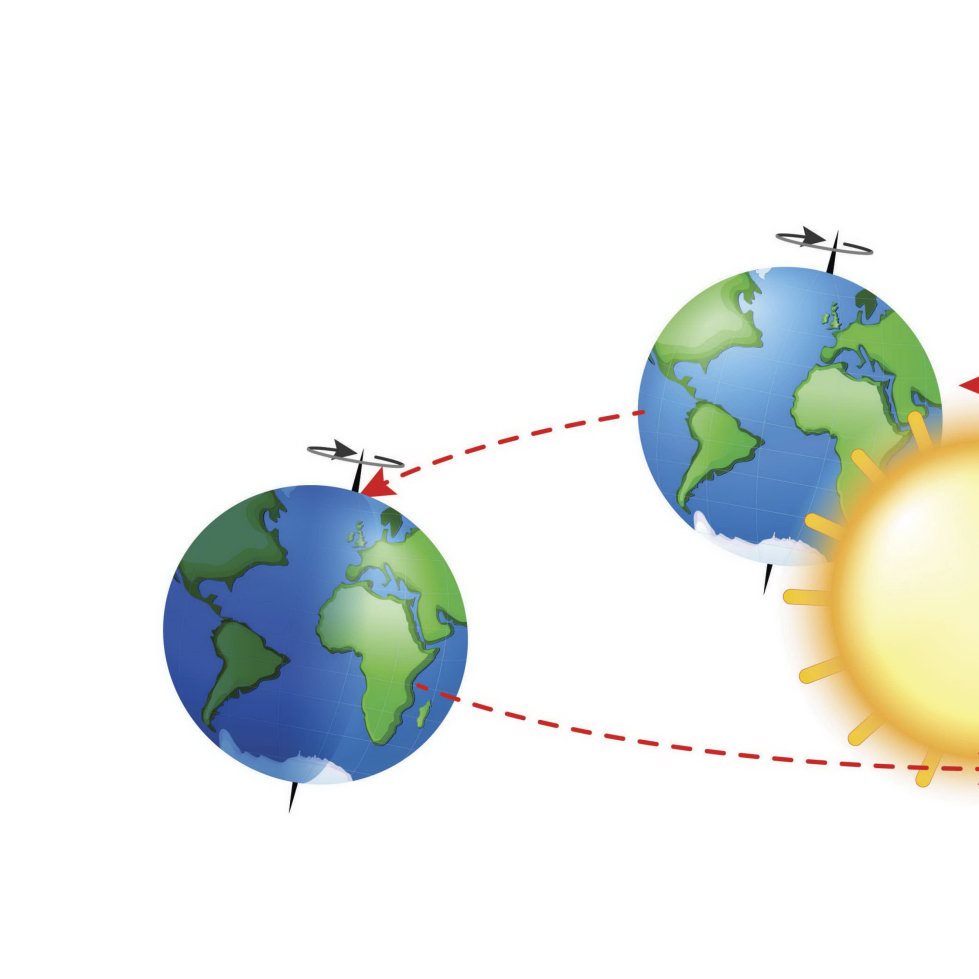
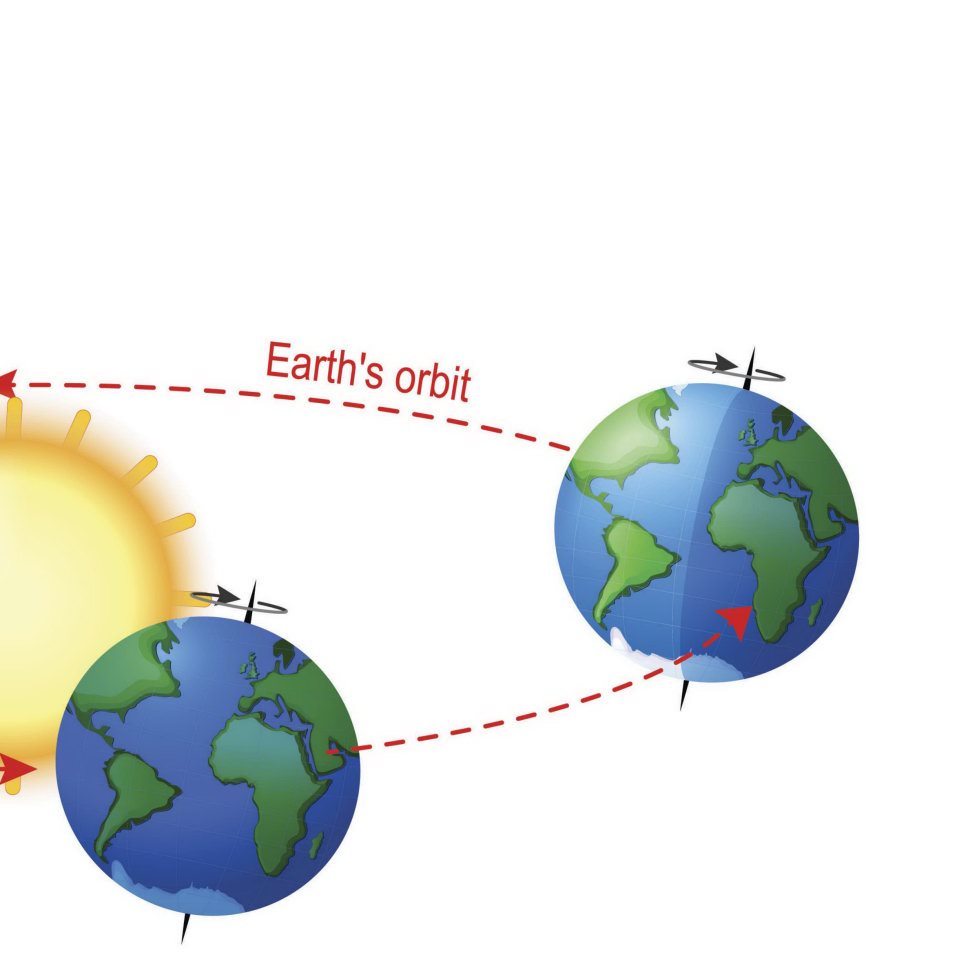
How Do Models Work ? Earth has f our seasons . Scientis ts can create a model to sho w wh y.
Win ter Spring Summer Fa l l
Earth is tilted on it s axis.
Earth Axis Summer Winter Equator Sun Axis Winter
It stays tilted as it goes ar ound the sun . Earth Axis Summer Winter Equator Sun
The model sho ws that the parts of Earth that get direct s unlight change as the planet circles the s un. Su n
The model help s s cientist s understand the fo ur seas ons.
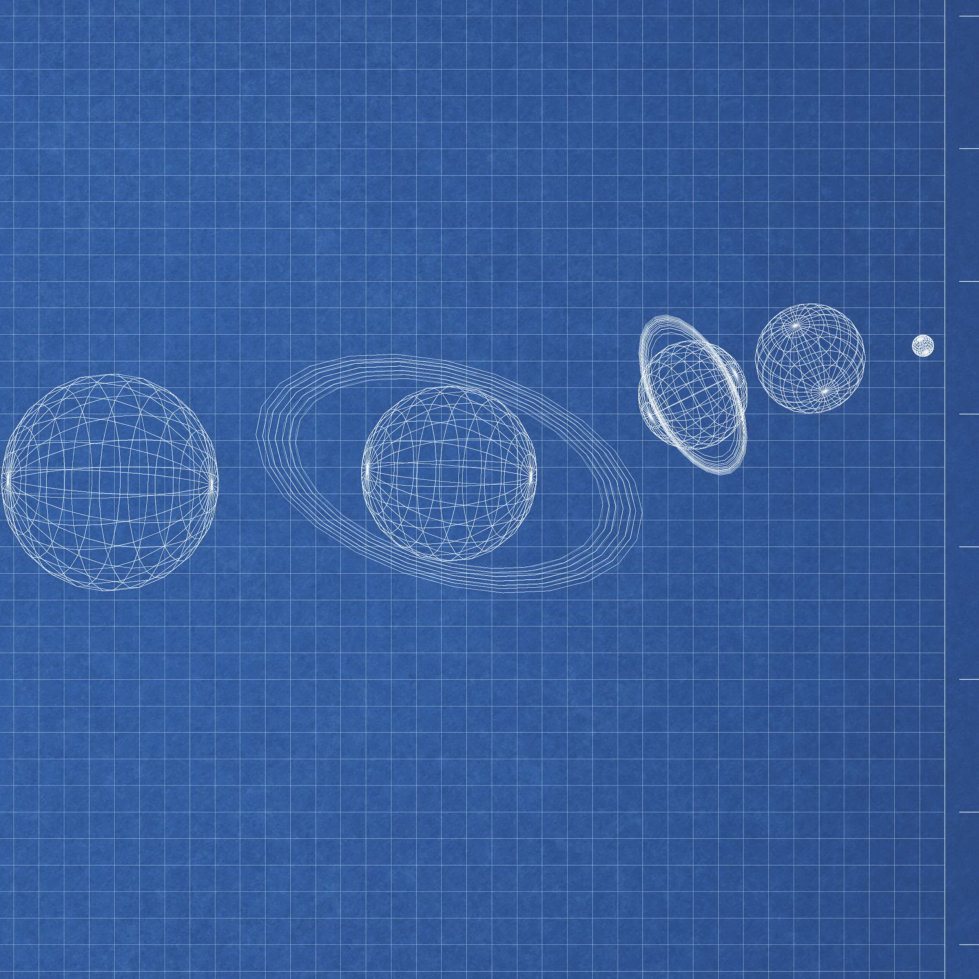
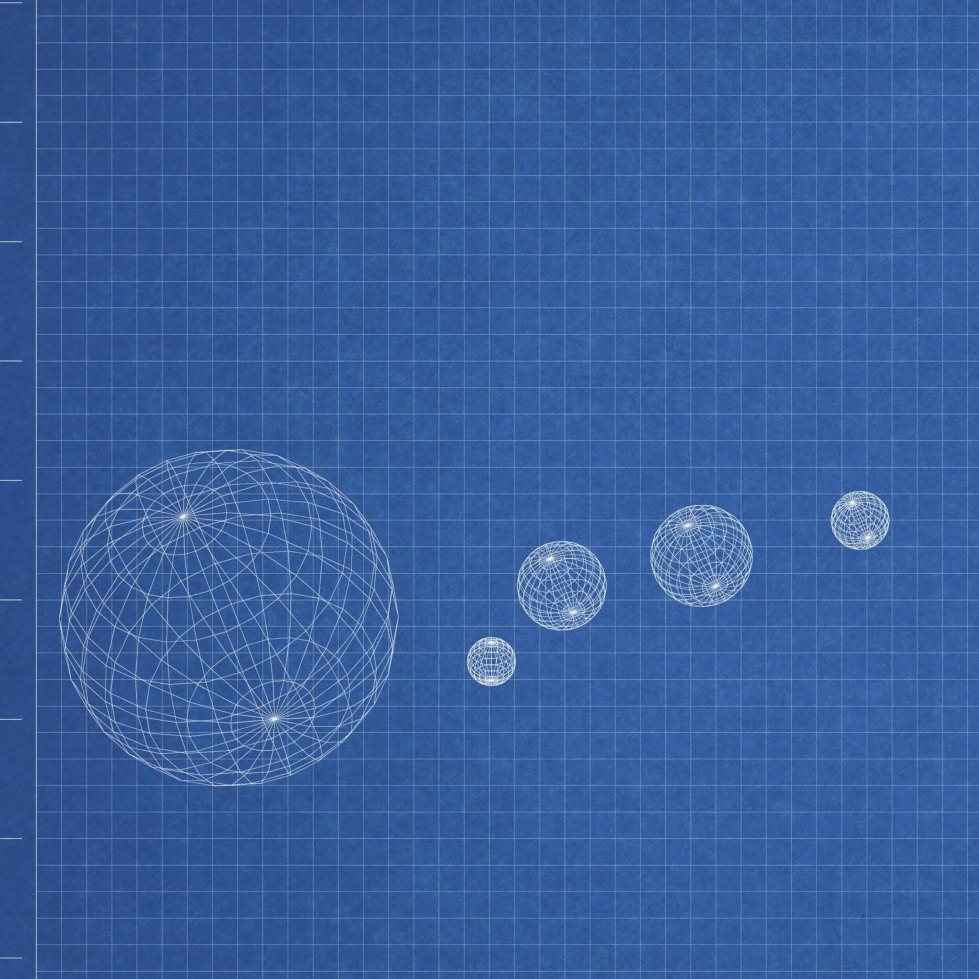
Our s olar system has eight planet s. Which one is smallest? Which one is largest? Arrange the planet s in their places around the s un. Ma ke a Solar S ystem Model
D irections: P lace the largest ball on the pav eme nt outside.
This ball repres ents the s un. U se chalk to dr aw eight so lar system rings around the su n. Plac e a ball on each ring to repres ent each planet . beach ball baske tball soccer ba ll voll eyball tennis ball baseball golf ball ping pong ball marble chalk Y ou will need:
data (DA Y- tuh): F a cts and inf ormation c ollected f or study . diagram (DY E-uh-gram): A drawing that e xpl ains parts of something using arr ows, colors, or shapes. engineers (en-juh-NEERS ): Peop le who design and build machines and structures.